Acoustic resonators are everywhere. In fact, there is a good chance you’re holding one in your hand right now. Most smart phones today use bulk acoustic resonators as radio frequency filters to filter out noise that could degrade a signal. These filters are also used in most Wi-Fi and GPS systems.
Acoustic resonators are more stable than their electrical counterparts, but they can degrade over time. There is currently no easy way to actively monitor and analyze the degradation of the material quality of these widely used devices.
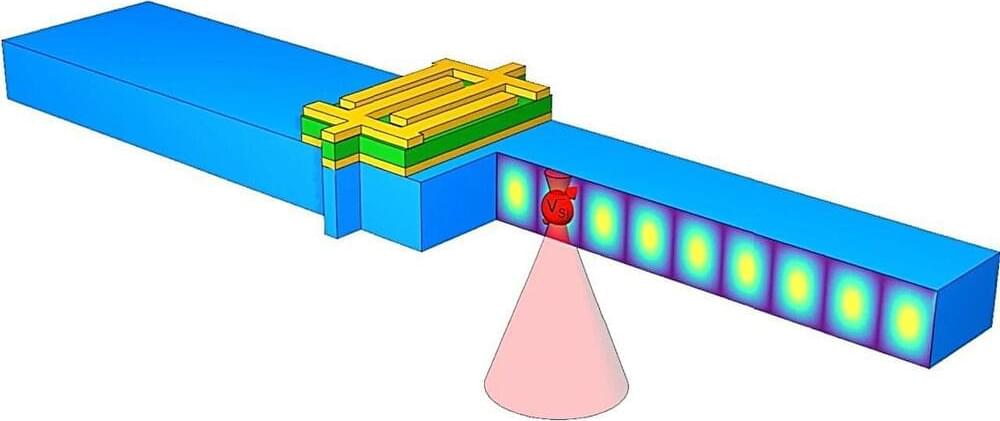
Now, researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), in collaboration with researchers at the OxideMEMS Lab at Purdue University, have developed a system that uses atomic vacancies in silicon carbide to measure the stability and quality of acoustic resonators. What’s more, these vacancies could also be used for acoustically-controlled quantum information processing, providing a new way to manipulate quantum states embedded in this commonly-used material.