Recent advances in the fields of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) have opened exciting new avenues for teleoperation, the remote control of robots to complete tasks in a distant location. This could, for instance, allow users to visit museums from afar, complete maintenance or technical tasks in spaces that are difficult to access or attend events remotely in more interactive ways.
Most existing teleoperation systems are designed to be deployed in specific settings and using a specific robot. This makes them difficult to apply in different real-world environments, greatly limiting their potential.
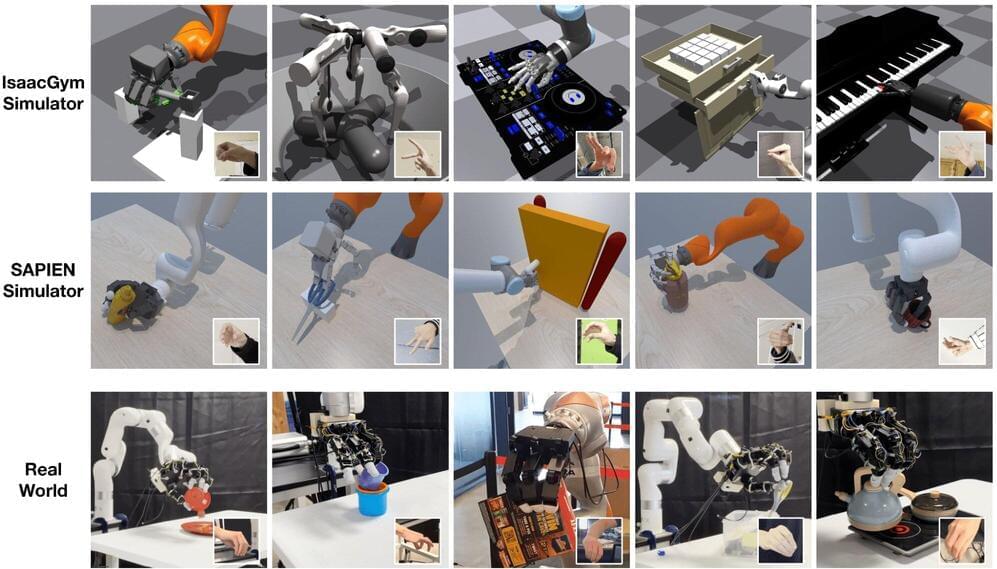
Researchers at NVIDIA and UC San Diego recently created AnyTeleop, a computer vision–based teleoperation system that could be applied to a wider range of scenarios. AnyTeleop, introduced in a paper pre-published on arXiv, enables the remote operation of various robotic arms and hands to tackle different manual tasks.