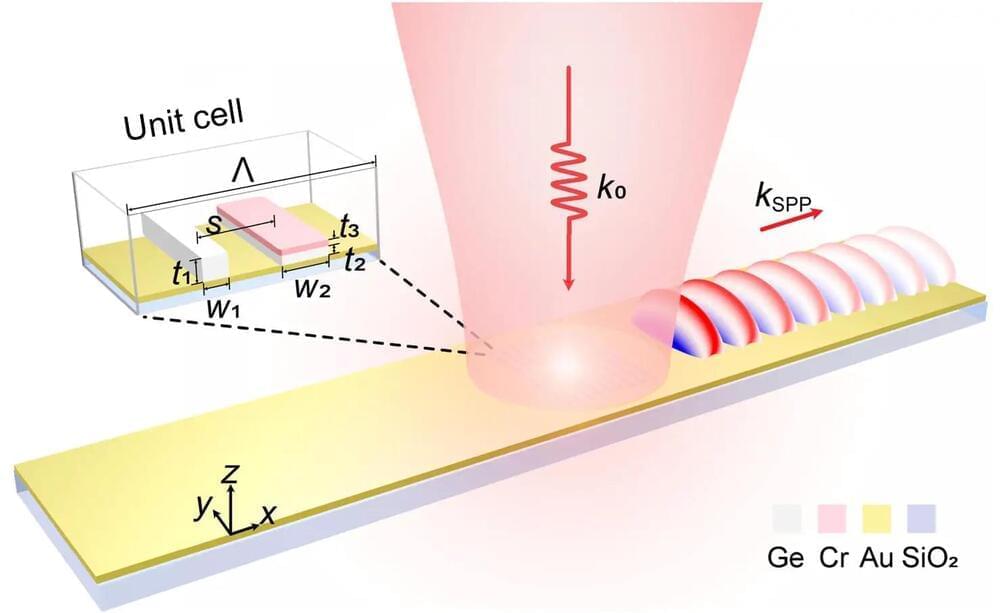
Scientists from Korea’s POSTECH and the US’ Northeastern University have successfully manipulated light using non-Hermitian meta-gratings, turning optical loss into a beneficial tool. They’ve developed a new method for controlling light direction using specially designed meta-grating couplers. This breakthrough could advance quantum sensor research and lead to a range of new applications, such as disease diagnosis and pollution detection.
Light is a very delicate and vulnerable physical phenomenon. Light can be absorbed or reflected at the surface of a material depending on the matter’s properties or change its form and be converted into thermal energy. Upon reaching a metallic material’s surface, light also tends to lose energy to the electrons inside the metal, a broad range of phenomena we call “optical loss.”
Production of ultra-small optical elements that utilize light in various ways is very difficult since the smaller the size of an optical component results in a greater optical loss. However, in recent years, the non-Hermitian theory, which uses optical loss in an entirely different way, has been applied to optics research. New findings in physics are being made adopting non-Hermitian theory that embraces optical loss, exploring ways to make use of the phenomenon, unlike general physics where optical loss is perceived as an imperfect component of an optical system. A ‘blessing in disguise’ is that which initially seems to be a disaster but which ultimately results in good luck. This research story is a blessing in disguise in physics.