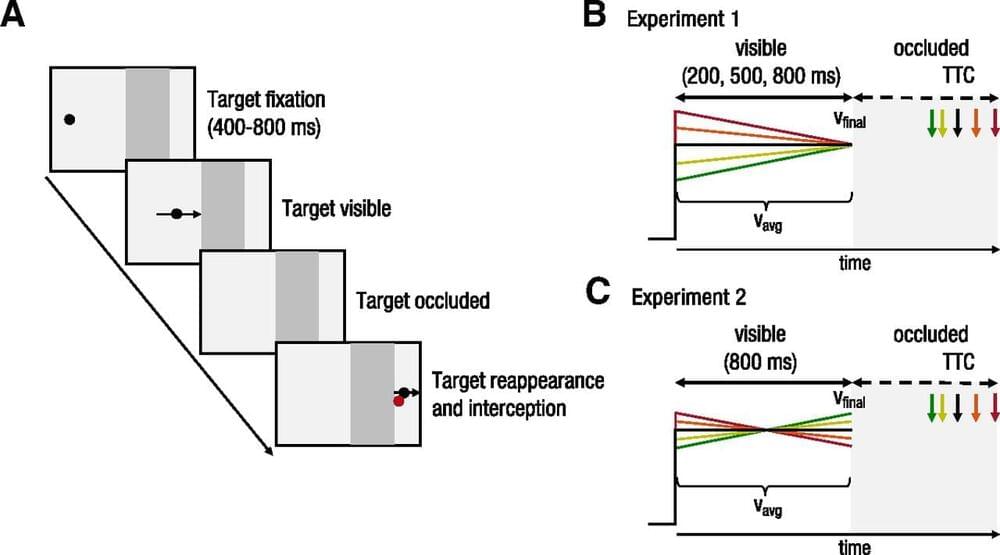
Objects in our visual environment often move unpredictably and can suddenly speed up or slow down. The ability to account for acceleration when interacting with moving objects can be critical for survival. Here, we investigate how human observers track an accelerating target with their eyes and predict its time of reappearance after a temporal occlusion by making an interceptive hand movement. Before occlusion, observers smoothly tracked the accelerating target with their eyes. At the time of occlusion, observers made a predictive saccade to the location where they subsequently intercepted the target with a quick pointing movement.