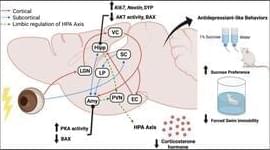
Given that visual impairment is bi-directionally associated with depression, we examined whether transcorneal electrical stimulation (TES), a non-invasive treatment for visual disorders, can ameliorate depressive symptoms.
The putative antidepressant-like effects of TES and the underlying mechanisms were investigated in an S334ter-line-3 rat model of retinal degeneration and a rat model of chronic unpredictable stress (CUS).
TES was administered daily for 1 week in S334ter-line-3 and CUS rats. The effects of TES on behavioral parameters, plasma corticosterone levels, and different aspects of neuroplasticity, including neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and apoptosis, were examined.