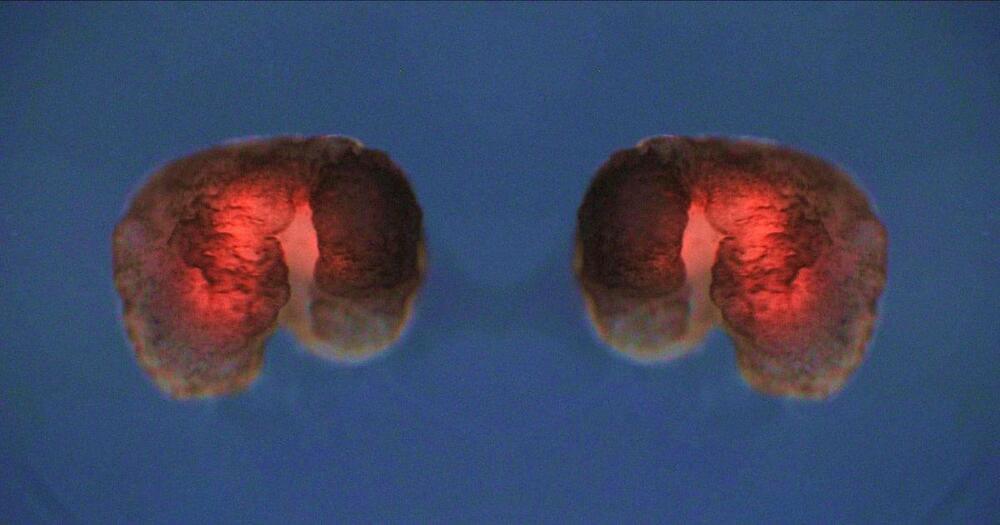
Scientists have created synthetic organisms that can self-replicate. Known as “Xenobots,” these tiny millimeter-wide biological machines now have the ability to reproduce — a striking leap forward in synthetic biology.
Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 0, a joint team from the University of Vermont, Tufts University, and Harvard University used Xenopus laevis frog embryonic cells to construct the Xenobots.
Their original work began in 2020 when the Xenobots were first “built.” The team designed an algorithm that assembled countless cells together to construct various biological machines, eventually settling on embryonic skin cells from frogs.