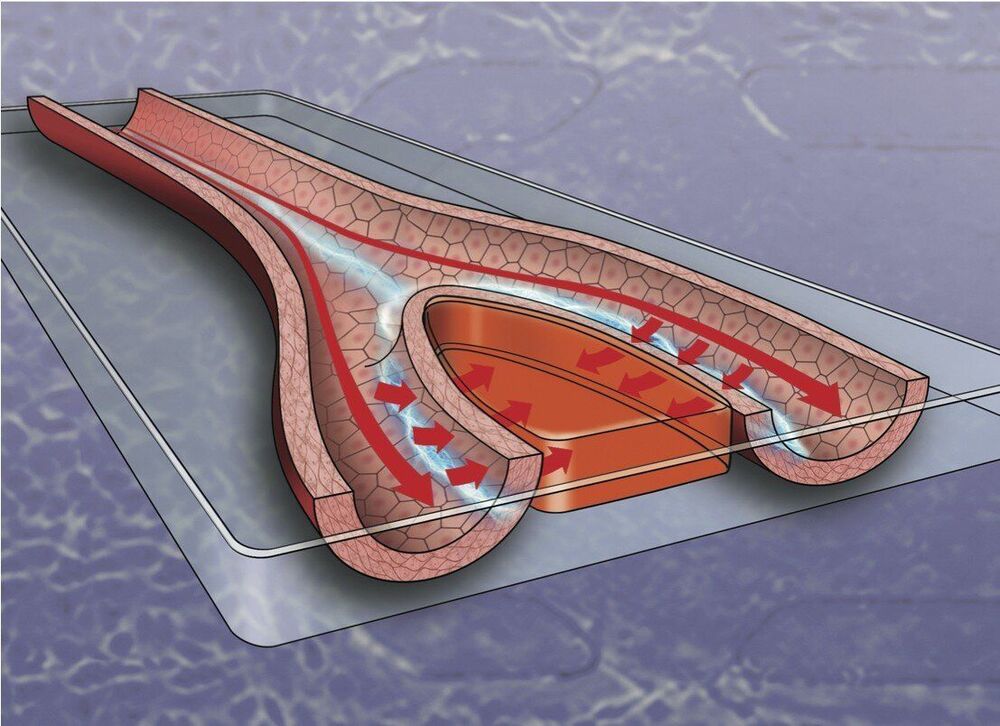
Electric stimulation may be able to help blood vessels carry white blood cells and oxygen to wounds, speeding healing, a new study suggests.
The study, published in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Lab on a Chip, found that steady electrical stimulation generates increased permeability across blood vessels, providing new insight into the ways new blood vessels might grow.
The electrical stimulation provided a constant voltage with an accompanying electric current in the presence of fluid flow. The findings indicate that stimulation increases permeability of the blood vessel—an important characteristic that can help wound-healing substances in the blood reach injuries more efficiently.