Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men. Patients are determined to have prostate cancer primarily based on PSA, a cancer factor in blood. However, as diagnostic accuracy is as low as 30%, a considerable number of patients undergo additional invasive biopsy and thus suffer from resultant side effects, such as bleeding and pain.
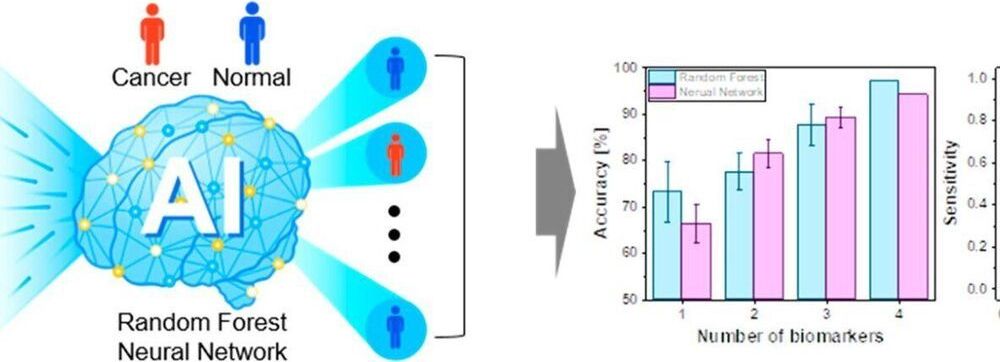
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that the collaborative research team led by Dr. Kwan Hyi Lee from the Biomaterials Research Center and Professor In Gab Jeong from Asan Medical Center developed a technique for diagnosing prostate cancer from urine within only 20 minutes with almost 100% accuracy. The research team developed this technique by introducing a smart AI analysis method to an electrical-signal-based ultrasensitive biosensor.
As a noninvasive method, a diagnostic test using urine is convenient for patients and does not need invasive biopsy, thereby diagnosing cancer without side effects. However, as the concentration of cancer factors is low in urine, urine-based biosensors are only used for classifying risk groups rather than for precise diagnosis thus far.