Targeted genome editing tools, such as meganucleases (MGN), zinc-finger nucleases (ZFN), transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) and more recently the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) have revolutionized most biomedical research fields. Such tools allow to precisely edit the genome of eukaryotic cells by inducing double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) breaks at specific loci. Relying on the cell endogenous repair pathways, dsDNA breaks can then be repaired by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR) allowing the removal or insertion of new genetic information at a desired locus.
Among the above-mentioned tools, CRISPR-Cas9 is currently the most simple and versatile method for genome engineering. Indeed, in the two-component system, the bacterial-derived nuclease Cas9 (for CRISPR-associated protein 9) associates with a single-guide RNA (sgRNA) to target a complementary DNA sequence and induce a dsDNA break. Therefore, by the simple modification of the sgRNA sequence, users can specify the genomic locus to be targeted. Consistent with the great promises of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering and gene therapy, considerable efforts have been made in developing efficient tools to deliver the Cas9 and the sgRNA into target cells ex vivo either by transfection of plasmids coding for the nucleases, transduction with viral-derived vectors coding for the nucleases or by direct injection or electroporation of Cas9-sgRNA complexes into cells.
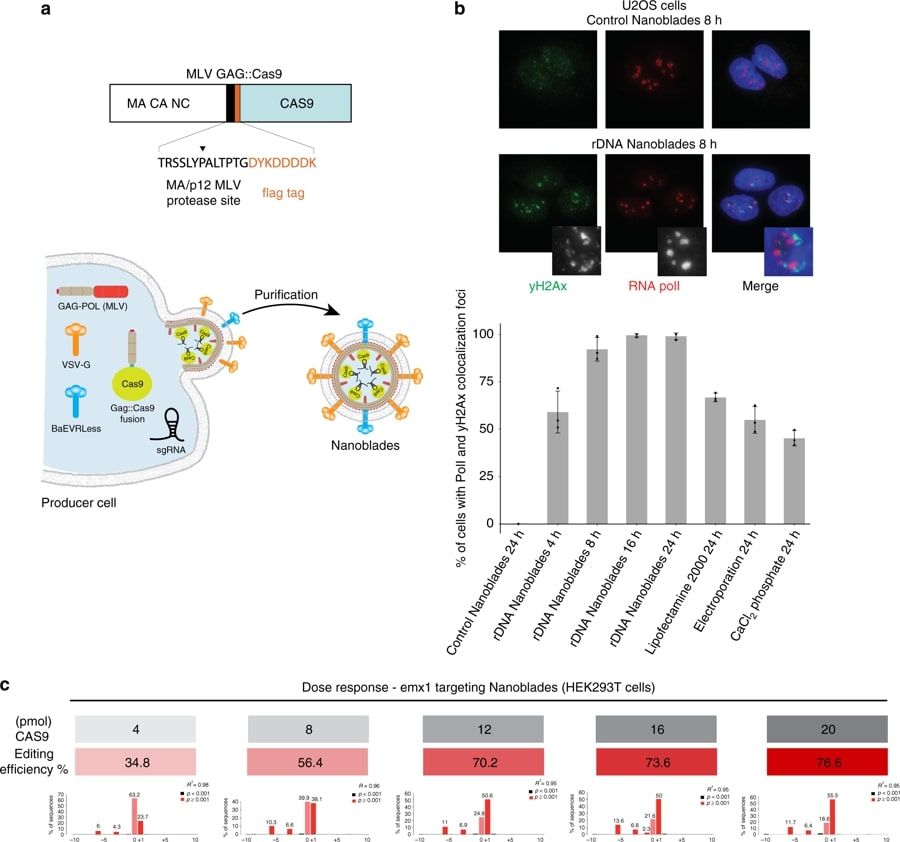
Researchers have designed Nanoblades, a protein-delivery vector based on friend murine leukemia virus (MLV) that allows the transfer of Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) to cell lines and primary cells in vitro and in vivo. Nanoblades deliver the ribonucleoprotein cargo in a transient and rapid manner without delivering a transgene and can mediate knock-in in cell lines when complexed with a repair template. Nanoblades can also be programmed with modified Cas9 proteins to mediate transient transcriptional activation of targeted genes.