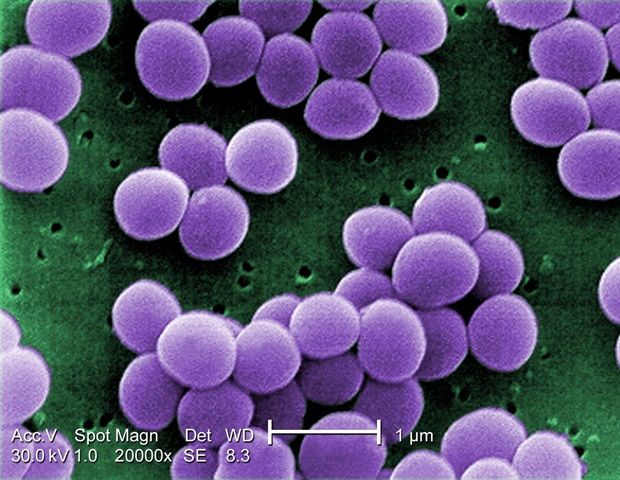
The Staphylococcus aureus bacterium is one of the commonest pathogens and can even cause sepsis. The new antibiotic dalbavancin is very effective against many bacterial pathogens. However, resistance to the antibiotic was seen to develop during the long-term treatment of a patient with an infection caused by an implanted cardiac device. A team of researchers led by infectiologists from the Division of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine within the Department of Medicine I at MedUni Vienna, Manuel Kussmann and Heimo Lagler, have now described the phenotypical and genotypical mechanism of this development of resistance for the first time. The study was published in leading journal “Emerging Microbes & Infections”.
Staphylococci are bacteria and are part of the normal flora on the skin of humans and animals. Approximately 20% of the Austrian population permanently carry the germ, which is often located in the nasal cavity. There are harmless variants, which only cause mild symptoms, if any at all. In serious cases, the pathogen can find its way into the bloodstream and cause endocarditis and sepsis.
A problematic strain is Staphylococcus aureus, which can be acquired outside hospital but also in hospital as a so-called “hospital-acquired infection”. There are multi-resistant forms of it, which do not necessarily cause serious illness in healthy people. However, in weakened hospital patients or where the natural skin barrier is damaged, infection can result in complications. Nowadays dalbavancin, a latest generation antibiotic, is one of the drugs successfully used to treat multi-resistant bacteria. One of the advantages of this drug is its very long half-life of approximately nine days, so that intravenous treatment can be given on an outpatient basis. However, clinical experience has shown that, sooner or later, resistance develops to any therapeutic use of new antibiotics, so it was just a matter of time with this one.