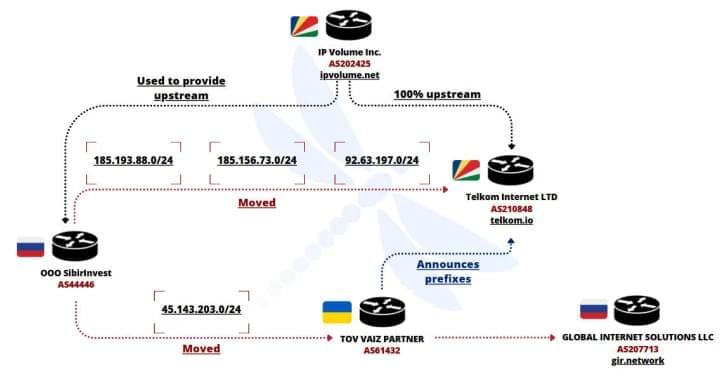
Lazarus Group used PondRAT, ThemeForestRAT, and RemotePE in a 2024 DeFi attack, likely via Chrome zero-day.



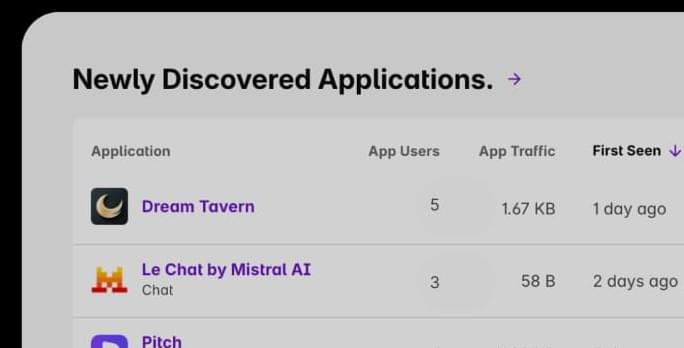
MITs State of AI in Business report revealed that while 40% of organizations have purchased enterprise LLM subscriptions, over 90% of employees are actively using AI tools in their daily work. Similarly, research from Harmonic Security found that 45.4% of sensitive AI interactions are coming from personal email accounts, where employees are bypassing corporate controls entirely.
This has, understandably, led to plenty of concerns around a growing “Shadow AI Economy”. But what does that mean and how can security and AI governance teams overcome these challenges?

Questions to inspire discussion.
🗓️ Q: When will more details about Tesla’s master plan part 4 be revealed? A: Elon Musk will add specifics to the master plan part 4 at the upcoming annual shareholder meeting on November 6th, including key milestones for achieving sustainable abundance.
AI and Manufacturing.
🧠 Q: What is Elon Musk’s focus regarding AI development? A: Musk is prioritizing the development of AI compute capacity and deep learning models, as evidenced by his focus on XAI and Grock 5, to drive innovation in Tesla’s products and services.
🏭 Q: How does Tesla plan to improve its manufacturing processes? A: Tesla aims to create a custom AI solution using Grock agents to develop a cybernetic organism capable of manufacturing humanoids more efficiently than current Tesla methods.
🤖 Q: What is the potential timeline for Grock 5 to achieve AGI? A: Elon Musk believes Grock 5 has a chance to become AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) by next year, potentially allowing Tesla to achieve supremacy in manufacturing through superior AI.
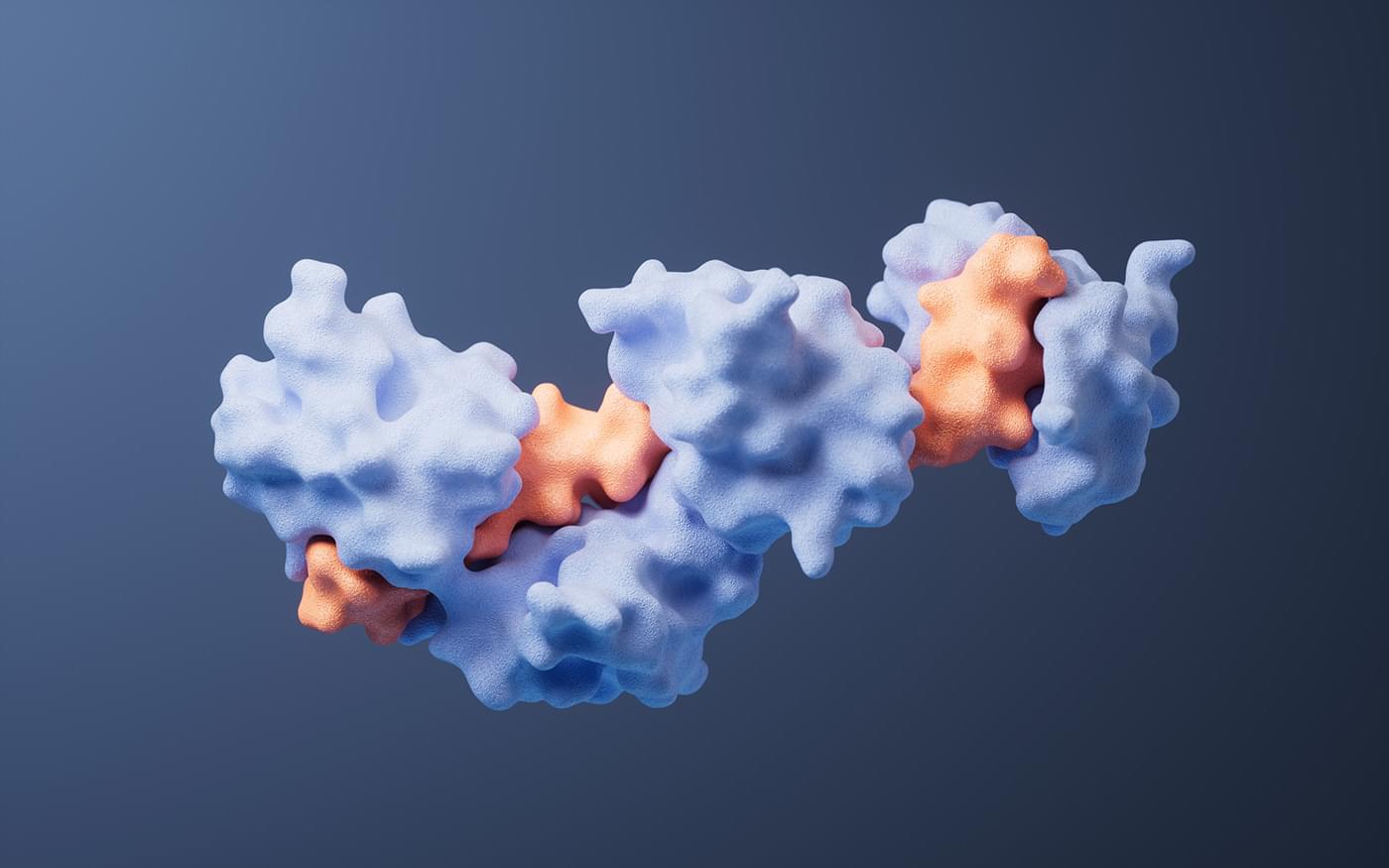

Scientists at Mount Sinai have created an artificial intelligence system that can predict how likely rare genetic mutations are to actually cause disease. By combining machine learning with millions of electronic health records and routine lab tests like cholesterol or kidney function, the system produces “ML penetrance” scores that place genetic risk on a spectrum rather than a simple yes/no. Some variants once thought dangerous showed little real-world impact, while others previously labeled uncertain revealed strong disease links.