In theory, quantum physics can bypass the hard mathematical problems at the root of modern encryption. A new proof shows how.


Astronomers may have caught a still-forming planet in action, carving out an intricate pattern in the gas and dust that surrounds its young host star. Using ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), they observed a planetary disc with prominent spiral arms, finding clear signs of a planet nestled in its inner regions. This is the first time astronomers have detected a planet candidate embedded inside a disc spiral.
“We will never witness the formation of Earth, but here, around a young star 440 light-years away, we may be watching a planet come into existence in real time,” says Francesco Maio, a doctoral researcher at the University of Florence, Italy, and lead author of this study, published on July 21 in Astronomy & Astrophysics.

The red supergiant Betelgeuse likely has a companion star, astronomers have confirmed.
Long theorized to share an orbit with Betelgeuse — an extremely bright star that may go supernova in the next few thousand years — a sun-size companion star has finally appeared in unique observations taken with the Gemini North telescope high on Hawaii’s Mauna Kea.

An academic whose work reaches beyond the Ivory Tower is rare. Scholarly writing tends to be highly technical, filled with footnotes and references, and often lacks a compelling narrative to captivate the reader. Not to mention that the work itself is usually deemed irrelevant and impractical for public knowledge.
The American philosopher Daniel Dennett (1942−2024) was, without a doubt, one of these generational thinkers who transcended the academic box. Why? His writing is filled with clear and interesting thought experiments, allowing anyone to grasp his theories, which span from philosophy, cognitive science and evolutionary biology to farming, sailing, and religion. Any curious person can find a relevant topic relating to their life in Dennett’s vast body of work, and it will likely have them questioning whether they actually understood the topic in the first place.
To celebrate the life and work of Dennett, the aptly named Dennett Prize was introduced in 2024. Like Dennett, the winner should “challenge received ideas and introduce new perspectives.” The prize is presented as part of the International Center for Consciousness Studies (ICCS) annual conference, held this year in Heraklion, Crete, earlier this month. The inaugural winner of the Dennett Prize was given to Andy Clark, professor of cognitive philosophy at the University of Sussex.


Researchers at the University of California, Irvine have discovered a new state of quantum matter. The state exists within a material that the team reports could lead to a new era of self-charging computers and ones capable of withstanding the challenges of deep space travel.
“It’s a new phase of matter, similar to how water can exist as liquid, ice or vapor,” said Luis A. Jauregui, professor of physics & astronomy at UC Irvine and corresponding author of the new paper in Physical Review Letters.
“It’s only been theoretically predicted—no one has ever measured it until now.”
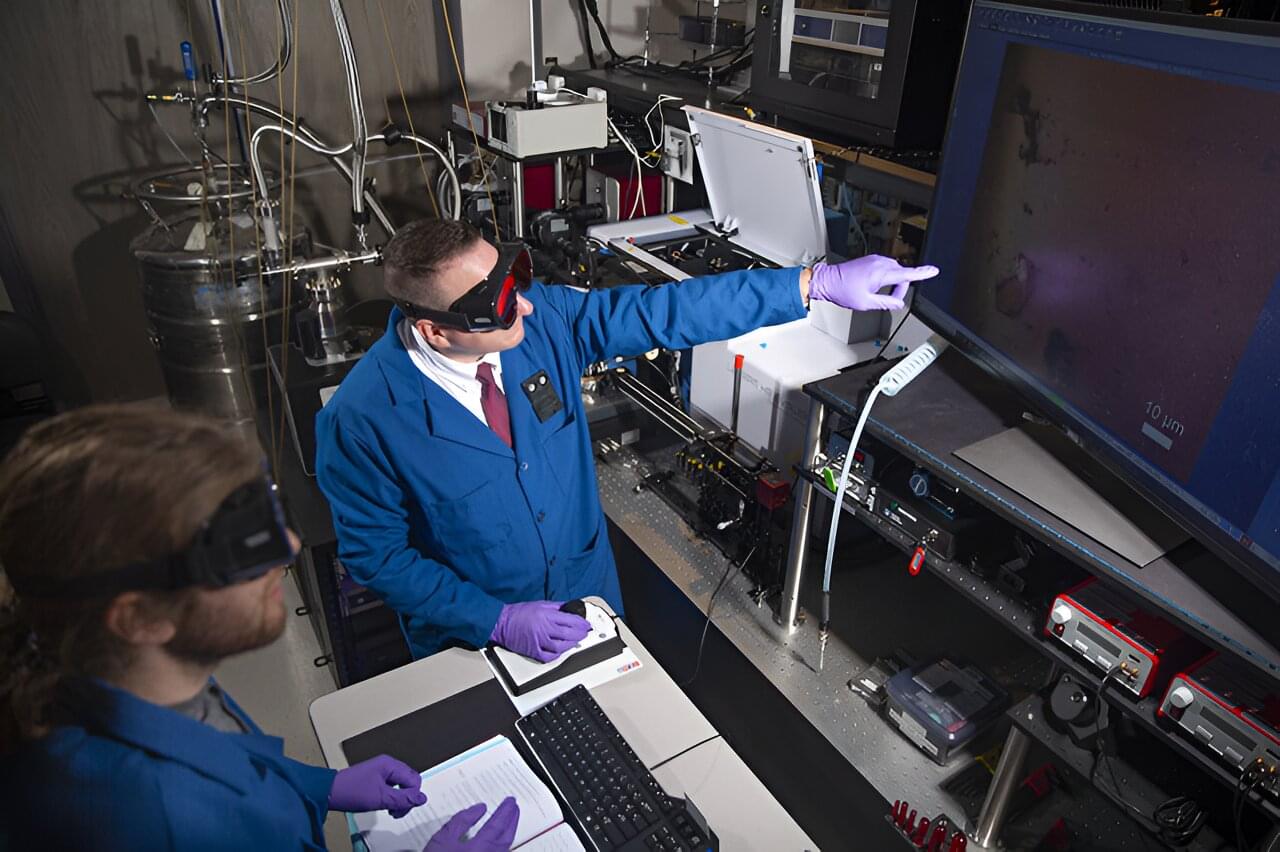

New research into topological phases of matter may spur advances in innovative quantum devices. As described in a new paper published in the journal Nature Communications, a research team including Los Alamos National Laboratory scientists used a novel strain engineering approach to convert the material hafnium pentatelluride (HfTe5) to a strong topological insulator phase, increasing its bulk electrical resistance while lowering it at the surface, a key to unlocking its quantum potential.
“I’m excited that our team was able to show that the elusive and much-sought-after topological surface states can be made to become a predominant electrical conduction pathway,” said Michael Pettes, scientist with the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies (CINT) at the Laboratory.
“This is promising for the development of types of quantum optoelectronic devices, dark matter detectors and topologically protected devices such as quantum computers. And the methodology we demonstrate is compatible for experimentation on other quantum materials.”