The brain’s ability to learn from rewards fluctuates with natural hormonal cycles, a new study in rats shows. Researchers report in Nature Neuroscience that peak estrogen levels amplify the dopamine signals that drive reinforcement learning.


After graduating from Hosei University, Hara worked at Denso, a Toyota Group subsidiary, where he began developing a barcode system. [ 6 ] In 1992, at Denso’s development department (later Denso Wave), he was tasked with creating a new 2D code to efficiently track automotive components. [ 7 ] [ 8 ] [ 9 ] [ 10 ] One day during a lunchtime game of go, he realized the black-and-white patterns could encode information. [ 6 ] He also researched publications to find a unique proportion for the position pattern to ensure readability. [ 11 ] The code was introduced in 1994. [ 12 ]
In 2021, QR codes were being used to book and track COVID-19 tests and contact tracing. [ 6 ] Hara has stated that he would like to develop QR codes for additional medical purposes, including imaging such as x-rays or electrocardiogram data. [ 2 ] Hara still works for Denso as of 2024. [ 1 ]
[ edit ].
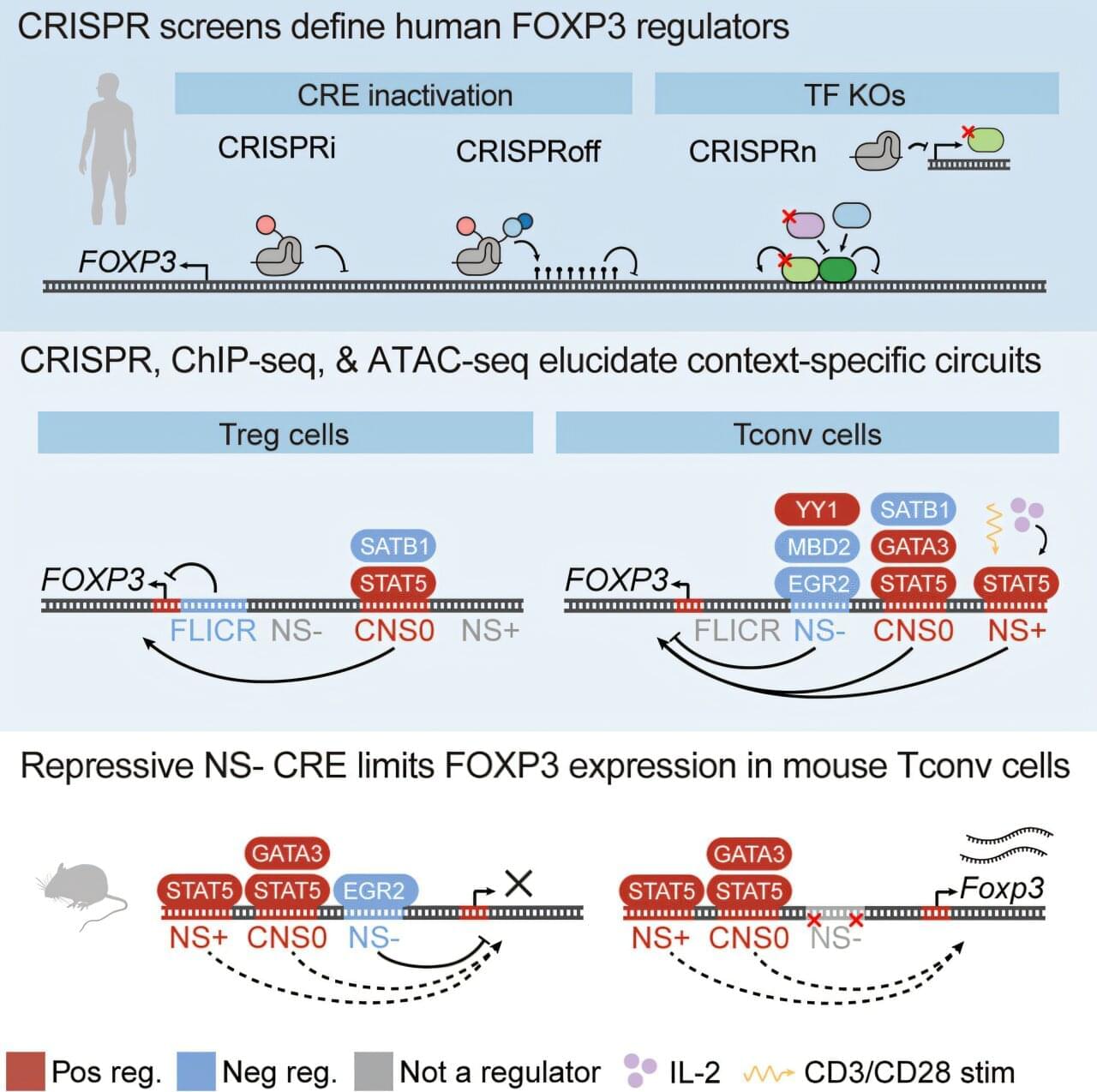
The immune system faces a delicate balancing act: It must be aggressive enough to fight infections and cancer, yet restrained enough to avoid attacking the body’s own tissues.
More than two decades ago, researchers identified a gene called FOXP3 as playing a critical role in maintaining this balance and preventing autoimmune disease—work that garnered this year’s Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
Now, scientists at Gladstone Institutes and UC San Francisco (UCSF) have mapped the intricate network of genetic switches that immune cells use to fine-tune levels of FOXP3. Their findings, published in Immunity, have important implications for developing immune therapies and address a long-standing mystery about why this gene behaves differently in humans than in mice.

This Neurology Education Teaching Neurovisual by Sutherland and Gummerson details the Head-Impulse-Nystagmus-Test-of-Skew (HINTS) exam, which uses special maneuvers to identify central etiologies of acute vestibular syndrome with greater sensitivity than hyperacute MRI.
Letters to the Editor.
The Letters section represents an opportunity for ongoing author debate and post-publication peer review. View our submission guidelines for Letters to the Editor before submitting your comment.

Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a highly prevalent disorder with limited therapeutic options. The central amygdala (CeA) is a critical brain region as dysregulation within the CeA and the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) system are associated with AUD pathology. CeA CRF1 receptors regulate alcohol drinking and have served as a therapeutic target in alcohol treatment. One emerging potential therapeutic for AUD is psilocybin. Psilocybin has been shown to decrease drinking in some clinical studies however the effects are variable and mechanisms underlying these effects are poorly understood. Psilocybin can engage many brain regions, including the CeA, and may produce therapeutic effects on drinking through interactions with CeA CRF1 neurons. The current study explores the effects of psilocin, the active metabolite of psilocybin, on voluntary ethanol drinking and CeA CRF1 activity to understand the potential mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of psilocin. Psilocin acutely decreased ethanol consumption in mice exposed to two different models of chronic ethanol exposure without producing changes in locomotor behavior. Psilocin increased CeA activation and decreased relative CRF1 activation in CeA sub-regions from ethanol-naïve female CRF1:GFP mice. These results were also observed in chronic ethanol-exposed mice at 24hr and 72hr withdrawal timepoints. Psilocin increased corticosterone at 24hr withdrawal but not at 72hr withdrawal. Collectively, these results demonstrate that psilocin engages CeA circuitry and decreases relative CRF1 activation, in parallel with acute reductions in drinking. These results contribute to our understanding of the mechanisms underlying the actions of psilocin and inform the interpretation of therapeutic effects in clinical studies.
Significance Statement Alcohol is one of the most commonly-used substances that dysregulates brain regions involved in emotional processing and stress. An important regulator of the stress response is the neuropeptide known as corticotropin releasing factor (CRF). Alcohol can dysregulate brain regions through the engagement of corticotropin releasing factor receptor 1 (CRF1)-containing neurons and thus promote continued alcohol use. Although alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a highly prevalent condition, few treatment options are available. Psilocybin, a psychedelic prodrug that is broken down into the active metabolite, psilocin, has emerged as a potential treatment for AUD in recent studies. The current study explores the effects of psilocin on alcohol drinking and central amygdala CRF1-containing neurons in female mice to better understand potential therapeutic mechanisms.
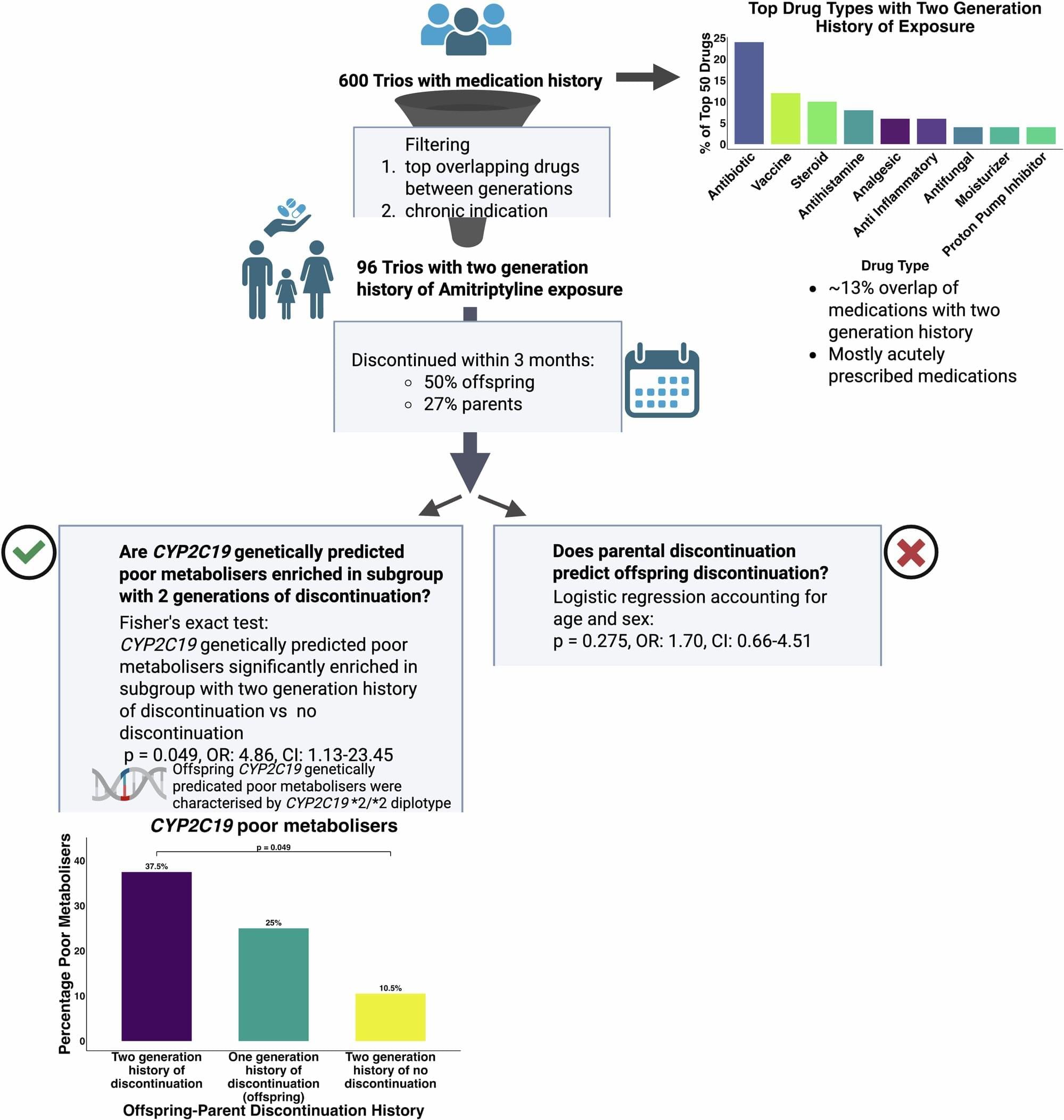
A new study from Queen Mary University of London shows that a family’s experience with certain medicines could help doctors predict how future generations will respond to the same drugs.
The researchers found that people were almost five times more likely to have a genetic difference affecting how they process antidepressants if both they and a parent had stopped taking the same medication early.
Published in Communications Medicine, the study looked at 600 British, Bangladeshi and Pakistani families from the Genes and Health Project—one of the world’s largest community genetics studies.
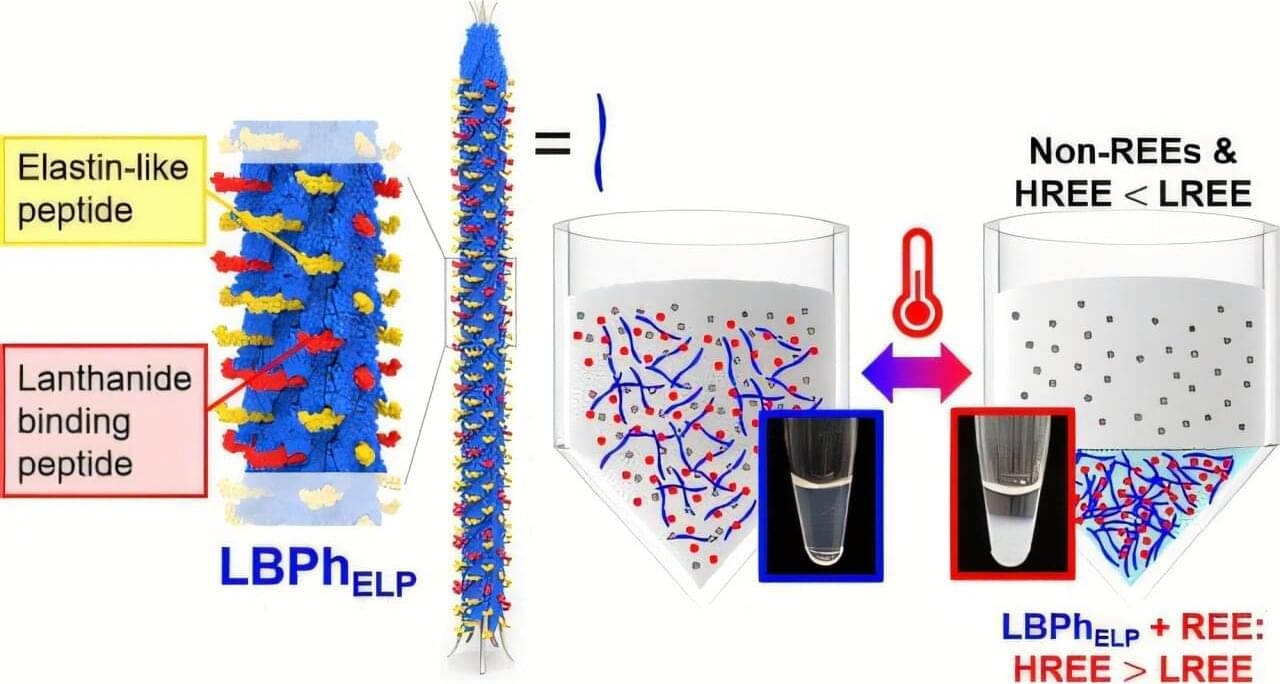
Today’s high-tech electronics and green energy technologies would not function without rare earth elements (REEs). These 17 metals possess unique properties essential to creating items like the phosphors that illuminate our mobile phone displays and the powerful magnets used in electric vehicles and wind turbines. But extracting these substances from raw materials is a dirty process that relies on toxic chemicals and leaves behind polluted waste.
Now, a team of UC Berkeley-led researchers may have solved this problem—thanks to a tiny virus.
As reported in Nano Letters, the researchers genetically engineered a harmless virus to act like a “smart sponge” that grabs rare earth metals from water, and, with a gentle change in temperature and acidity (pH), releases them for collection. Their unusual, groundbreaking approach could lead to a “clean” biological alternative to traditional extraction methods for REEs and other critical elements.

Black holes, regions of spacetime in which gravity is so strong that nothing can escape, are intriguing and extensively studied cosmological phenomena. Einstein’s general theory of relativity predicts that when two black holes merge, they emit ripples in spacetime known as gravitational waves.
Once the gravitational waves originating from black hole mergers fade, subtle hints of these waves could remain, known as late-time gravitational-wave tails. While the existence of these tails has been widely theorized about in the past, it was not yet conclusively confirmed.
Researchers at Niels Bohr Institute, University of Lisbon and other institutes worldwide recently performed black hole merger simulations based on Einstein’s general relativity equations, to further probe the existence of late-time gravitational-wave tails. Their simulations, outlined in a paper in Physical Review Letters, suggest that these tails not only exist, but could also have a larger amplitude than originally predicted and could thus be observed in future experiments.