A new report from the Commercial Space Federation warns that China could soon overtake the U.S. in the “new space race.” The country’s rapid progression starkly contrasts the limitations imposed on NASA by record-breaking budget cuts.


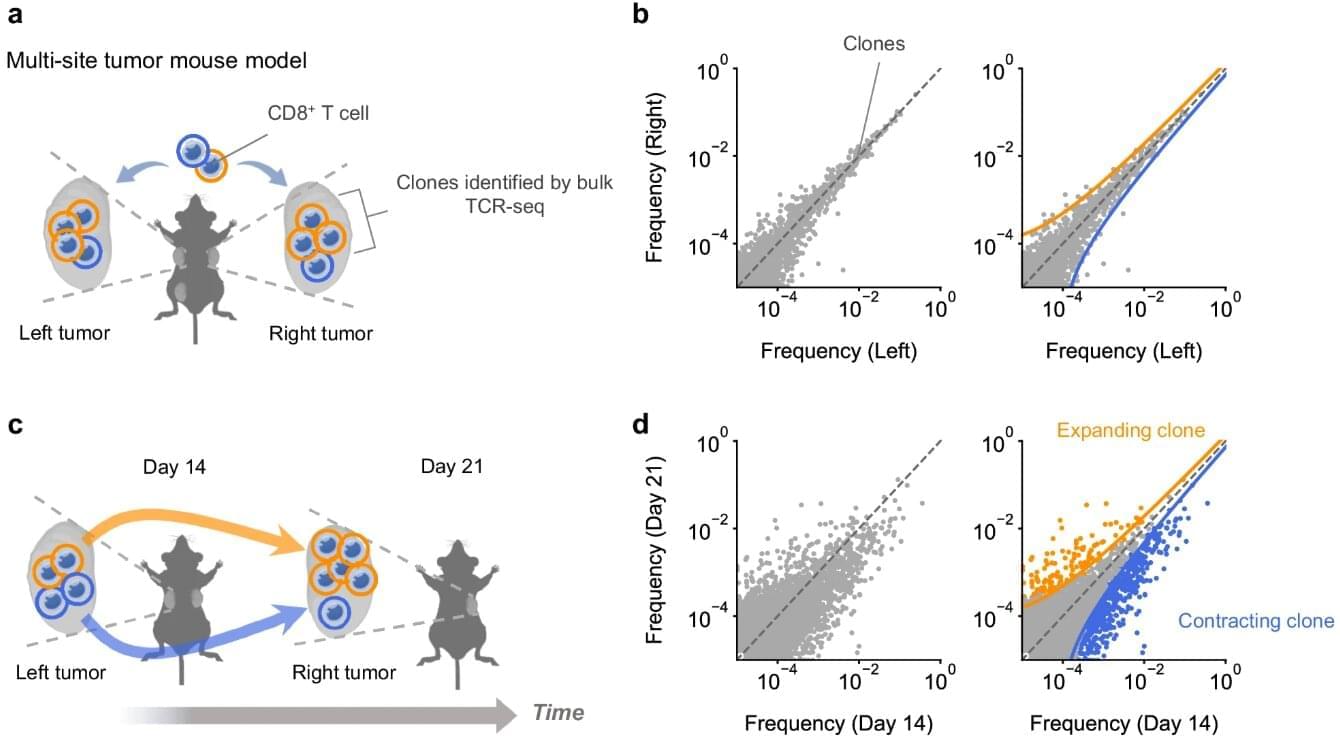
The ability of immune cells—particularly CD8+ T cells—to launch a rapid burst of proliferation inside tumors is key to the success of modern day cancer immunotherapies. However, the factors and mechanisms that drive this burst in proliferation remain poorly understood, making it difficult to predict which patients will benefit from treatment. A deeper understanding of this T cell burst could also guide the development of new therapies that enhance T cell proliferation and improve treatment outcomes.
To tackle this challenge, an international team of researchers led by Associate Professor Satoshi Ueha and Professor Kouji Matsushima from the Research Institute for Biomedical Sciences, Tokyo University of Science (TUS), Japan, developed a novel approach to monitor CD8⁺ T cell activity over time. Their findings, published in the journal Nature Communications on October 20, 2025, sheds new light on how T cells expand in the tumor—and how their expansion can be predicted, and ultimately, therapeutically reactivated.
“The development of immunotherapies has been hindered by our inability to comprehensively monitor their effects on immune cells —particularly cancer-fighting T cells—over time,” explains Dr. Ueha. “Building on our previous work, we developed a method to track these cells longitudinally in the tumor, allowing us to gain deeper insights into the burst of proliferation that drives effective anti-tumor responses.”

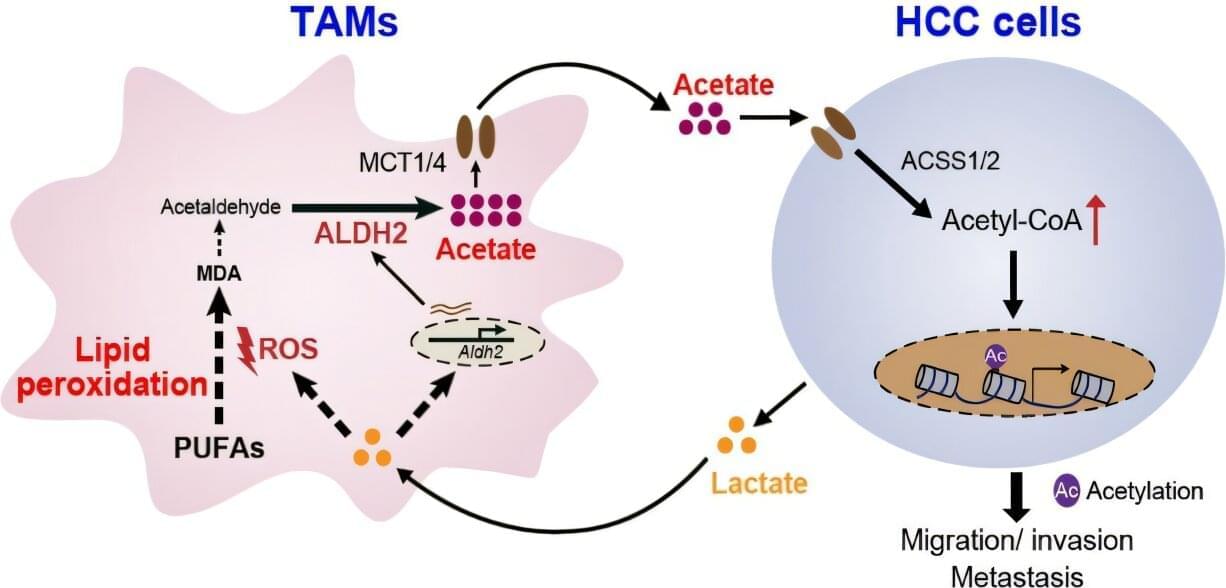
Chinese researchers have revealed a mechanism that triggers metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)—the most common type of primary liver cancer—through the production of acetate by tumor-associated macrophages.
Acetate is important to cancer metastasis because it promotes the synthesis of acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), which is a pivotal metabolic intermediate in the catabolism of glucose, lipids, and amino acids, as well as the biosynthesis of lipids and the TCA cycle. Acetyl-CoA also functions as a signaling molecule due to its role in lysine acetylation. Increased acetyl-CoA production is characteristic of metastatic cancers.
Researchers have known that acetate levels in the blood are significantly lower than in cancer tissues, suggesting the presence of acetate-producing cells within the cancer microenvironment. However, the exact source of acetate in the cancer microenvironment was previously unclear.
Doctors say another pandemic could arrive sooner than most people think. In this new video, you’ll find out why the risk is rising, the simple signs that tell experts a real outbreak has begun, and when that official Day One would likely be called.
🔔 Don’t forget to SUBSCRIBE! 🔔
SUGGEST A TOPIC:
https://bit.ly/suggest-an-infographic… Come chat with me: / discord 🔖 MY SOCIAL PAGES TikTok ►
/ theinfographicsshow Facebook ►
/ theinfographicsshow 📝 SOURCES: https://freepaste.link/vhx93r0mwj All videos are based on publicly available information unless otherwise noted.
💬 Come chat with me: / discord.
🔖 MY SOCIAL PAGES
TikTok ► / theinfographicsshow.
Facebook ► / theinfographicsshow.
📝 SOURCES:


According to a new study, offline social networks, revealed by co-location data, predict U.S. voting patterns more accurately than online social connections or residential sorting. Michele Tizzoni and colleagues analyzed large-scale data on co-location patterns from Meta’s Data for Good program, which collates anonymized data collected from people who enabled location services on the Facebook smartphone app. Their results are published in PNAS Nexus.
Colocation is defined as two people being within the same map tile, which is less than 600×600 meters, depending on latitude. The political affiliation of each person was inferred from their county of residence.
This data was compared with Facebook friendships and residential proximity for all U.S. counties, along with individual survey responses from 2,420 Americans regarding their offline and online social networks during the 2020 presidential election. For the residential proximity measurement, the voter registrations of the closest 1,000 neighbors were used.
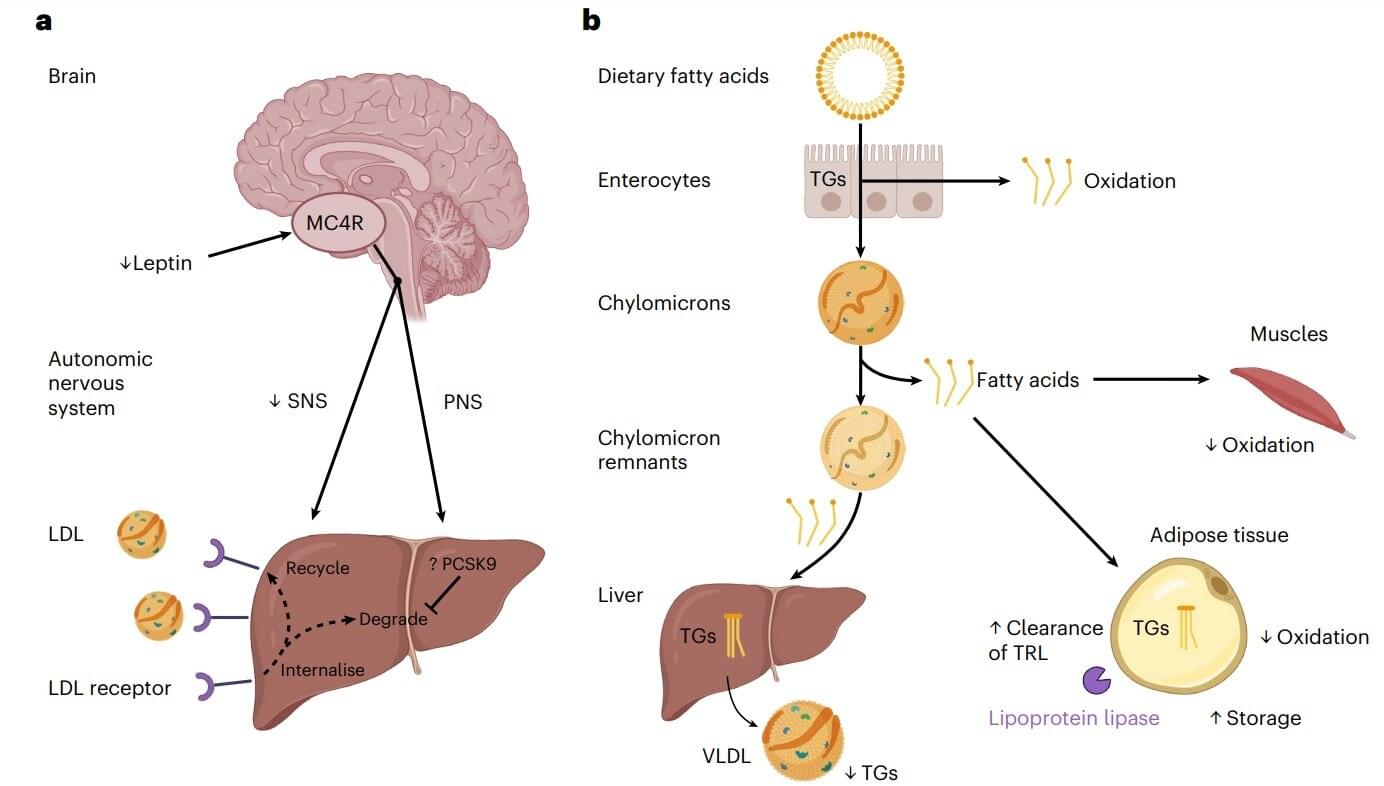
Deficiency of the gene melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) is linked with obesity among adults. A recent study has found that the same deficiency also leads to surprising outcomes such as reduced risk of heart disease, lower cholesterol, and triglycerides. These results contradict the well-established correlation between obesity and cardiovascular diseases.
The researchers scanned the genetic profiles of 7,719 children from the Genetics of Obesity Study (GOOS) cohort. They identified 316 probands—first person in a family to draw medical attention to a genetic disorder —and 144 adult family members with obesity due to loss-of-function (LoF) MC4R mutations.
Even after adjusting for weight, these individuals showed better blood pressure profiles and cardiovascular health when compared to 336,728 controls from the UK Biobank.

In recognition of Breast Cancer Awareness Month, join us for a live webinar to uncover the complexity of tumor biology and the surprising resilience of normal tissue. This event will feature two expert-led presentations: one demonstrating how protein multiplexing and quantitative imaging uncover the hidden heterogeneity of breast tumors, and another examining how natural tissue remodeling can both suppress and influence oncogenic transformation. A live discussion and Q&A session will follow, giving you the opportunity to engage directly with leading researchers and gain valuable insights to improve cancer diagnosis, guide therapy decisions, and inform prevention strategies. All sessions will be available on demand, allowing flexible access for continued learning and engagement.
Featured Talks: