Find what’s new in ovarian cancer, including current progress in treatment with drugs that block DNA repair. Selected NCI-supported programs that address ovarian cancer are also described.
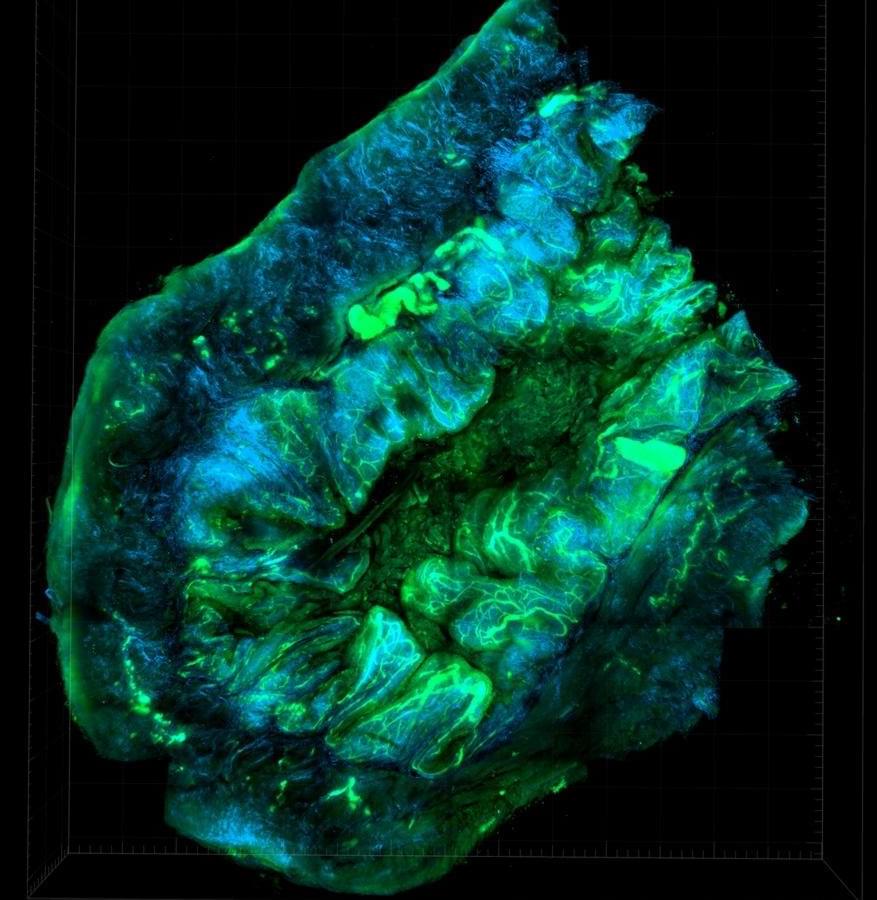

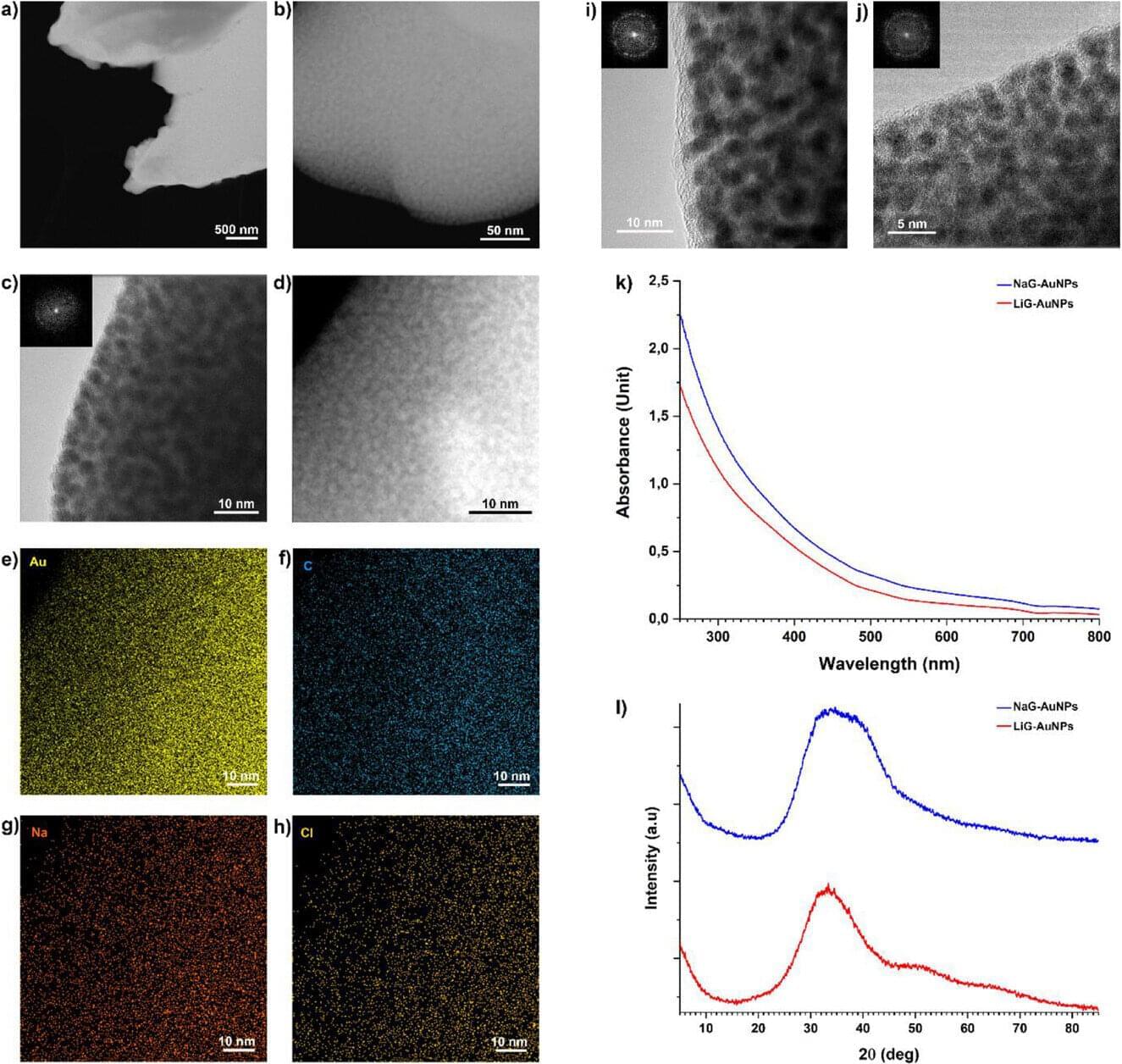
Tiny gold particles that act as carriers for lithium can be delivered directly to the brain in the form of a nasal spray. Developed by scientists at the Università Cattolica Rome campus/Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, the new nanotechnological device can be used for the treatment and prevention of neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases.
Lithium is already in clinical use for manic-depressive syndrome, but in oral formulation it is not free of side effects. It is used to combat neuropsychiatric diseases such as bipolar disorder, neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, and brain infections such as those caused by Herpes Simplex Virus type 1, which several recent studies have linked to an increased risk of neurological diseases.
Published in the journal Advanced Materials and already patented, the idea is the result of a study that demonstrated that it is possible to directly inhibit the activity of an enzyme that plays a key role in the development of these diseases (glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, GSK-3β) directly in the brain by using lithium delivered by intranasally administered gold nanoparticles.

Imagine tiny machines, smaller than a virus, spinning inside cancer cells and rewiring their behavior from within. No surgery, no harsh chemicals, just precision at the molecular level.
Two researchers from the Artie McFerrin Department of Chemical Engineering at Texas A&M University are investigating light-activated molecular motors—nanometer-sized machines that can apply mechanical forces from within cells to target and selectively disrupt cancerous activity.
Chemical engineering professor Dr. Jorge Seminario and postdoctoral associate Dr. Diego Galvez-Aranda have contributed to pioneering research by demonstrating a new frontier in non-invasive cancer therapies. The recently published manuscript in the Journal of the American Chemical Society continues this line of investigation.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/

There’s a long-held belief in diabetes prevention that weight loss is the main way to lower disease risk. Our new study challenges this.
For decades, people diagnosed with prediabetes—a condition affecting up to one in three adults depending on age—have been told the same thing by their doctors: eat healthily and lose weight to avoid developing diabetes.
This approach hasn’t been working for all. Despite unchanged medical recommendations for more than 20 years, diabetes prevalence continues rising globally. Most people with prediabetes find weight-loss goals hard to reach, leaving them discouraged and still at high risk of diabetes.

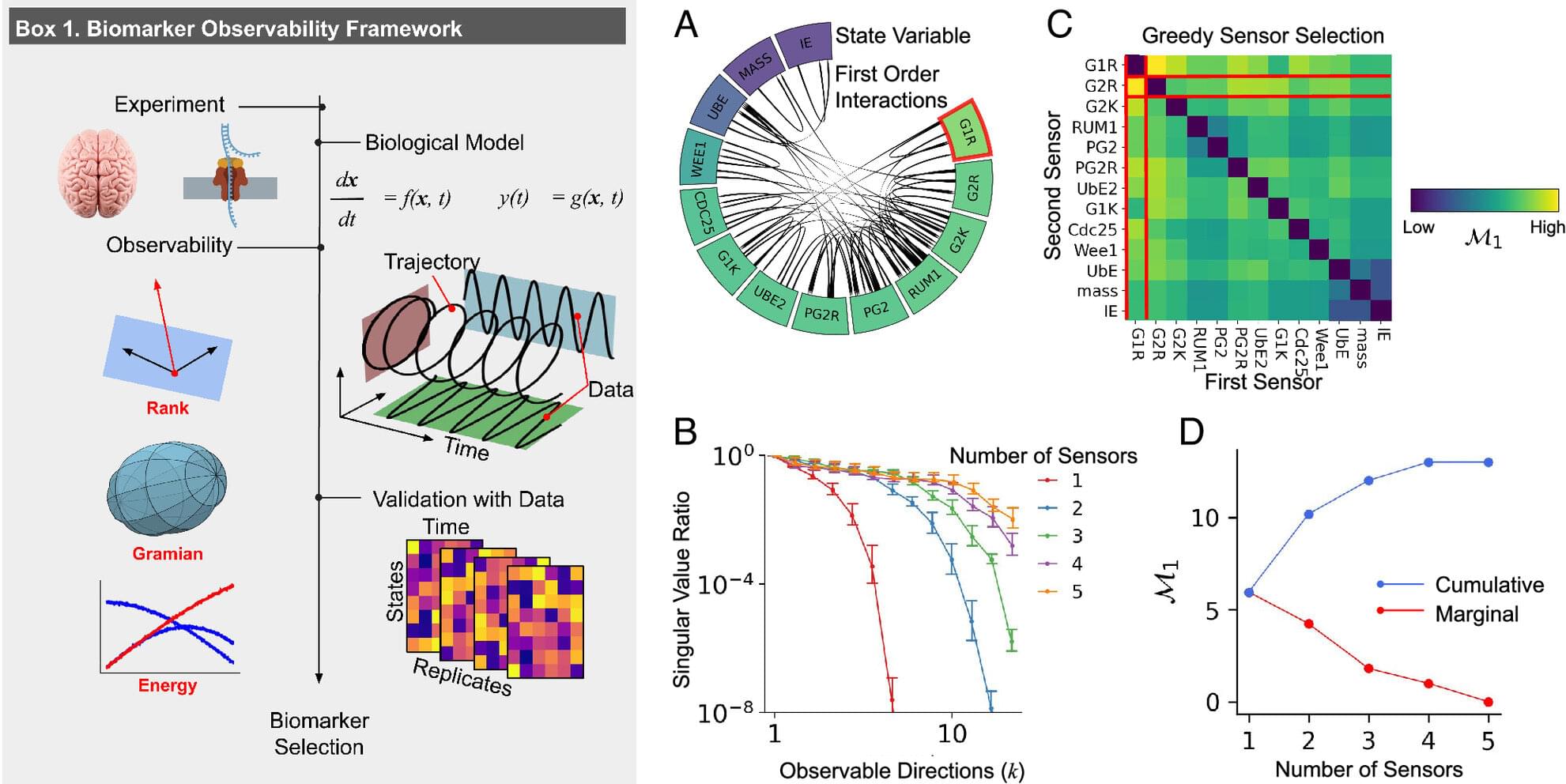
People often compare the genome to a computer’s program, with the cell using its genetic code to process environmental inputs and produce appropriate responses.
But the machine metaphor can be extended even further to any biological system, and applying established concepts of engineering to biology could revolutionize how scientists make their observations within biology, according to research from University of Michigan.
In a paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Indika Rajapakse, Ph.D., Joshua Pickard, Ph.D. (now an Eric and Wendy Schmidt Postdoctoral Fellow at the Broad Institute), and their team propose that fundamental principles of control theory and observability can be applied to study biological processes that change over time.
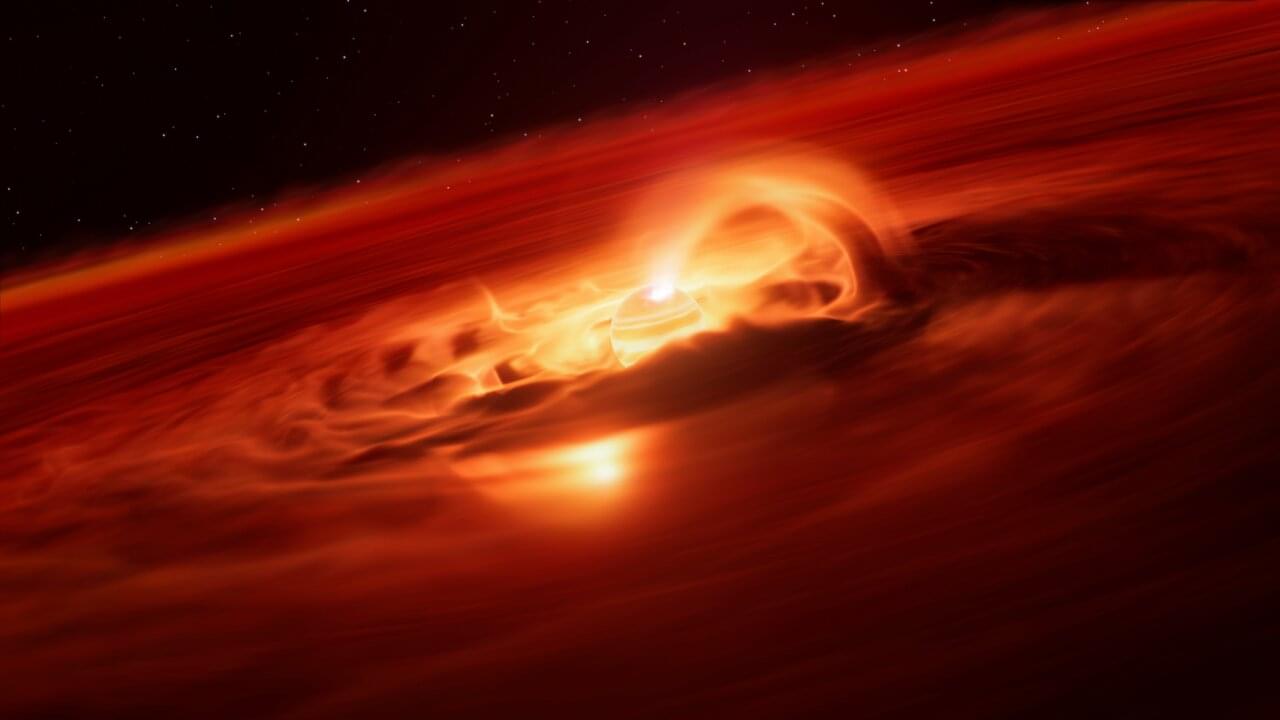

Astronomers have identified an enormous ‘growth spurt’ in a so-called rogue planet. Unlike the planets in our Solar System, these objects do not orbit stars, free-floating on their own instead. The new observations, made with the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT), reveal that this free-floating planet is eating up gas and dust from its surroundings at a rate of six billion tonnes a second. This is the strongest growth rate ever recorded for a rogue planet, or a planet of any kind, providing valuable insights into how they form and grow.
“People may think of planets as quiet and stable worlds, but with this discovery we see that planetary-mass objects freely floating in space can be exciting places,” says Víctor Almendros-Abad, an astronomer at the Astronomical Observatory of Palermo, National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), Italy and lead author of the new study.
The newly studied object, which has a mass five to 10 times the mass of Jupiter, is located about 620 light-years away in the constellation Chamaeleon. Officially named Cha 1107–7626, this rogue planet is still forming and is fed by a surrounding disc of gas and dust. This material constantly falls onto the free-floating planet, a process known as accretion. However, the team led by Almendros-Abad has now found that the rate at which the young planet is accreting is not steady.
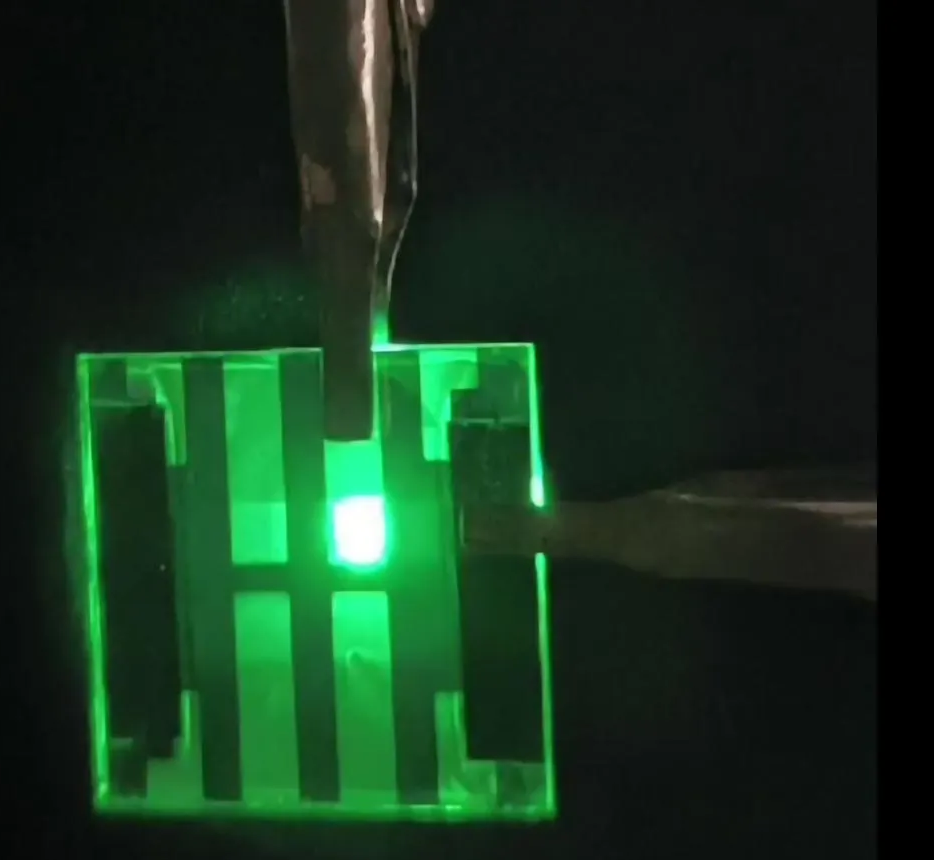
Scientists have developed an ultra-thin, paper-like LED that emits a warm, sunlike glow, promising to revolutionize how we light up our homes, devices, and workplaces. By engineering a balance of red, yellow-green, and blue quantum dots, the researchers achieved light quality remarkably close to natural sunlight, improving color accuracy and reducing eye strain.