A qubit is the delicate, information-processing heart of a quantum device. In the coming decades, advances in quantum information are expected to give us computers with new, powerful capabilities and detectors that can pick up atomic-scale signals in medicine, navigation and more. The realization of such technologies depends on having reliable, long-lasting qubits.
Now, researchers have taken an important step in understanding the rules necessary for the design of useful, efficient qubits.
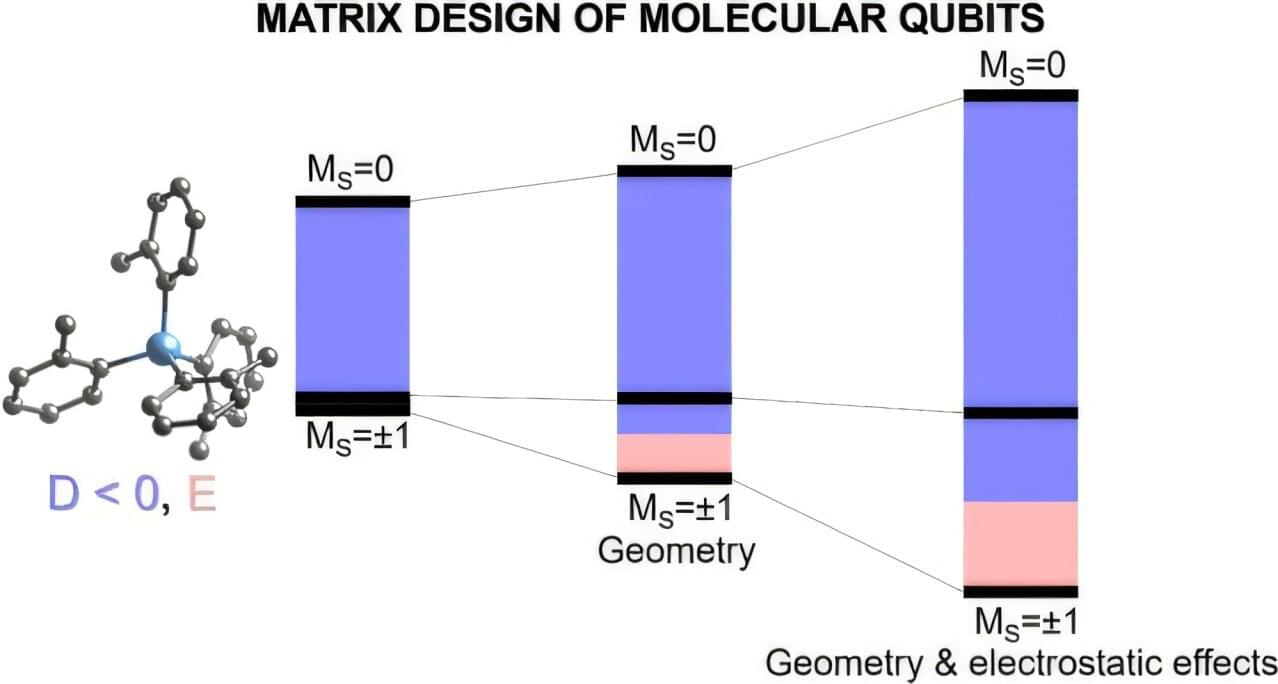
Using advanced computer modeling, the researchers came up with a way to accurately predict and fine-tune key magnetic properties of a type of device called a molecular qubit. They also figured out which factors in the material that the qubit sits in affect this tuning the most and calculated how long the qubits can live.