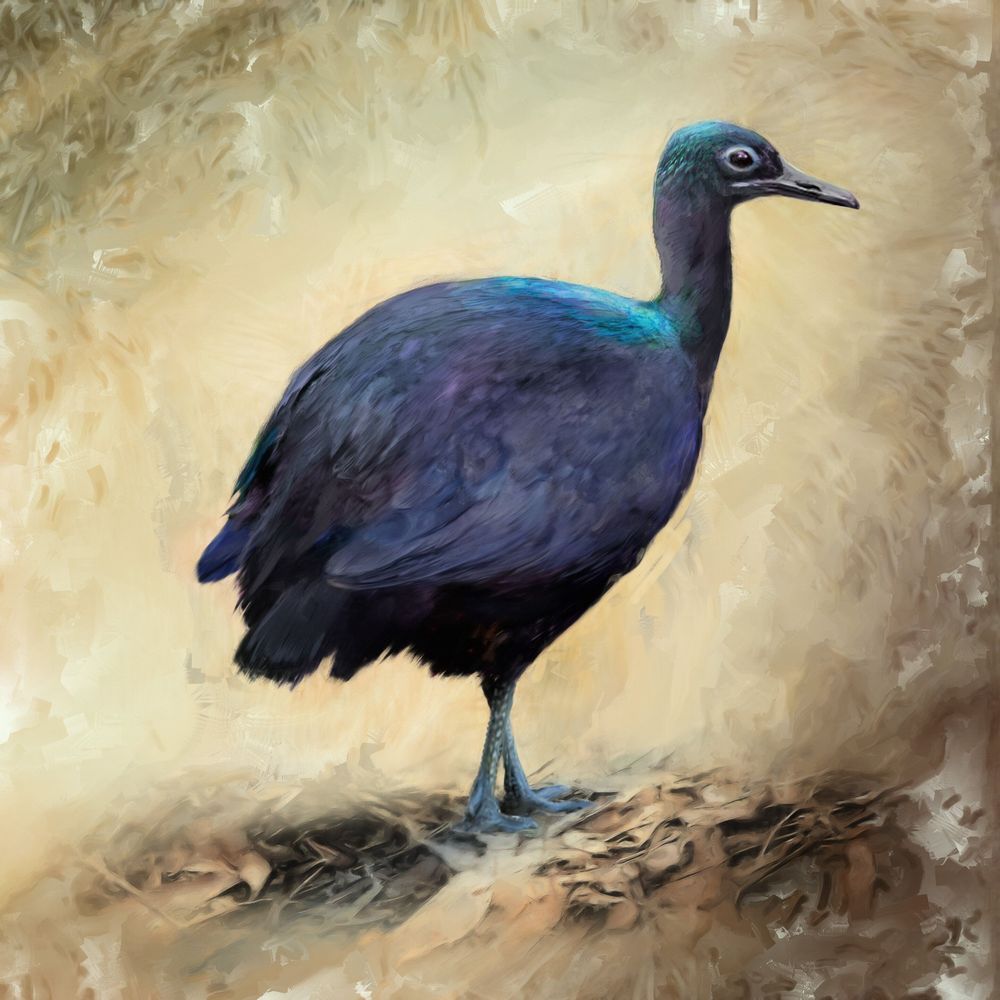
Cassowaries are big flightless birds with blue heads and dinosaur-looking feet; they look like emus that time forgot, and they’re objectively terrifying. They’re also, along with their ostrich and kiwi cousins, part of the bird family that split off from chickens, ducks, and songbirds 100 million years ago. In songbirds and their relatives, scientists have found that the physical make-up of feathers produce iridescent colors, but they’d never seen that mechanism in the group that cassowaries are part of—until now. In a double-whammy of a paper in Science Advances, researchers have discovered both what gives cassowary feathers their glossy black shine and what the feathers of birds that lived 52 million years ago looked like.
“A lot of times we overlook these weird flightless birds. When we’re thinking about what early birds looked like, it’s important to study both of these two sister lineages that would have branched from a common ancestor 80 million or so years ago,” says Chad Eliason, a staff scientist at the Field Museum and the paper’s first author.
“Understanding basic attributes—like how colors are generated—is something we often take for granted in living animals. Surely, we think, we must know everything there is to know? But here, we started with simple curiosity. What makes cassowaries so shiny? Chad found an underlying mechanism behind this shine that was undescribed in birds. These kinds of observations are key to understanding how color evolves and also inform how we think about extinct species,” says Julia Clarke, a paleontologist at the Jackson School of Geosciences at the University of Texas at Austin and the paper’s senior author. Eliason began conducting research for this paper while working with Clarke at the University of Texas as part of a larger project funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF EAR 1355292) to study how flightless birds like cassowaries have evolved their characteristic features.