In some cases, it makes the concept of traveling to alternate futures a reality.


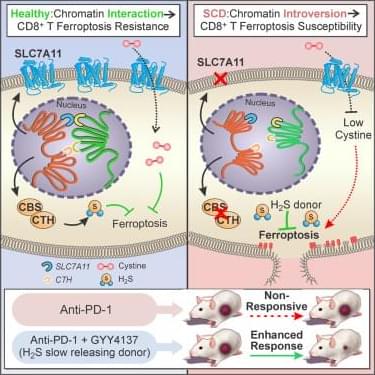
How sickle cell disease suppresses antitumor immunity.
Sickle cell disease (SCD) have a higher risk of developing certain cancers than the general population, but the mechanisms driving this increased risk remain unclear.
SCD inhibits CD8+ T cell function in the tumor microenvironment, potentially affecting cancer immunotherapy.
The researchers reveal that SCD alters the 3D genome architecture of CD8+ T cells, triggering ferroptosis and impairing antitumor response resulting in reduced expression of anti-ferroptotic genes, including SLC7A11 and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) biogenesis genes, thereby increasing susceptibility to ferroptosis.
They also demonstrate that hydrogen sulfide treatment rescued SLC7A11 expression, mitigated ferroptosis and enhanced immune and anti-tumor responses, thereby offering new avenues for precision immunotherapy in patients with inherited disorders. https://sciencemission.com/Sickle-cell-disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD) inhibits CD8+ T cell function in the tumor microenvironment, potentially affecting cancer immunotherapy. Zhao, Hu, Deng, et al. reveal that SCD alters the 3D genome architecture of CD8+ T cells, triggering ferroptosis and impairing anti-tumor responses, which can be reversed by hydrogen sulfide treatment, offering new avenues for precision immunotherapy in patients with inherited disorders.

A new study published in JAMA Psychiatry makes the case that symptom provocation may significantly improve the clinical effectiveness of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), a noninvasive brain stimulation method used to treat depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and nicotine dependence.
The study was conceptualized, designed and supervised by Heather Burrell Ward, MD, assistant professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences and director of Neuromodulation Research, in collaboration with Simon Vandekar, Ph.D., associate professor of Biostatistics and Daniel Bello and Megan Jones, two students in their respective labs.
This is the first large-scale meta-analysis to examine whether deliberately triggering symptoms immediately before administering rTMS enhances treatment outcomes.
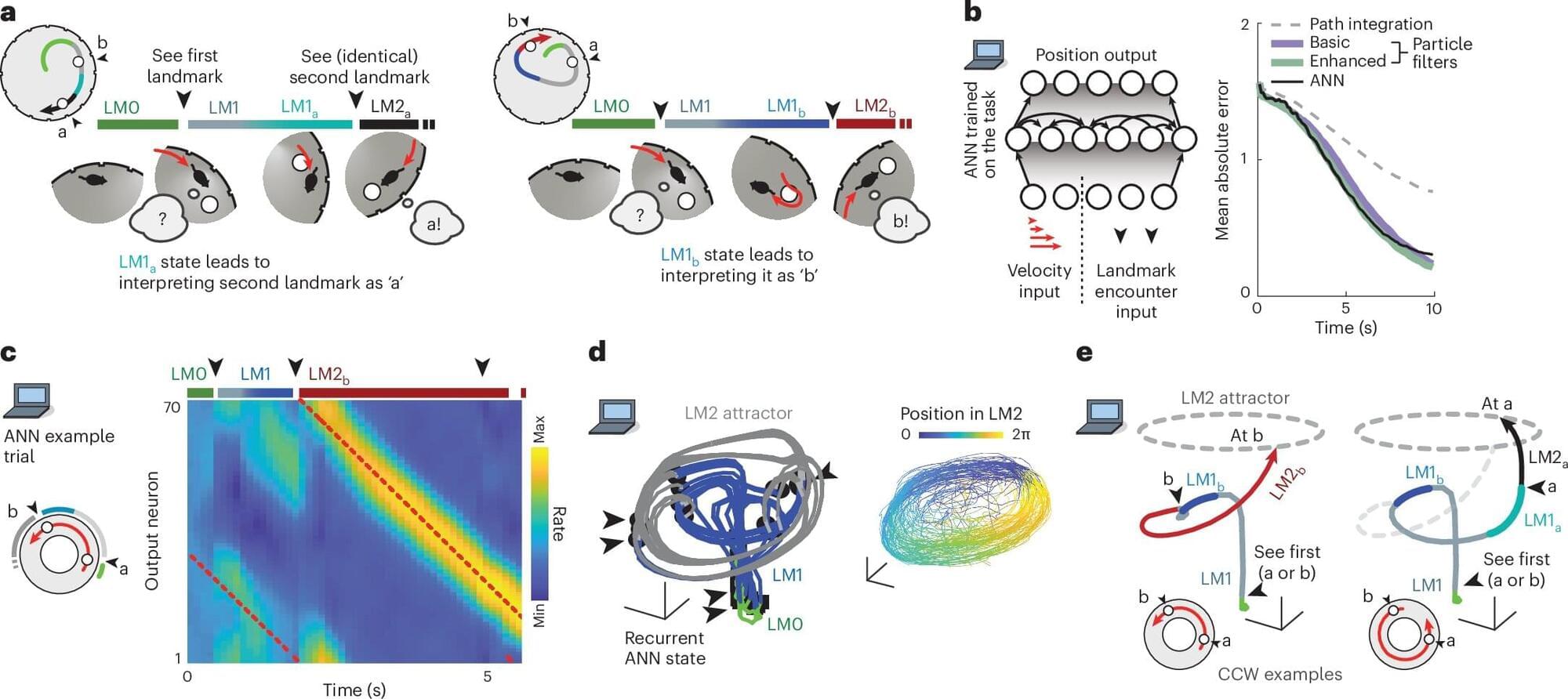
When navigating a place that we’re only somewhat familiar with, we often rely on unique landmarks to help make our way. However, if we’re looking for an office in a brick building, and there are many brick buildings along our route, we might use a rule like looking for the second building on a street, rather than relying on distinguishing the building itself.
Until that ambiguity is resolved, we must hold in mind that there are multiple possibilities (or hypotheses) for where we are in relation to our destination. In a study of mice, MIT neuroscientists have now discovered that these hypotheses are explicitly represented in the brain by distinct neural activity patterns.
This is the first time that neural activity patterns that encode simultaneous hypotheses have been seen in the brain. The researchers found that these representations, which were observed in the brain’s retrosplenial cortex (RSC), not only encode hypotheses but also could be used by the animals to choose the correct way to go.
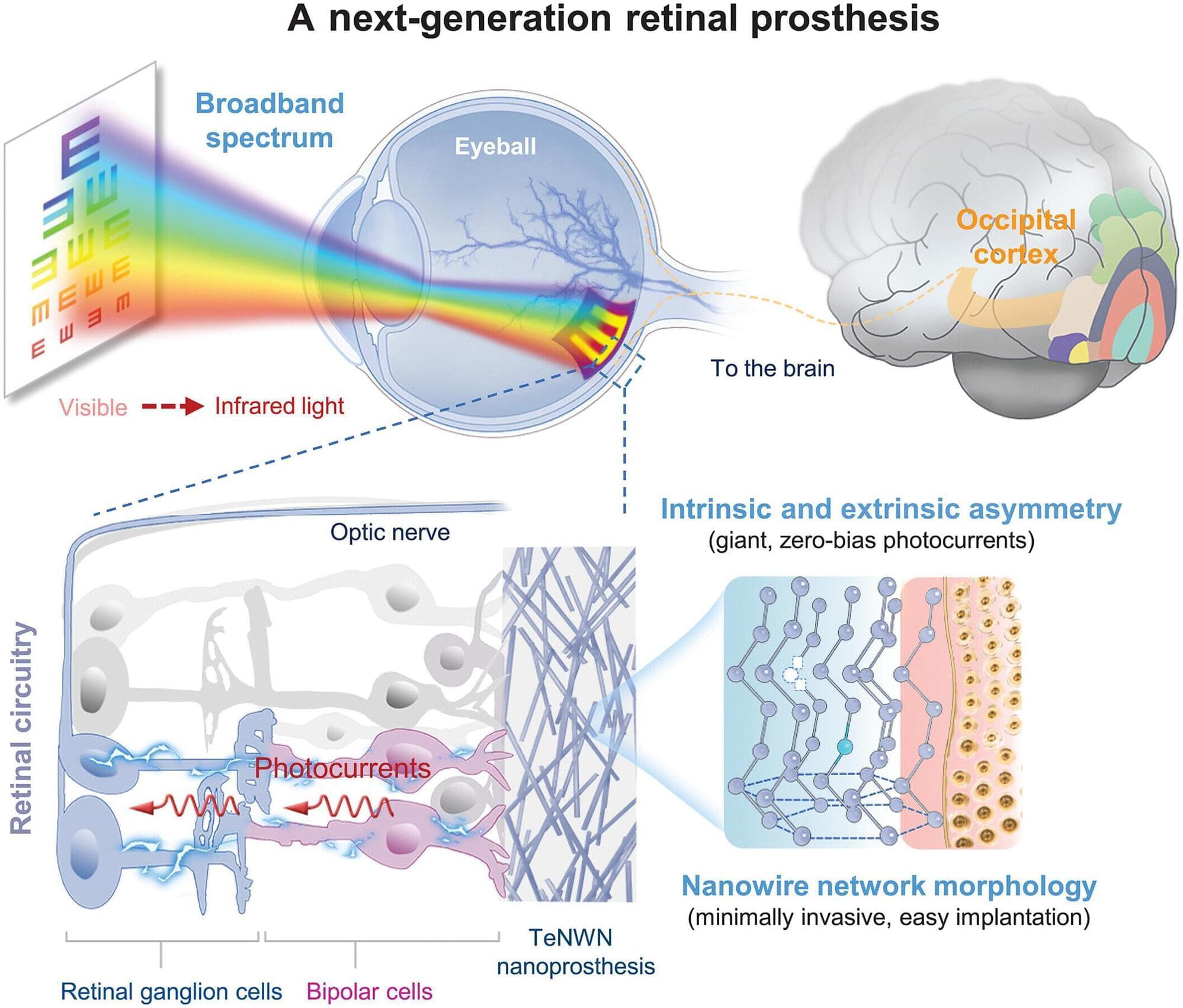
A team from Fudan University, the Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, the Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications and Shaoxin Laboratory, all in China, has developed a retinal prosthesis woven from metal nanowires that partially restored vision in blind mice.
In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes how they created tellurium nanowires and interlaced them to create a retinal prosthesis. Eduardo Fernández, with University Miguel Hernández, in Spain, has published a Perspective piece in the same journal issue outlining the work done by the team on this new effort.
Finding a way to cure blindness has been a major goal for scientists for many years, and such efforts have paid off for some types of blindness, such as those caused by cataracts. Other types of blindness associated with damage to the retina, however, have proven too difficult to overcome in most cases. For this research, the team in China tried a new approach to treating such types of blindness by building a mesh out of a semiconductor and affixing it to the back of the eye, where it could send signals to the optic nerve.
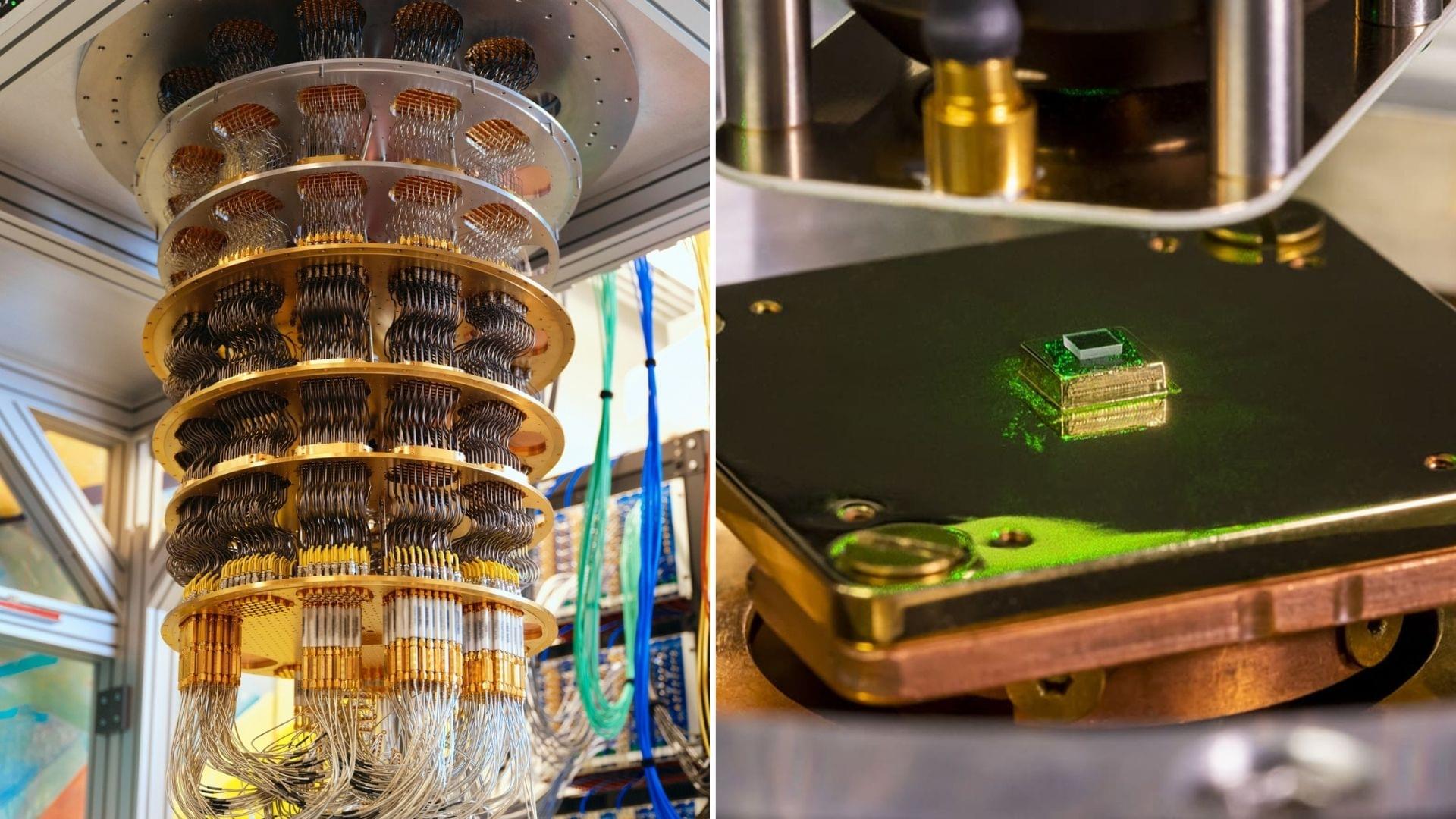


World’s first on-chip error-resistant photonic qubit signals a major leap for scalable, modular quantum computing.