Spanish scientists have created the first human–monkey chimera, and in the process sparked an ethical debate.


UC San Francisco researchers have discovered how a mutation in a gene regulator called the TERT promoter—the third most common mutation among all human cancers and the most common mutation in the deadly brain cancer glioblastoma—confers “immortality” on tumor cells, enabling the unchecked cell division that powers their aggressive growth.
The research, published September 10, 2018 in Cancer Cell, found that patient-derived glioblastoma cells with TERT promoter mutations depend on a particular form of a protein called GABP for their survival. GABP is critical to the workings of most cells, but the researchers discovered that the specific component of this protein that activates mutated TERT promoters, a subunit called GABP-ß1L, appears to be dispensable in normal cells: Eliminating this subunit using CRISPR-based gene editing dramatically slowed the growth of the human cancer cells in lab dishes and when they were transplanted into mice, but removing GABP-ß1L from healthy cells had no discernable effect.
“These findings suggest that the ß1L subunit is a promising new drug target for aggressive glioblastoma and potentially the many other cancers with TERT promoter mutations,” said study senior author Joseph Costello, Ph.D., a leading UCSF neuro-oncology researcher.



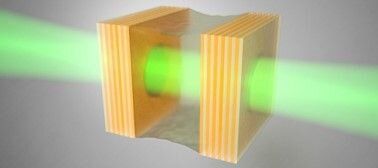
A simple drop of olive oil in a system of photons bouncing between two mirrors has revealed universal aspects of phase transitions in physics. Researchers at AMOLF used an oil-filled optical cavity in which light undergoes phase transitions similar to those in boiling water. The system they studied has memory because the oil causes photons to interact with themselves. By varying the distance between the two mirrors and measuring the transmission of light through the cavity, they discovered a universal law describing phase transitions in systems with memory. These results are published on April 15th in Physical Review Letters.
The Interacting Photons research group at AMOLF studies nonlinearity and noise in photonic systems. One of such systems is a cavity, formed by two mirrors facing each other at a close distance. Within the cavity, light bounces back and forth as it is reflected by the mirrors. Putting something inside such an optical cavity, changes the properties of the system. “We created a system with memory by placing a drop of olive oil inside the cavity,” says group leader Said Rodriguez. “The oil mediates effective photon-photon interactions, which we can see by measuring the transmission of laser light through this cavity.”

Fyodor R., Refund Institute
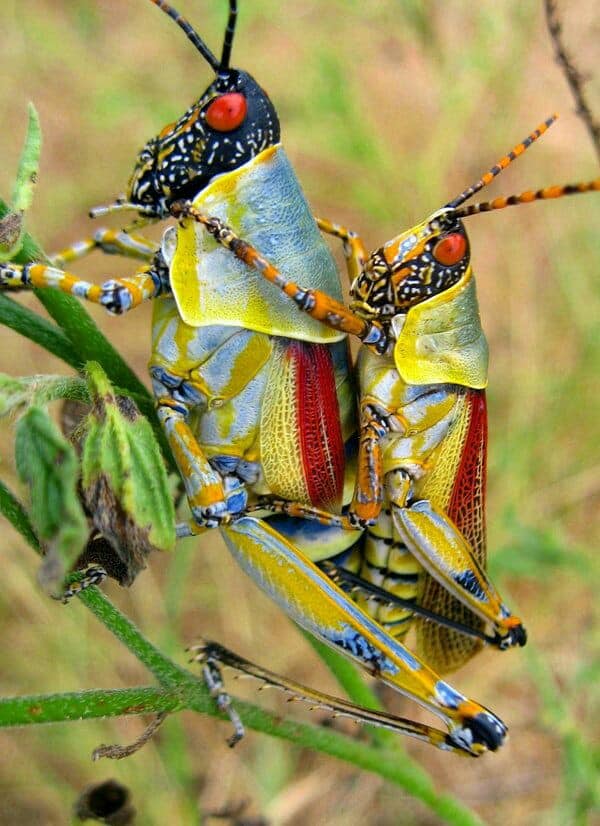
👽Locust Swarm
👽Part I: New Terrain, destination Iran
(See map picture 2)
New swarms are currently forming from Kenya to Iran, according to the United Nations locust watch website. Addressing the outbreak requires urgent, additional funding and technical help from developed countries, Cheke said, because the tiny size and budget of the United Nation’s Food and Agricultural Organization team responsible for locust monitoring and control is already overwhelmed.
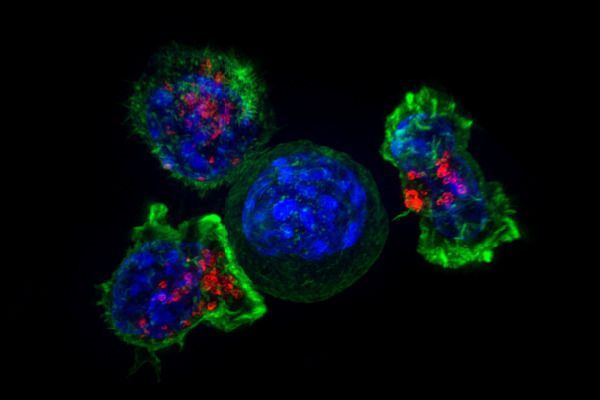
Networks are at the heart of everything from communications systems to pandemics. Now researchers have found that a unique type of network also underlies the structures of critical cellular compartments known as membraneless organelles. These findings may provide key insights into the role of these structures in both disease and cellular operations.
“Prior to this study, we knew the basic physical principle by which these protein-rich compartments form — they condense from the cytoplasm into liquid droplets like dew on a blade of grass,” said David Sanders, a post-doctoral researcher in Chemical and Biological Engineering at Princeton University. “But unlike dew drops, which are composed of a single component (water), cellular droplets are intimidatingly complex. Our work uncovers surprisingly simple principles that we think are universal to the assembly of liquid organelles, and opens new frontiers into studying their role in health and disease.”
Sanders is the lead author in an article in the journal Cell describing a blueprint for the assembly of these liquid structures, also called condensates. The researchers looked closely at two types of condensates, stress granules and processing bodies (“P-bodies”). In the Cell paper, researchers directed by Clifford Brangwynne, a professor of Chemical and Biological Engineering at Princeton and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, combined genetic engineering and live cell microscopy approaches to reveal the rules underlying the assembly and structure of stress granules, and why they remain distinct from their close relatives, P-bodies.

Google plans to add a Zoom-like gallery view to its business- and education-focused Meet videoconferencing service and let users start calls and join meetings right from Gmail, Google’s GM and VP of G Suite Javier Soltero told Reuters in an interview. The additions come amid huge growth for Meet as families, students, and workers use the service while at home due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The upcoming gallery view will let users display up to 16 meeting participants in one frame, according to Reuters. That functionality is coming later this month, said Soltero. Zoom’s gallery view, by contrast, lets you see the thumbnails of up to 49 people in one screen, if you have a powerful enough CPU to display them all.
