Experts wonder how genetic engineering will eventually reshape the natural world.
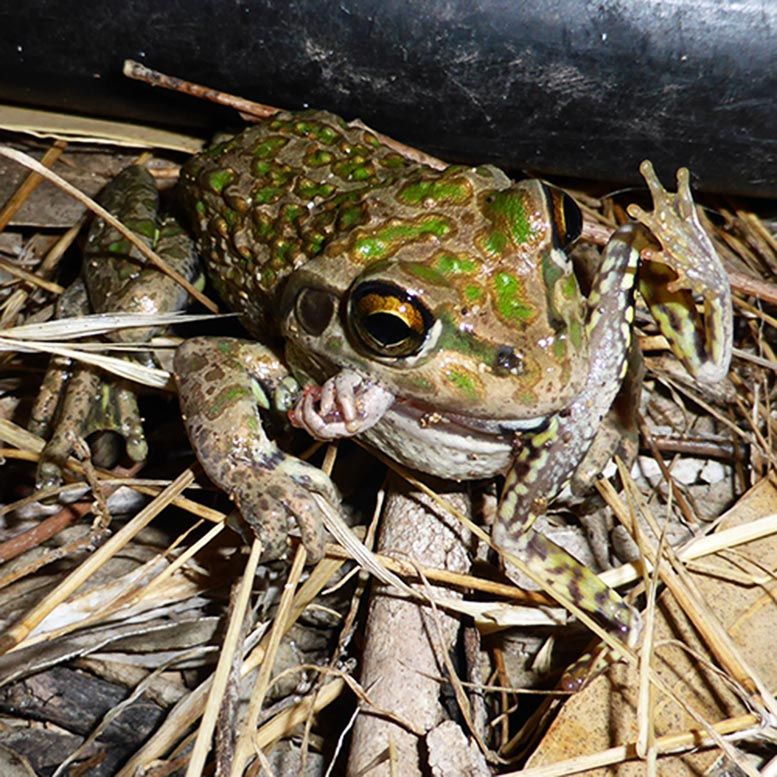




“The state government should consider managing the invasive population of spotted-thighed frogs at Streaky Bay. This should include education programs to inform people about what to do if they find a frog, as well as the feasibility of exterminating the population in South Australia.
“Importantly, if you do see one of these critters in your travels – leave it be. We don’t want it hitchhiking any further.”
Reference: ” Indiscriminate feeding by an alien population of the spotted-thighed frog (Litoria cyclorhyncha) in southern Australia and potential impacts on native biodiversity” by Christine M. Taylor, Gunnar Keppel, Shaun O’Sullivan, Stefan Peters, Gregory D. Kerr and Craig R. Williams, 9 April 2020, Australian Journal of Zoology. DOI: 10.1071/ZO19042
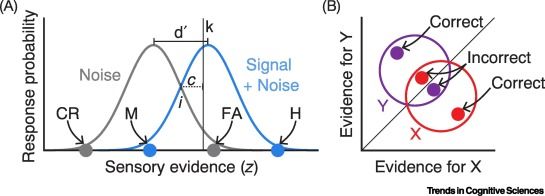
Making rapid decisions on the basis of sensory information is essential to everyday behaviors. Why, then, are perceptual decisions so variable despite unchanging inputs?
Spontaneous neural oscillations have emerged as a key predictor of trial-to-trial
Perceptual variability. New work casting these effects in the framework of models.
While watching the launch of SpaceX Crew Dragon, I noticed that, once the astronauts came out of the elevator in the fixed service structure, they had to ‘climb up’ one level using the stairs, before entering the white room through the crew access arm. I’m curious to know why doesn’t the elevator take them directly to the crew access arm level?
Earlier, I thought the reason might be due to the height difference between the side hatches on the Space Shuttle and Crew Dragon. But after seeing the following image it became evident that the difference is more than one level:
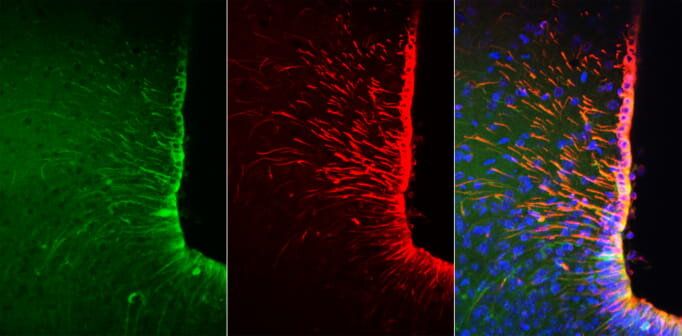
It has previously been discovered that tanycytes—cells found in part of the brain that controls energy levels —detect nutrients in food and tell the brain directly about the food we have eaten.
Tanycytes do this by responding to amino acids found in foods, via the same receptors that sense the flavor of amino acids (“umami” taste), which are found in the taste buds of the tongue.
In the paper ‘Hypothalamic tanycytes generate acute hyperphagia through activation of the arcuate neuronal network.’ published today, the 8th June, in the journal PNAS, researchers from the School of Life Sciences at the University of Warwick, explain how tanycytes can increase appetite.
Our lungs, bones, blood vessels and other major organs are made up of cells, and one way our bodies keep us healthy is by using protein messengers known as ligands that bind to receptors on the surfaces of cells to regulate our biological processes. When those messages get garbled, it can make us ill with a host of different diseases.

The Cognitive Debt hypothesis proposes that repetitive negative thinking (RNT), a modifiable process common to many psychological risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) may itself increase risk. We sought to empirically examine relationships between RNT and markers of AD, compared with anxiety and depression symptoms.

