Researchers from CSIRO’s Data61, the data and digital specialist arm of Australia’s national science agency, have developed a world-first set of techniques to effectively ‘vaccinate’ algorithms against adversarial attacks, a significant advancement in machine learning research.
International team spearheaded by researchers at McGill University has discovered a biological mechanism that could explain heightened somatic awareness, a condition where patients experience physical discomforts for which there is no physiological explanation.
:0000000 imagine a ship covered in blackhole metal face_with_colon_three
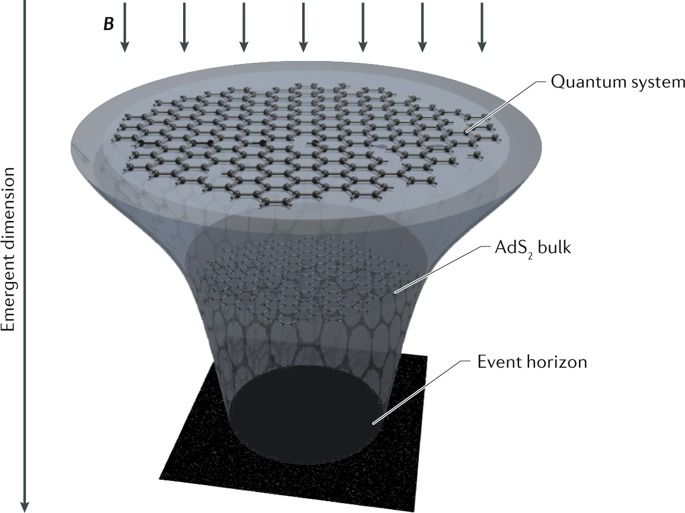
Holographic quantum matter exhibits an intriguing connection between quantum black holes and more conventional (albeit strongly interacting) quantum many-body systems. This connection is manifested in the study of their thermodynamics, statistical mechanics and many-body quantum chaos. In this Review, we discuss these connections, focusing on the most promising example of holographic quantum systems to date – the family of Sachdev–Ye–Kitaev (SYK) models. The SYK models are simple quantum mechanical models that have the potential to holographically realize quantum black holes. We examine various proposals for the experimental realizations of SYK models, including ultracold gases, graphene flakes, semiconductor quantum wires and 3D topological insulators. These approaches offer the exciting prospect of accessing black hole physics and thus addressing many important questions regarding quantum gravity in the laboratory.
Though it may be hard to believe that there is already an “established” method of doing something such as 3D-printing biological tissue, there does indeed seem to be one. It utilizes microscale scaffolds – which a newly-developed technique does away with the need for.
While we all know that billionaires control a substantial amount of the world’s wealth – in fact, current projections see the richest 1% controlling 2/3 of it by 2030. But, did you know that when they aren’t investing in space shuttles, underground Hyperloops and sprawling tech campuses, the super-rich are looking at a range of mind-blowing methods to increase their lifespan?
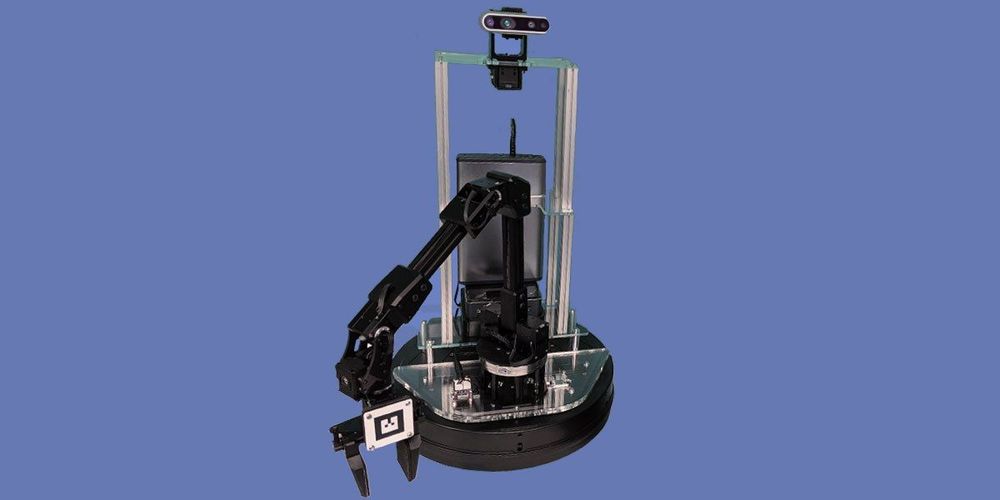
Anyone who tells you the robot apocalypse is upon us—that the machines will not stop stealing our jobs, that they are gearing up to chase us through the streets while doing backflips and fighting off stick-wielding humans—has never tried to program a robot. It’s difficult to get a machine to do so much as move an arm, which requires the precise control and coordination of joint angles and torque.
The difficulty of programming robots is a problem that Facebook, of all companies, wants to fix. Today the social network continues its unlikely dive into robotics by open-sourcing a new robot framework, known as PyRobot, that could simplify the way researchers program their machines, and could even make it easier for non-robotics types to jump into the field. If programming robots has so far been something like wading through a command-line interface, PyRobot promises to be like gliding through the sleekness of macOS. At least, that’s the hope: Many others have tried and failed to do this kind of thing.