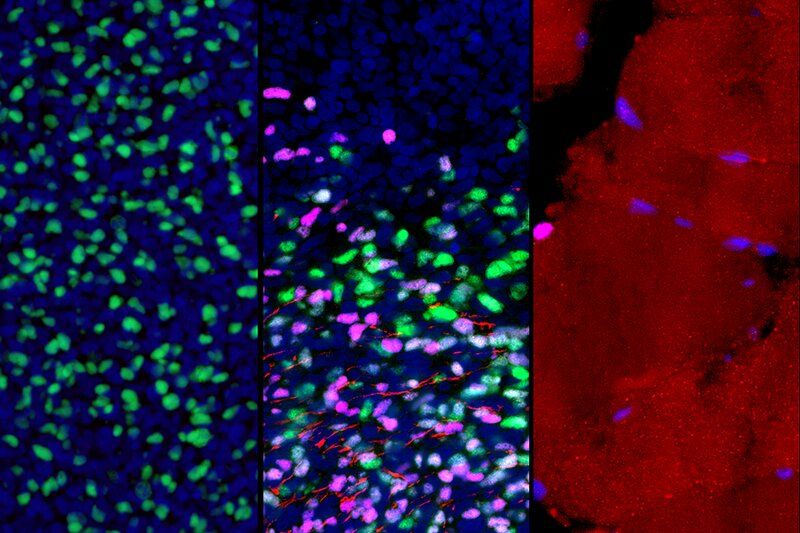
Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute and Loma Linda University Health have demonstrated the promise of applying magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to predict the efficacy of using human neural stem cells to treat a brain injury—a first-ever “biomarker” for regenerative medicine that could help personalize stem cell treatments for neurological disorders and improve efficacy. The researchers expect to test the findings in a clinical trial evaluating the stem cell therapy in newborns who experience a brain injury during birth called perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury (HII). The study was published in Cell Reports.
“In order for stem cell therapies to benefit patients, we need to be thoughtful and scientific about who receives these treatments,” says Evan Y. Snyder, M.D., Ph.D., professor and director of the Center for Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine at Sanford Burnham Prebys, and corresponding study author. “I am hopeful that MRI, which is already used during the course of care for these newborns, will help ensure that infants who experience HII get the best, most appropriate treatment possible. In the future, MRI could help guide the use of stem cells to treat—or in some instances, not treat—additional brain disorders such as spinal cord injury and stroke.”
Scientists now understand that, in many instances, human neural stem cells are therapeutic because they can protect living cells—in contrast to “re-animating” or replacing nerve cells that are already dead. As a result, understanding the health of brain tissue prior to a stem cell transplant is critical to the treatment’s potential success. Tools that help predict the efficacy of neural stem cell therapy could increase the success of clinical trials, which are ongoing in people with Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injury and additional neurological conditions, while also sparing people who will not respond to treatment from an invasive procedure that offers false hope.