Using a targeted gene epigenome editing approach in the developing mouse brain, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers reversed one gene mutation that leads to the genetic disorder WAGR syndrome, which causes intellectual disability and obesity in people. This specific editing was unique in that it changed the epigenome—how the genes are regulated—without changing the actual genetic code of the gene being regulated.
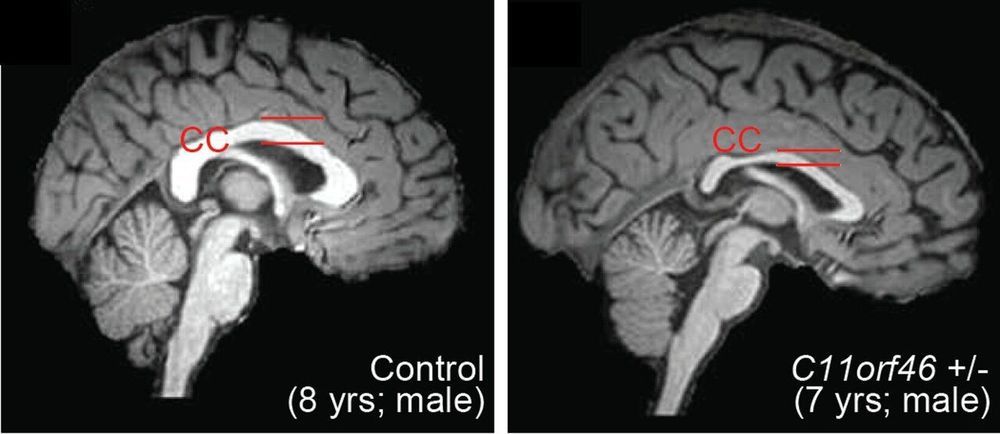
The researchers found that this gene, C11orf46, is an important regulator during brain development. Specifically, it turns on and off the direction-sensing proteins that help guide the long fibers growing out of newly formed neurons responsible for sending electrical messages, helping them form into a bundle, which connects the two hemispheres of the brain. Failure to properly form this bundled structure, known as the corpus callosum, can lead to conditions such as intellectual disability, autism or other brain developmental disorders.
“Although this work is early, these findings suggest that we may be able to develop future epigenome editing therapies that could help reshape the neural connections in the brain, and perhaps prevent developmental disorders of the brain from occurring,” says Atsushi Kamiya, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.