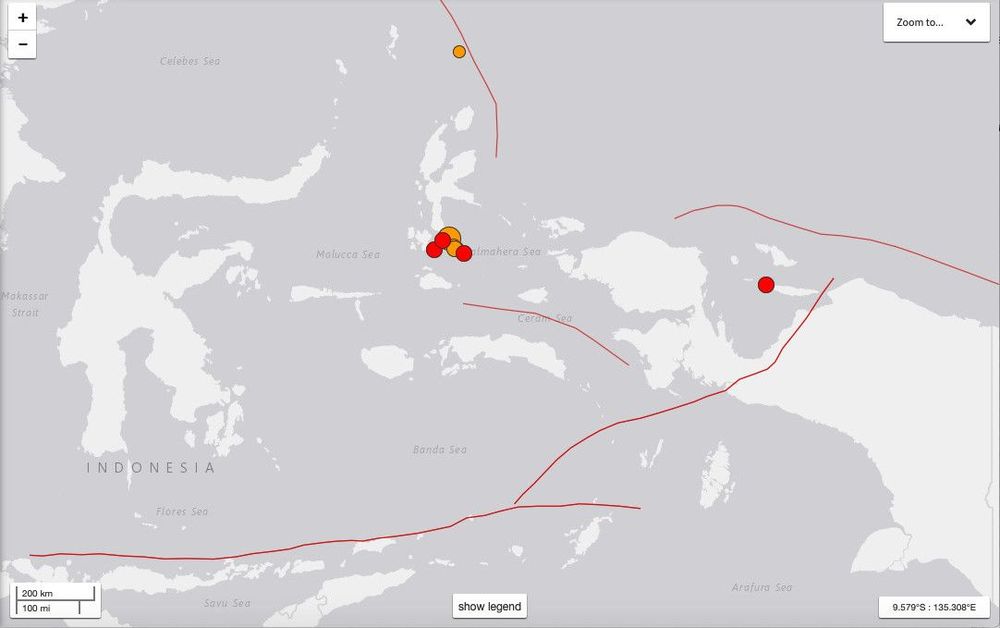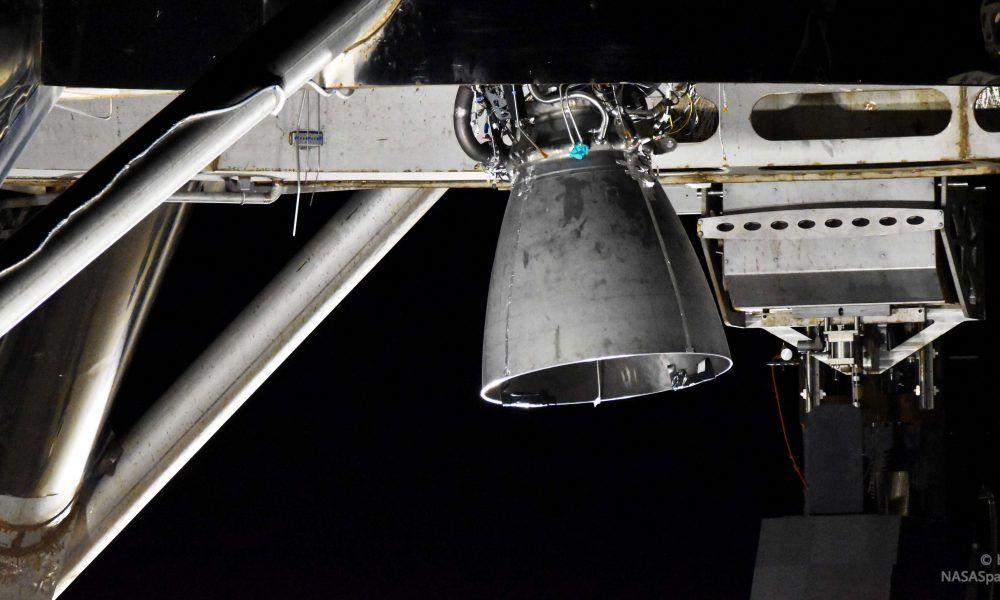
On the evening of July 12th, SpaceX technicians put Starhopper’s freshly-installed Raptor – serial number 06 (SN06) – through a simple but decidedly entertaining test, effectively wiggling the engine in circles.
Designed to verify that Raptor’s thrust vectoring capabilities are in order and ensure that Starhopper and the engine are properly communicating, the wiggle test is a small but critical part of pre-flight acceptance and a good indicator that the low-fidelity Starship prototype is nearing its first hover test(s). Roughly 48 hours after a successful series of wiggles, Starhopper and Raptor proceeded into the next stage of pre-flight acceptance, likely the final more step before a tethered static fire.
Routine for all Falcon rockets, SpaceX’s exceptionally rigorous practice of static firing all hardware at least once (and often several times) before launch has unsurprisingly held firm as the company proceeds towards integrated Starhopper and Starship flight tests. Despite the fact that Raptor SN06 completed a static fire as recently July 10th, SpaceX will very likely put Starhopper and its newly-installed Raptor through yet another pre-flight static fire, perhaps its fourth or fifth test this month.