Seeing sick-looking faces in virtual reality triggers brain circuit changes related to threat detection and boosts activity of certain immune cells.
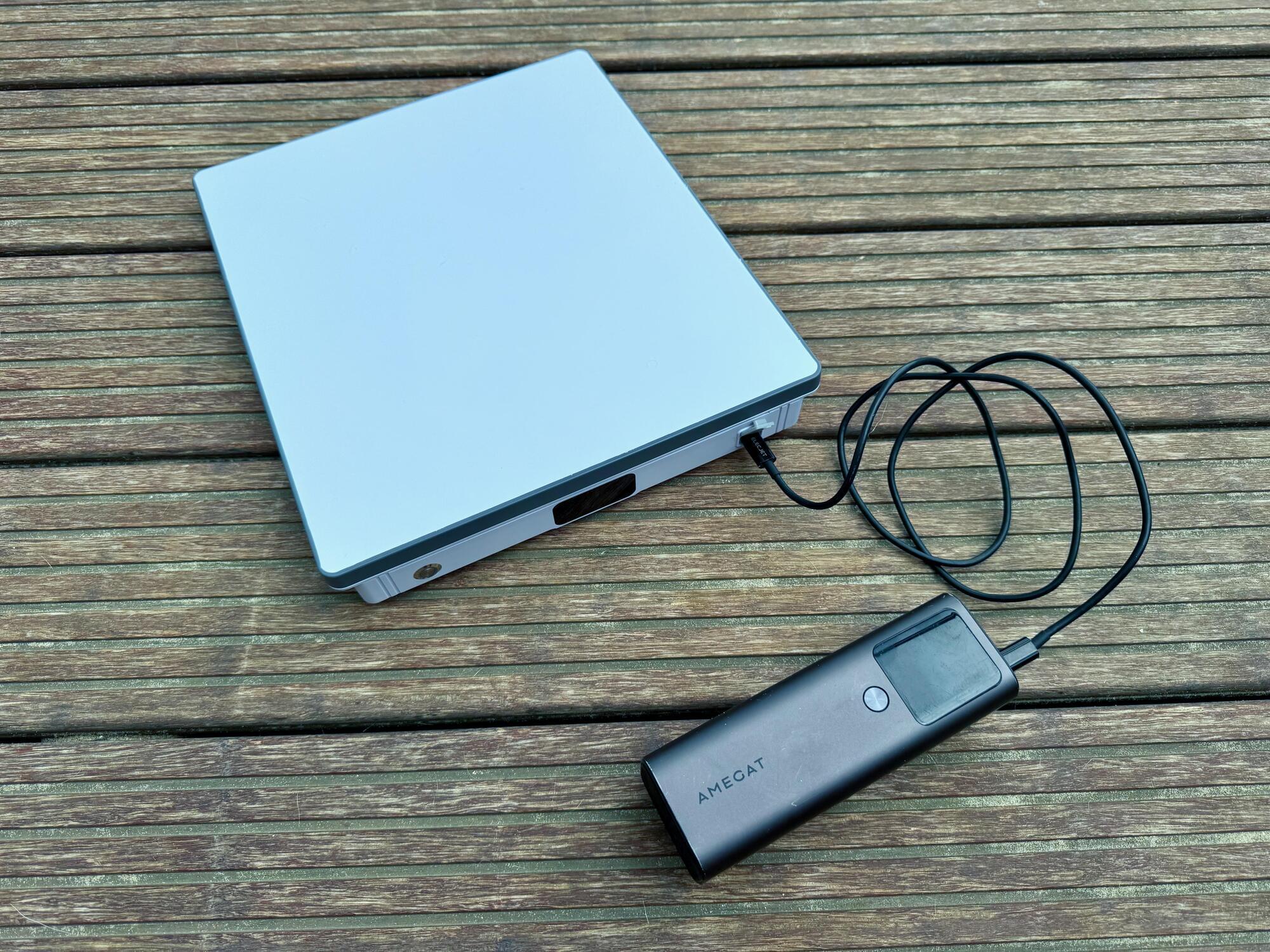




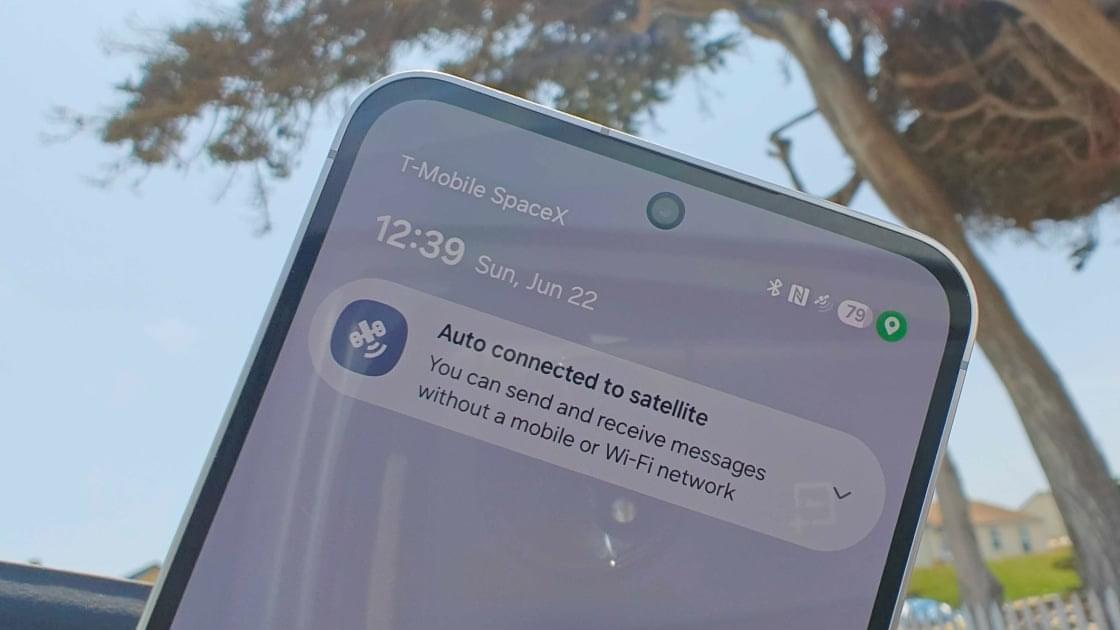
Starlink is a life-changing Internet service that connects people and villages too remote for towers and cables to reach. My own Starlink Mini has been critical in helping me pursue life as a digital nomad from almost anywhere in Europe. And right now, Starlink’s the only game in town for relatively cheap and fast consumer internet that can be quickly deployed into data dead spots.
My overriding thought after using the PeakDo LinkPower for the last few weeks is this: why doesn’t SpaceX make one of these?

We are entering the third phase of generative AI.
A team of UC Merced researchers has shown that tiny artificial cells can accurately keep time, mimicking the daily rhythms found in living organisms. Their findings shed light on how biological clocks stay on schedule despite the inherent molecular noise inside cells.
The study, published in Nature Communications, was led by bioengineering Professor Anand Bala Subramaniam and chemistry and biochemistry Professor Andy LiWang. The first author, Alexander Zhang Tu Li, earned his Ph.D. in Subramaniam’s lab.
Biological clocks—also known as circadian rhythms —govern 24-hour cycles that regulate sleep, metabolism and other vital processes. To explore the mechanisms behind the circadian rhythms of cyanobacteria, the researchers reconstructed the clockwork in simplified, cell-like structures called vesicles. These vesicles were loaded with core clock proteins, one of which was tagged with a fluorescent marker.

Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto researchers are reporting that targeted RNA sequencing can detect clinically actionable alterations in 87% of tumors and provide decisive findings where DNA-seq either fails, returns no variant, or is not informative.
Cancer treatments have seen tremendous improvements in recent years, in part due to highly specific targeting and diagnostic techniques.
DNA-based methods dominate molecular cancer diagnostics but struggle to detect gene fusions and assess splice site consequences. RNA sequencing enables sensitive fusion detection and direct assessment of transcript-level disruption caused by splicing mutations.
