More human than human.
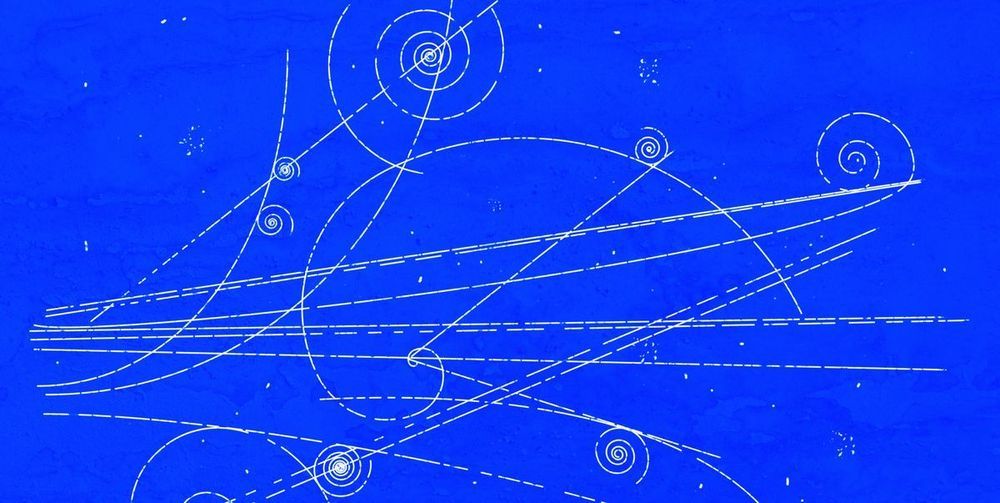
In 2016, Attila Krasznahorkay made news around the world when his team published its discovery of evidence of a fifth force of nature. Now, the scientists are making news again with a second observation of the same force, which may be the beginning of a unified fifth force theory. The researchers have made their original LaTeX paper available prior to acceptance by a peer-reviewed journal. Study of the hypothesized fifth force, a subfield all by itself, is centered on trying to explain missing pieces in our understanding of physics, like dark matter, which could be expanded or validated by an important new discovery or piece of evidence.
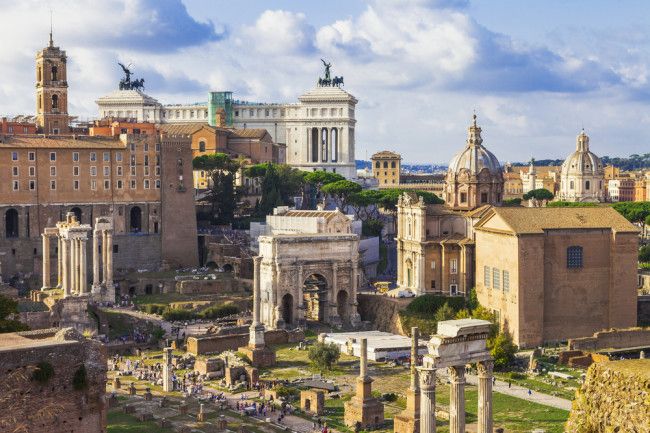
Roman citizens came from Europe, the Mediterranean, Africa and beyond. The ancient metropolis was a bone fide melting pot.
The trendy concept of “dopamine fasting” actually finds its roots in established addiction therapies.
They found 68,809 cases of anal cancer and 12,111 deaths from the disease.
The vast majority of these cases are associated with the human papillomavirus, but about three-quarters of American adults don’t know HPV causes the disease, a recent study, also led by Deshmukh, found.
He called the findings “shocking.”
Several newly published studies are reporting evidence affirming a growing hypothesis that links inflammation with cognitive deficits. As well as associating inflammation with the cognitive deficits seen in conditions such as bipolar disorder and Alzheimer’s, some research is even suggesting low-grade systemic inflammation in healthy subjects can result in mental sluggishness.
For some time patients suffering from chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease have reported mild cognitive deficits in association with their disease. Despite a number of correlational studies finding connections between inflammation and cognitive performance, homing in on any clear causal links has been a little tricky for scientists.
“Scientists have long suspected a link between inflammation and cognition, but it is very difficult to be clear about the cause and effect,” explains Ali Mazaheri, from the University of Birmingham. “For example, people living with a medical condition or being very overweight might complain of cognitive impairment, but it’s hard to tell if that’s due to the inflammation associated with these conditions or if there are other reasons.”
A custom-made aerial drone delivered a kidney to a Baltimore hospital, where it was transplanted into a patient who had been on dialysis for eight years.
Is there room for one more in the 2020 presidential race? Transhumanist Zoltan Istvan has declared he’s running for the White House as a Republican, complete with the campaign motto “Upgrading America” — a task he believes can be accomplished through futuristic technology and science.
One new press report describes him as “the cyborg who is running against Donald Trump.” Mr. Istvan appears ready.
“My team and I are ready to really push hard, get on primary ballots, and see if we can get conservatives to be more open-minded about the future. We’re excited that they will open up so that the far-left doesn’t totally own radical science and tech in the future. We think we can be instrumental in getting to GOP and libertarian conservatives to broaden their perspectives about these things,” Mr. Istvan told The Washington Times.
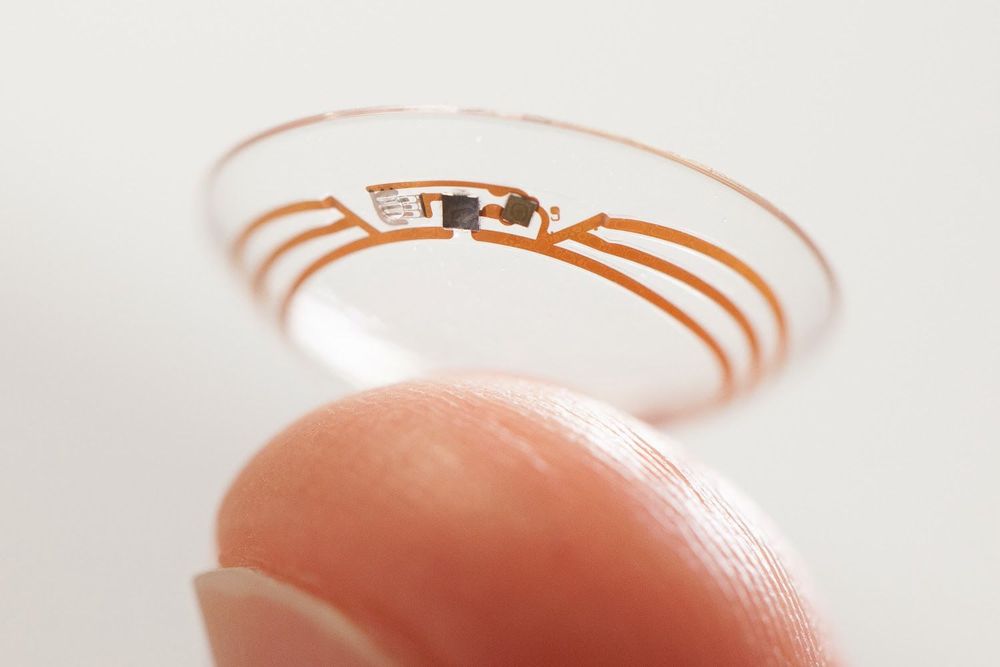
The notion of wearing lenses over our eyes to correct our vision dates back hundreds of years, with some even crediting Leonardo da Vinci as one of the first proponents of the idea (though that remains somewhat controversial). Material science and our understanding of the human eye have come a long way since, while their purpose has remained largely the same. In the age of wearable computers, however, scientists in the laboratories of DARPA, Google, and universities around the world see contact lenses not just as tools to improve our vision, but as opportunities to augment the human experience. But how? And why?
As a soft, transparent disc of plastic and silicone that you wear on your eyeball, a contact lens may seem like a very bad place to put electronics. But if you look beneath the surface, the idea of a smart contact lens has real merit, and that begins with its potential to improve our well-being.