Organoids, a ‘new approach methodology’, could forecast how drug candidates perform and help developers make informed decisions, by offering insights into toxicology and personalized medicine.


Developmental time (or time to maturity) strongly correlates with an animal’s maximum lifespan, with late-maturing individuals often living longer. However, the genetic mechanisms underlying this phenomenon remain largely unknown. This may be because most previously identified longevity genes regulate growth rate rather than developmental time. To address this gap, we genetically manipulated prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH), the primary regulator of developmental timing in Drosophila, to explore the genetic link between developmental time and longevity. Loss of PTTH delays developmental timing without altering the growth rate. Intriguingly, PTTH mutants exhibit extended lifespan despite their larger body size. This lifespan extension depends on ecdysone signaling, as feeding 20-hydroxyecdysone to PTTH mutants reverses the effect. Mechanistically, loss of PTTH blunts age-dependent chronic inflammation, specifically in fly hepatocytes (oenocytes). Developmental transcriptomics reveal that NF-κB signaling activates during larva-to-adult transition, with PTTH inducing this signaling via ecdysone. Notably, time-restricted and oenocyte-specific silencing of Relish (an NF-κB homolog) at early 3rd instar larval stages significantly prolongs adult lifespan while delaying pupariation. Our study establishes an aging model that uncouples developmental time from growth rate, highlighting NF-κB signaling as a key developmental program in linking developmental time to adult lifespan.

The world’s largest solar telescope, the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope in Hawaii, has reached an important milestone. After almost 15 years of preparation, the German instrument for the Inouye Solar Telescope, the Visible Tunable Filtergraph (VTF), has now taken its first images. The imaging spectro-polarimeter was developed and built at the Institute for Solar Physics (KIS) in Freiburg (Germany). The Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (MPS) in Göttingen (Germany) is a partner in the project.
The data published now were obtained during the technical commissioning of the instrument. VTF analyzes the sunlight captured by the Inouye Solar Telescope in more detail than ever before and, among other things, extracts information on the flow velocity of the solar plasma and the magnetic field strength at the visible surface of the Sun and in the directly adjacent gas layers above. Even in the current technical test phase, VTF is making smallest structures visible. In later scientific operation, when the data is extensively post-processed, the resolution will improve further.
With a primary mirror diameter of four meters, the Inouye Solar Telescope is the largest in the world. Thanks to the optimal observational conditions on the Hawaiian volcano Haleakala and the use of sophisticated methods of image stabilization and reconstruction, the Inouye Solar Telescope has been providing breathtakingly detailed views of our star since 2022: it can make smallest structures visible. To extract as much detailed information as possible about our star from sunlight, the Inouye Solar Telescope is gradually being equipped with additional scientific instruments. They process the incoming light, for example by examining individual wavelength ranges or polarization states of the light separately. Four of the five instruments are already in operation. The latest addition, the world’s largest spectro-polarimeter VTF, is the most powerful of them. As part of the technical commissioning, the first images of the Sun have now been taken with VTF.
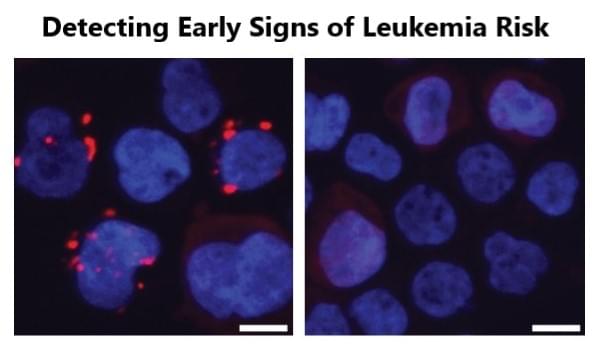
New findings in Nature reveal how age-related gut changes fuel the growth of pre-leukemic blood cells. Scientists at Cincinnati Children’s along with an international team of researchers have discovered a surprising new connection between gut health and blood cancer risk — one that could transform how we think about aging, inflammation, and the early stages of leukemia.
As we grow older — or in some cases, when gut health is compromised by disease — changes in the intestinal lining allow certain bacteria to leak their byproducts into the bloodstream. One such molecule, produced by specific bacteria, acts as a signal that accelerates the expansion of dormant, pre-leukemic blood cells, a critical step to developing full-blown leukemia.
The team’s findings — published April 23, 2025, in the journal Nature — lay out for the first time how this process works. The study also suggests that this mechanism may reach beyond leukemia to influence risk for other diseases and among older people who share a little-known condition called clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP).
ITrust Capital: Use code IMPACTGO when you sign up and fund your account to get a $100 bonus at https://impacttheory.co/iTrustCapitalMay.
Shopify: Sign up for your one-dollar-per-month trial period at https://impacttheory.co/ShopifyApr.
On this mind-bending episode of Impact Theory, Tom Bilyeu sits down with Ben Lamm, the visionary entrepreneur behind Colossal Biosciences, to explore a world that sounds straight out of science fiction—yet is rapidly becoming our reality. Together, they pull back the curtain on the groundbreaking technology making de-extinction not only possible, but increasingly practical, from resurrecting woolly mammoths and dire wolves to saving endangered species and unraveling the secrets of longevity.
Ben explains how CRISPR gene editing has unlocked the power to make precise DNA changes—editing multiple genes simultaneously, synthesizing entirely new genetic blocks, and pushing the limits of what’s possible in biology and conservation. The conversation dives deep into the technical hurdles, ethical questions, and the unexpected magic of re-engineering life itself, whether it’s creating hairier, “woolly” mice or tackling the colossal challenge of artificial wombs and universal eggs.
But this episode goes way beyond Jurassic Park fantasies. Tom and Ben debate the future of human health, gene selection through IVF, the specter of eugenics, global competition in biotechnology, and how AI will soon supercharge the pace of biological engineering. They even touch on revolutionary solutions to our plastic crisis and what it means to inspire the next generation of scientists.
Get ready to have your mind expanded. This is not just a podcast about bringing back extinct creatures—it’s a deep dive into the next frontiers of life on Earth, the technologies changing everything, and the choices we’ll face as architects of our own biology. Let’s get legendary.
00:00 Meet Ben Lamm.
At AI Ascent 2025, Jeff Dean makes a bold prediction: we will have AI systems operating at the level of junior engineers within a year. Discover how the pioneer behind Google’s TPUs and foundational AI research sees the technology evolving, from specialized hardware to more organic, brain-inspired systems.
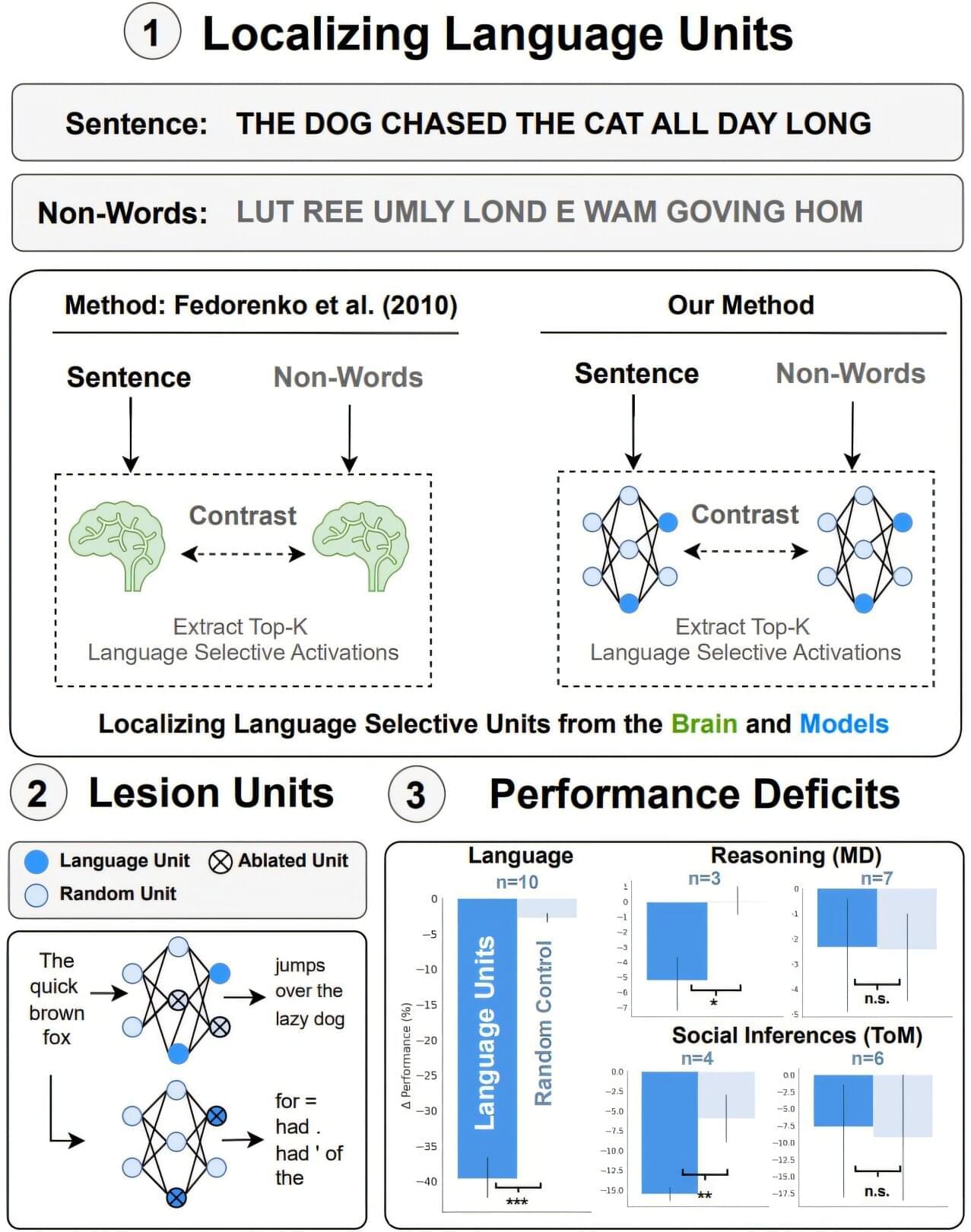
EPFL researchers have discovered key “units” in large AI models that seem to be important for language, mirroring the brain’s language system. When these specific units were turned off, the models got much worse at language tasks.
Large language models (LLMs) are not just good at understanding and using language, they can also reason or think logically, solve problems and some can even predict the thoughts, beliefs or emotions of people they interact with.
Despite these impressive feats, we still don’t fully understand how LLMs work “under the hood,” particularly when it comes to how different units or modules perform different tasks. So, researchers in the NeuroAI Laboratory, part of both the School of Computer and Communication Sciences (IC) and the School of Life Sciences (SV), and the Natural Language Processing Laboratory (IC), wanted to find out whether LLMs have specialized units or modules that do specific jobs. This is inspired by networks that have been discovered in human brains, such as the Language Network, Multiple Demand Network and Theory of Mind network.