You can improve your brain health with the right diet. Eat these 11 foods to boost your memory and focus, help prevent disease and keep sharp as you age.


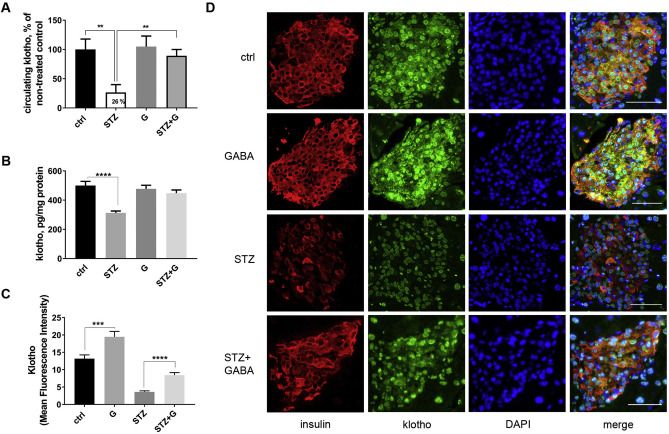
Systemic gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) therapy prevents or ameliorates type 1 diabetes (T1D), by suppressing autoimmune responses and stimulating pancreatic beta cells. In beta cells, it increases insulin secretion, prevents apoptosis, and induces regeneration. It is unclear how GABA mediates these effects. We hypothesized that Klotho is involved. It is a multi-functional protein expressed in the kidneys, brain, pancreatic beta cells, other tissues, and is cell-bound or soluble. Klotho knockout mice display accelerated aging, and in humans Klotho circulating levels decline with age, renal disease and diabetes. Here, we report that GABA markedly increased circulating levels of Klotho in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes. GABA also increased Klotho in the islet of Langerhans of normal mice, as well as the islets and kidneys of STZ-treated mice. In vitro, GABA stimulated production and secretion of Klotho by human islet cells. Knockdown (KD) of Klotho with siRNA in INS-1E insulinoma cells abrogated the protective effects of GABA against STZ toxicity. Following KD, soluble Klotho reversed the effects of Klotho deficiency. In human islet cells soluble Klotho protected against cell death, and stimulated proliferation and insulin secretion. NF-κB activation triggers beta-cell apoptosis, and both GABA and Klotho suppress this pathway. We found Klotho KD augmented NF-κB p65 expression, and abrogated the ability of GABA to block NF-κB activation. This is the first report that GABAergic stimulation increases Klotho expression. Klotho protected and stimulated beta cells and lack of Klotho (KD) was reversed by soluble Klotho. These findings have important implications for the treatment of T1D.
Circa 2017
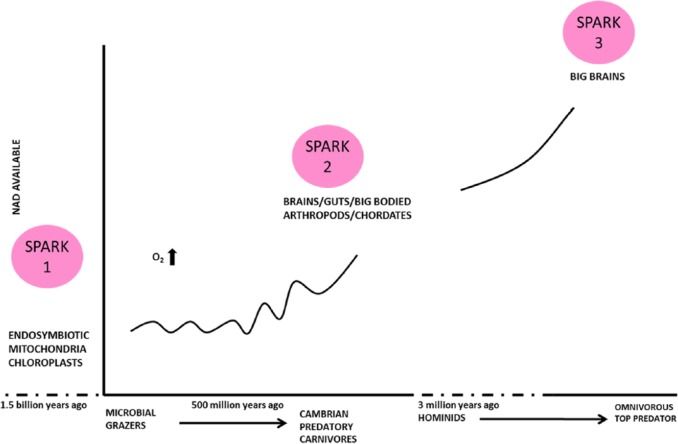
Hunting for meat was a critical step in all animal and human evolution. A key brain-trophic element in meat is vitamin B3 / nicotinamide. The supply of meat and nicotinamide steadily increased from the Cambrian origin of animal predators ratcheting ever larger brains. This culminated in the 3-million-year evolution of Homo sapiens and our overall demographic success. We view human evolution, recent history, and agricultural and demographic transitions in the light of meat and nicotinamide intake. A biochemical and immunological switch is highlighted that affects fertility in the ‘de novo’ tryptophan-to-kynurenine-nicotinamide ‘immune tolerance’ pathway. Longevity relates to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide consumer pathways. High meat intake correlates with moderate fertility, high intelligence, good health, and longevity with consequent population stability, whereas low meat/high cereal intake (short of starvation) correlates with high fertility, disease, and population booms and busts. Too high a meat intake and fertility falls below replacement levels. Reducing variances in meat consumption might help stabilise population growth and improve human capital.
Keywords: Meat, nicotinamide, evolution, NAD(H), vitamin B3, Malthus, fertility, immunological tolerance, longevity.
Rich fellas …their kids die out but we keep a-comin …we’ll go on forever, Pa, cos we’re the people.


But in recent years, Americans — Silicon Valley leaders included — have put too much faith in the private sector to ensure U.S. global leadership in new technology. Now we are in a technology competition with China that has profound ramifications for our economy and defense — a reality I have come to appreciate as chairman of two government panels on innovation and national security. The government needs to get back in the game in a serious way.
We can’t win the technology wars without the federal government’s help.


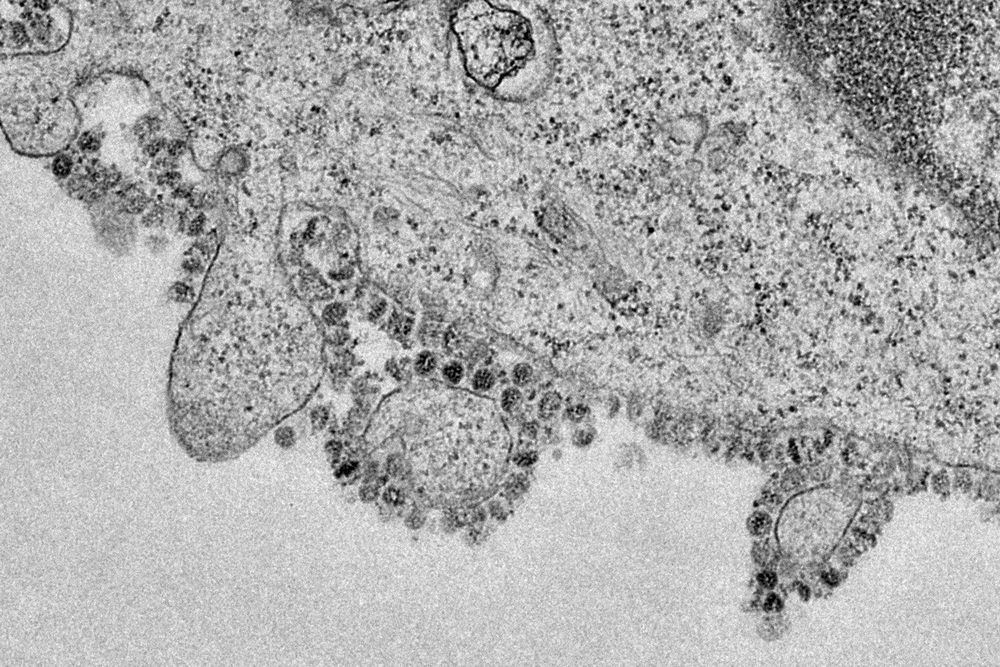
A novel coronavirus that first appeared in Wuhan, China, in December continues to sicken tens of thousands of people around the world – and scientists are working round the clock to better understand the virus, contain the outbreak, and treat the disease.
In the weeks since the outbreak, the disease has been named COVID-19 by the World Health Organization. (The virus itself has been named SARS-CoV-2 by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses).
UC San Francisco infectious disease expert Charles Chiu, MD, PhD, has been following the disease since its outbreak and provided the latest updates on what science has revealed about how the coronavirus is transmitted, what happens to someone who’s infected, and why a single diagnostic test may not be enough.
This colorized, 4K footage of New York City in 1911 will transport you to a different era.
This wearable chair will help doctors through long surgeries.