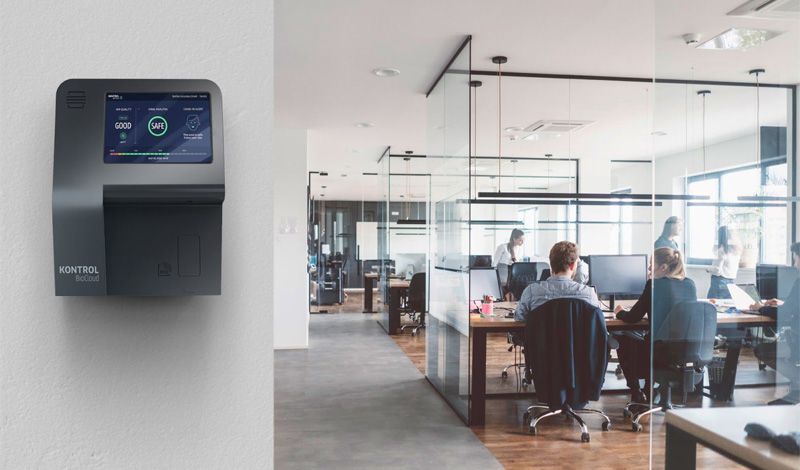
Kontrol Energy Corporation, a Canadian public Company, has launched BioCloud – an unobtrusive, wall-mounted technology which detects the presence of COVID-19 in the air. This can trigger an alert system giving real time notifications of the pathogen’s presence to facility managers, allowing outbreaks to be contained before they occur.
This represents a game changer in the fight against COVID-19, according to Kontrol. Immediate applications include schools, hospitals, long term care facilities and mass transit vehicles such as planes, trains and buses.
“There is a critical need for technology that can provide us with assurances that the workplaces, schools, healthcare environments and other spaces we physically occupy are safe and free of infectious disease. Today, we have that in BioCloud,” said Paul Ghezzi, Chief Executive Officer of Kontrol. “Our team has been working day and night since the onset of the pandemic to bring this exciting technology to market. It will be an invaluable tool to enhance the existing system of individual testing and contact tracing.”