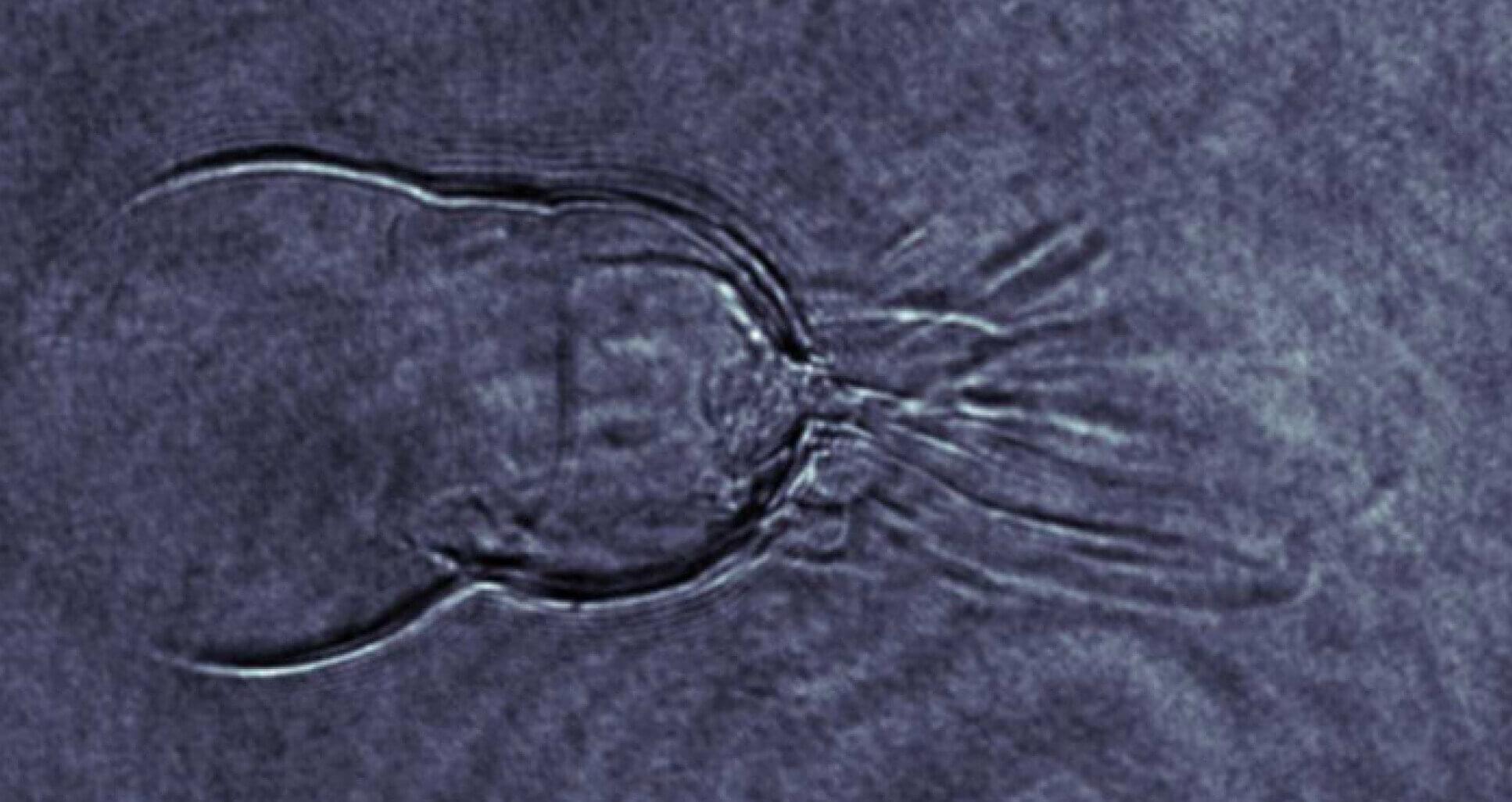
Touch a hot plate and your hand flies back. While the response is almost instant, researchers are still working to better understand the molecular mechanisms behind these sensations of heat and pain.
Now, investigators at the Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences at the University at Buffalo have uncovered how heat causes a critical receptor protein within cells to unfold and relay pain. This newfound activation mechanism could open up new therapeutic targets for treating pain and contribute to the development of needed alternatives to opioids.
The study is published in Proceedings of the National Academies of Sciences.