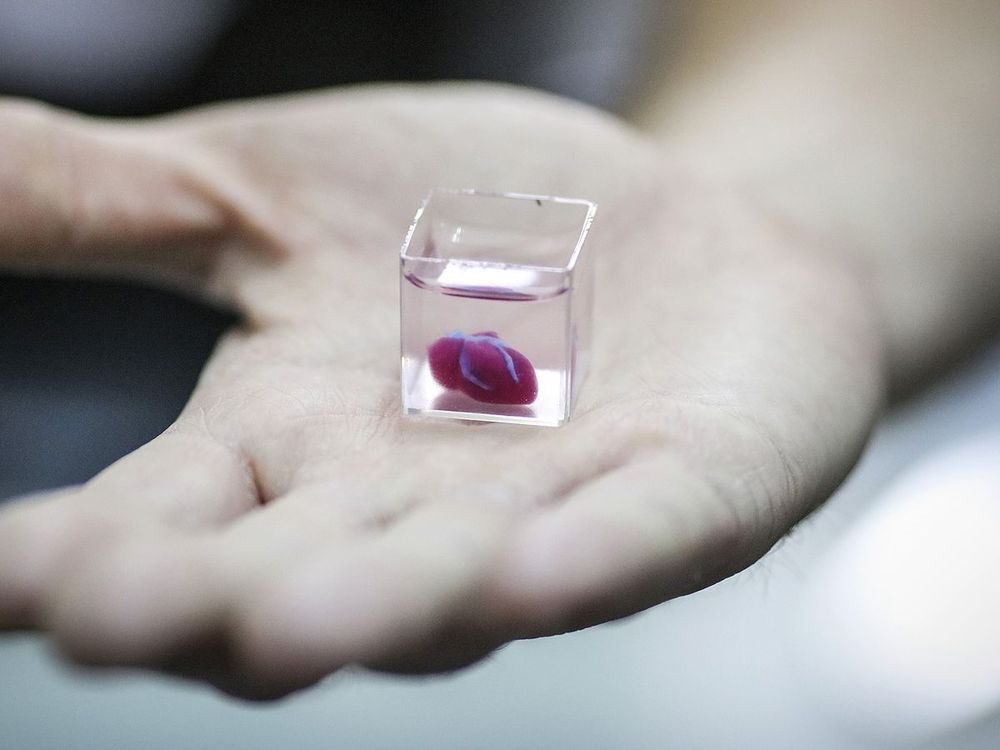
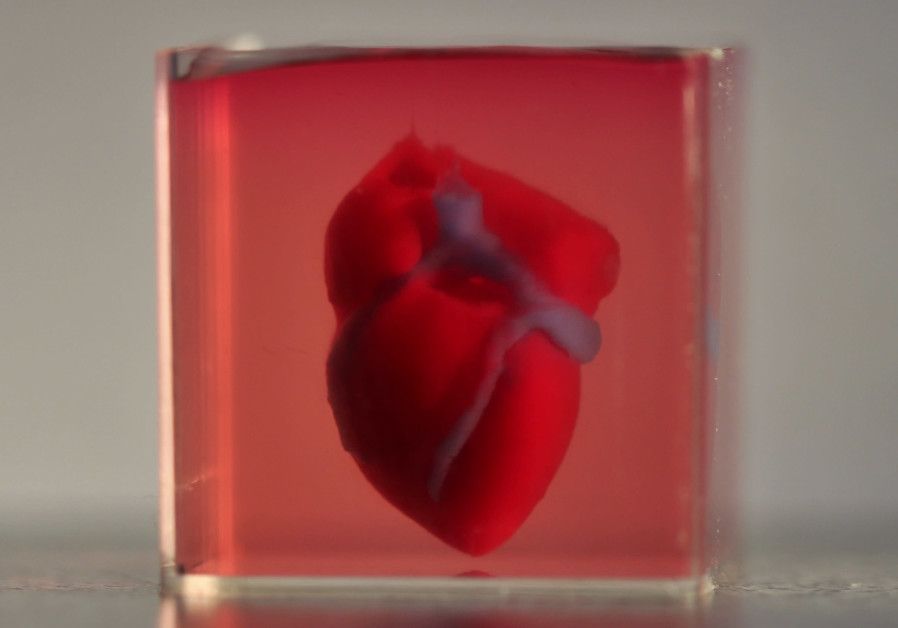
A team of Tel Aviv University researchers revealed the heart, which was made using a patient’s own cells and biological materials.
Israeli researchers have printed a 3D heart using a patient’s own cells, something they say could be used to patch diseased hearts — and possibly, full transplants.
The heart the Tel Aviv University team printed in about three hours is too small for humans — about 2.5 centimeters, or the size of a rabbit’s heart. But it’s the first to be printed with all blood vessels, ventricles and chambers, using an ink made from the patient’s own biological materials.
A Harvard physicist has shown that wormholes can exist: tunnels in curved space-time, connecting two distant places, through which travel is possible.
But don’t pack your bags for a trip to other side of the galaxy yet; although it’s theoretically possible, it’s not useful for humans to travel through, said the author of the study, Daniel Jafferis, from Harvard University, written in collaboration with Ping Gao, also from Harvard and Aron Wall from Stanford University.
“It takes longer to get through these wormholes than to go directly, so they are not very useful for space travel,” Jafferis said. He will present his findings at the 2019 American Physical Society April Meeting in Denver.
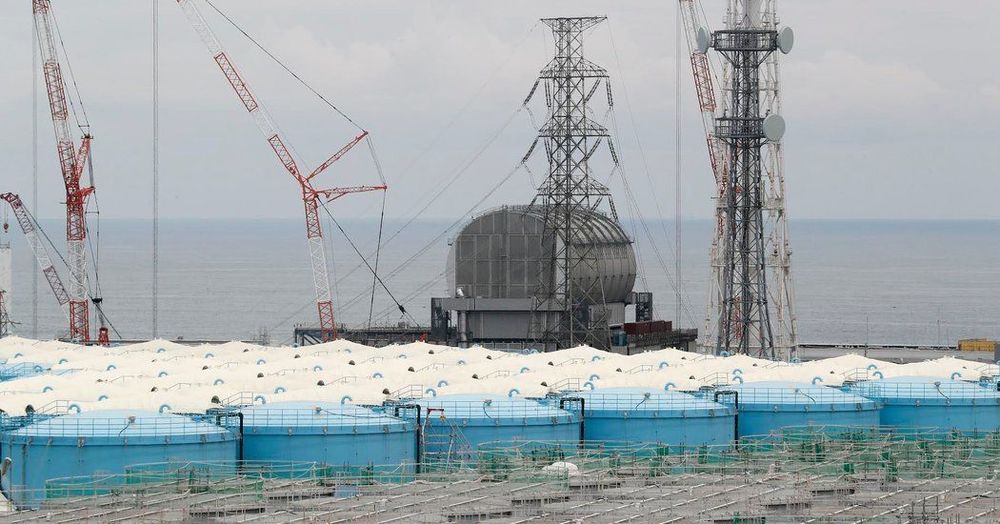
The operator of Japan’s ruined Fukushima nuclear power plant began removing radioactive fuel rods on Monday at one of three reactors that melted down after an earthquake and a tsunami in 2011, a major milestone in the long-delayed cleanup effort.
Thousands of former residents have been barred from the area around the plant for years as crews carried out a large-scale radioactive waste cleanup in the aftermath of the worst nuclear disaster since Chernobyl. The process of removing the fuel rods from a storage pool had been delayed since 2014 amid technical mishaps and high radiation levels.
The plant operator, Tokyo Electric Power, said in a statement that workers on Monday morning began removing the first of 566 spent and unspent fuel rods stored in a pool at the plant’s third reactor. A radiation-hardened robot had first located the melted uranium fuel inside the reactor in 2017.
Researchers have invented a new type of cancer immunotherapy by injecting tumours with a series of stimulants. The experimental therapy attracts the body’s own immune system’s attention, so it can come and destroy the cancerous masses.
The radical new approach has already shown promise in patients with an advanced form of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma that resists conventional treatments, and is currently being tested on a variety of stubborn cancers.
The result can be described as turning the tumours into “cancer vaccine factories”, because attracting the body’s immune cells to the cancer site is a method known as in situ vaccination.