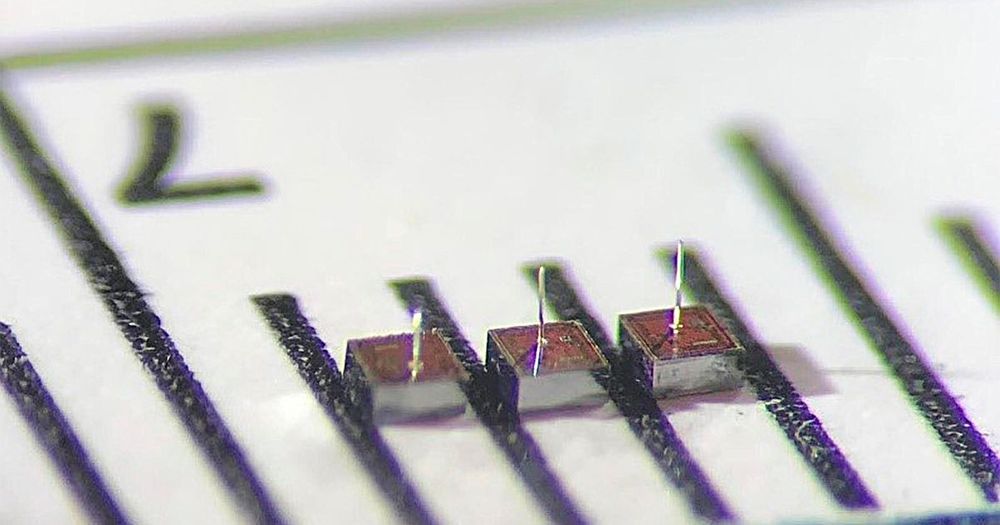
Brain-computer interfaces have managed some amazing feats: allowing paralyzed people to type words and move a robot using only their minds, to name two examples. Brown University neuroengineering professor Arto Nurmikko has had a hand in some of those developments, but even he says the technology is at only a rudimentary stage—the equivalent of the computer understanding the brain’s intention to bend a single finger.
“We’re trying to go from the bending-of-the-finger paradigm to tying shoe laces and even to the concert pianist level. That requires lots more spatial and temporal resolution from an electronic brain interface,” Nurmikko says. His team is hoping that kind of resolution will come along with the transition from a single, hard wired neural implant to a thousand or more speck-size neural implants that wirelessly communicate with computers outside the brain. At the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, engineers from Brown University, Qualcomm, and the University of California San Diego presented the final part of a communications scheme for these implants. It allows bidirectional communication between the implants and an external device with an uplink rate of 10 megabits per second and a downlink rate of 1 Mb/s.
“We believe that we are the first group to realize wireless power transfer and megabits per second communications” in a neural implant, says Wing Ching (Vincent) Leung, technical director at the Qualcomm Institute Circuits Lab at UC San Diego.