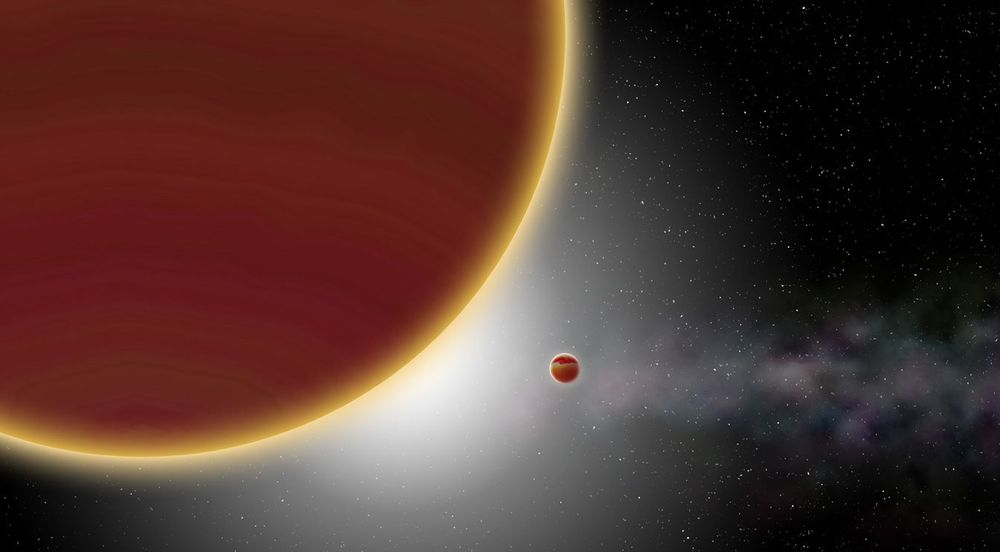
The last few decades of astronomical surveys have revealed several thousand exoplanets in the cosmos, but very few have ever been seen directly. We can only infer the presence of most exoplanets from their gravity or ability to block starlight. However, researchers using the Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile recently turned it toward a star 63 light-years away called Beta Pictoris to hunt for a gas giant (Beta Pictoris c), and they snapped an image of it.
Our current level of technology makes it almost impossible to image exoplanets directly. Compared with stars, planets are so dim that we usually can’t resolve them in the halo of light. Beta Pictoris c joins a list of less than two-dozen extrasolar worlds (including Pictoris b) that scientists have spied directly, and some of those are still highly contentious.
Scientists were able to get this new image thanks to all the interest in the Beta Pictoris system over the years. Beta Pictoris c and its sibling world Beta Pictoris b are less than two million years old. Pictoris b was discovered via direct imaging, which again, is quite rare. However, anomalies in its radial velocity prompted astronomers to look closer. Radial velocity analysis is a less common way of detecting exoplanets that relies on using telescopes to detect small wobbles in stars caused by the gravity of their planets. Just last year, a team discovered Beta Pictoris c while attempting to explain those anomalous radial velocity readings.