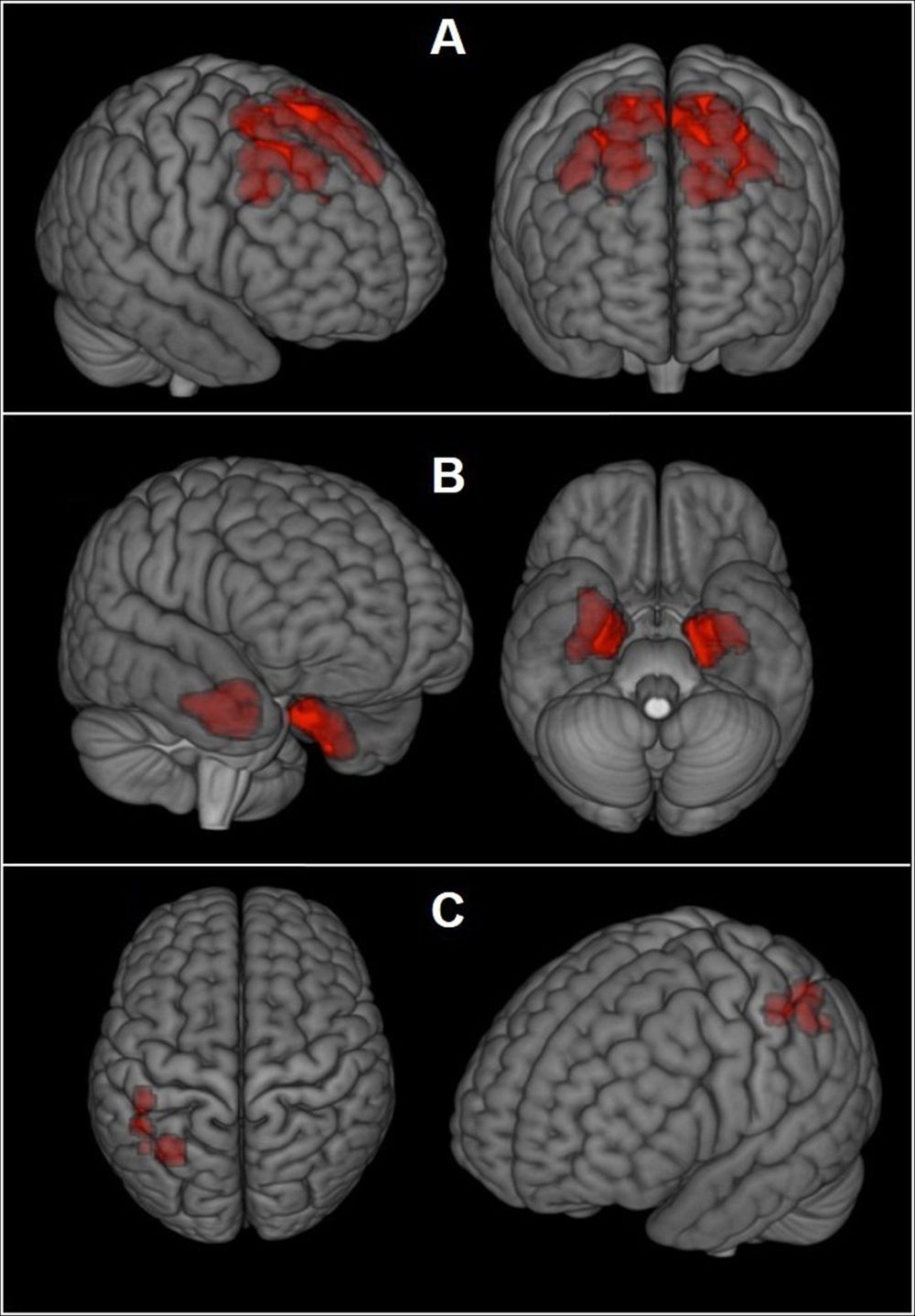
Researchers may be closing in on a way to check athletes while they’re alive for signs of a degenerative brain disease that’s been linked to frequent head blows. Experimental scans found higher levels of an abnormal protein tied to the disease in a study of former National Football League players who were having mood and thinking problems.
It’s the first time a major study has tested these scans for detecting chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or CTE, which is only diagnosed now after death, with brain autopsies.
Doctors are searching for a way to tell when players, veterans or others with concussions or other head injuries are at risk for permanent damage. It’s too soon to know if the scans will enable that — so far they only show that these athletes are different as a group; they can’t be used to say a particular player does or does not have CTE.