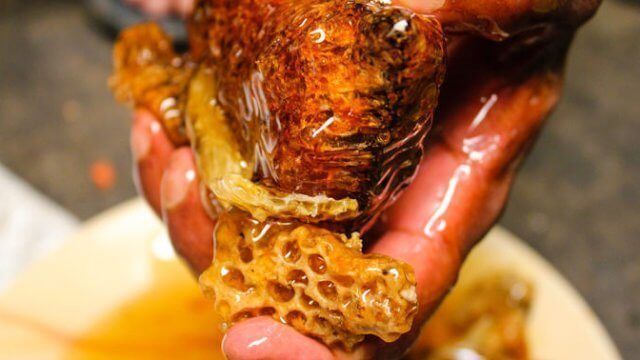
The health benefits of raw, unprocessed honey are well known, but in Australia, scientists recently made a startling discovery – that one particular, obscure type of honey is capable of killing just about everything scientists throw at it, including some of the worst bacteria known to man.
The findings were published in the European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (June 2009 edition), and could hold special significance at a time when many of the world’s top antibiotics are failing, especially against resistant “superbugs”.
The honey in question is known as manuka honey, which is produced in New Zealand and also goes by the name of jelly bush honey.