Oracle Cloud will offer Nvidia A100-powered instances by late summer.



Samsung and South Korean carrier SK Telecom today announced a new 5G smartphone dubbed Galaxy A Quantum.
The Samsung Galaxy A Quantum is the world’s first 5G smartphone equipped with a quantum random number generator (QRNG) chipset, which is developed by SK Telecom’s Switzerland-based subsidiary ID Quantique.
The QRNG chipset is the SKT IDQ S2Q000 and it enhances the security of the phone’s data by using quantum encryption technology to generate random numbers and create unpredictable secure keys.
Physicists have measured the flight times of electrons emitted from a specific atom in a molecule upon excitation with laser light. This has enabled them to measure the influence of the molecule itself on the kinetics of emission.
Photoemission – the release of electrons in response to excitation by light – is one of the most fundamental processes in the microcosm. The kinetic energy of the emitted electron is characteristic for the atom concerned, and depends on the wavelength of the light employed. But how long does the process take? And does it always take the same amount of time, irrespective of whether the electron is emitted from an individual atom or from an atom that is part of a molecule? An international team of researchers led by laser physicists in the Laboratory for Attosecond Physics (LAP) at LMU Munich and the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics (MPQ) in Garching has now probed the influence of the molecule on photoemission time.
The theoretical description of photoemission in 1905 by Albert Einstein marked a breakthrough in quantum physics, and the details of the process are of continuing interest in the world of science and beyond. How the motions of an elementary quantum particle such as the electron are affected within a molecular environment has a significant bearing on our understanding of the process of photoemission and the forces that hold molecules together.
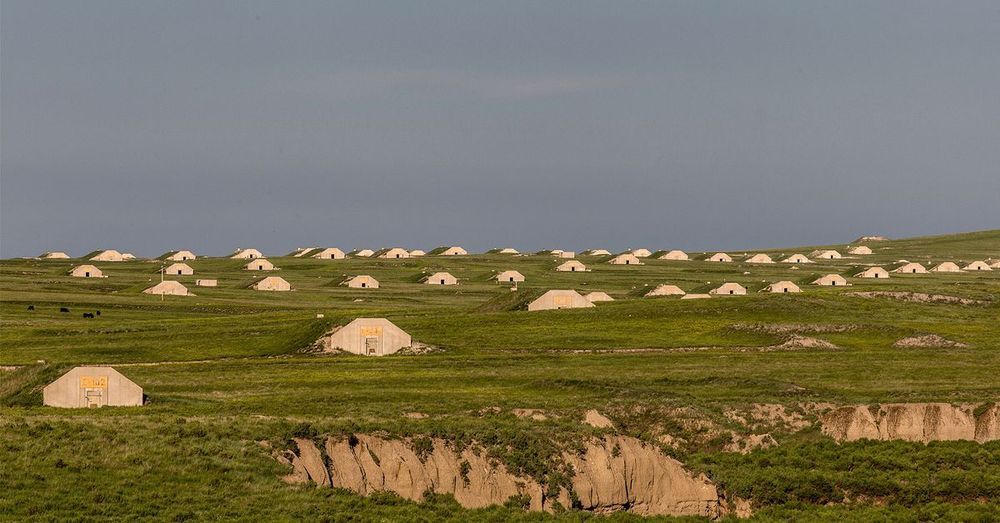

As COVID-19 brings the real estate market to a standstill, demand for doomsday bunkers is at an all-time high (or low since the structures are underground). The shelters were once signifiers of fringe prepper communities worried about the coming apocalypse. During the pandemic, they’ve become vacation homes. “People thought we were crazy because they never believed anything like this could happen,” says Vicino. “Now they’re seeing it. Everybody is a believer.”
Survival companies are capitalizing on coronavirus fears to sell bunkers that can withstand the apocalypse. But their claims about the virus are questionable.
It releases a constant stream of material called the solar wind, along with more occasional bursts of particles, material and energy that flow out into the solar system. Here on Earth, the effects of those events can range from issues like satellite problems and communications failures to stunning natural phenomena like airglow and auroras.
Here are a few ways we study the Sun, its effects on Earth, and everything in between to better understand when and how these events happen. Learn more about our research at http://nasa.gov/sunearth.
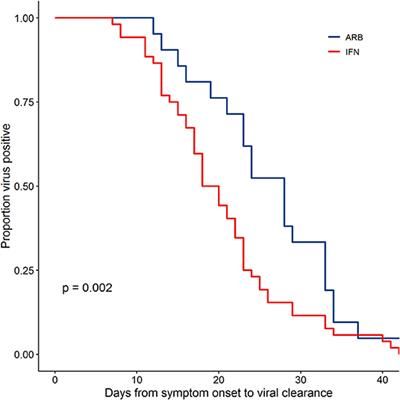
The global pandemic of COVID-19 cases caused by infection with SARS-CoV-2 is ongoing, with no approved antiviral intervention. We describe here the effects of treatment with interferon (IFN)-α2b in a cohort of confirmed COVID-19 cases in Wuhan, China. In this uncontrolled, exploratory study, 77 adults hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 were treated with either nebulized IFN-α2b (5 mU b.i.d.), arbidol (200 mg t.i.d.) or a combination of IFN-α2b plus arbidol. Serial SARS-CoV-2 testing along with hematological measurements, including cell counts, blood biochemistry and serum cytokine levels, and temperature and blood oxygen saturation levels, were recorded for each patient during their hospital stay. Treatment with IFN-α2b with or without arbidol significantly reduced the duration of detectable virus in the upper respiratory tract and in parallel reduced duration of elevated blood levels for the inflammatory markers IL-6 and CRP. These findings suggest that IFN-α2b should be further investigated as a therapy in COVID-19 cases.
In December 2019, an outbreak of pneumonia was reported in Wuhan, Hubei province, China, resulting from infection with a novel coronavirus (CoV), severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 is a novel, enveloped betacoronavirus with phylogenetic similarity to SARS-CoV (1). Unlike the coronaviruses HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63, and HCoV-HKU, that are pathogenic in humans and are associated with mild clinical symptoms, SARS-CoV-2 resembles both SARS-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), with the potential to cause more severe disease. A critical distinction is that CoVs that infect the upper respiratory tract tend to cause a mild disease, whereas CoVs that infect both upper and lower respiratory tracts (such as SARS-CoV-2 appears to be) may cause more severe disease. Coronavirus disease (COVID)-19, the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, has since spread around the globe as a pandemic.
In the absence of a SARS-CoV-2-specific vaccine or an approved antiviral, a number of antivirals are currently being evaluated for their therapeutic effectiveness. Type I IFNs-α/β are broad spectrum antivirals, exhibiting both direct inhibitory effects on viral replication and supporting an immune response to clear virus infection (2). During the 2003 SARS-CoV outbreak in Toronto, Canada, treatment of hospitalized SARS patients with an IFN-α, resulted in accelerated resolution of lung abnormalities (3). Arbidol (ARB) (Umifenovir) (ethyl-6-bromo-4-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-5-hydroxy-1-methyl-2 [(phenylthio)methyl]-indole-3-carboxylate hydrochloride monohydrate), a broad spectrum direct-acting antiviral, induces IFN production and phagocyte activation. ARB displays antiviral activity against respiratory viruses, including coronaviruses (4).
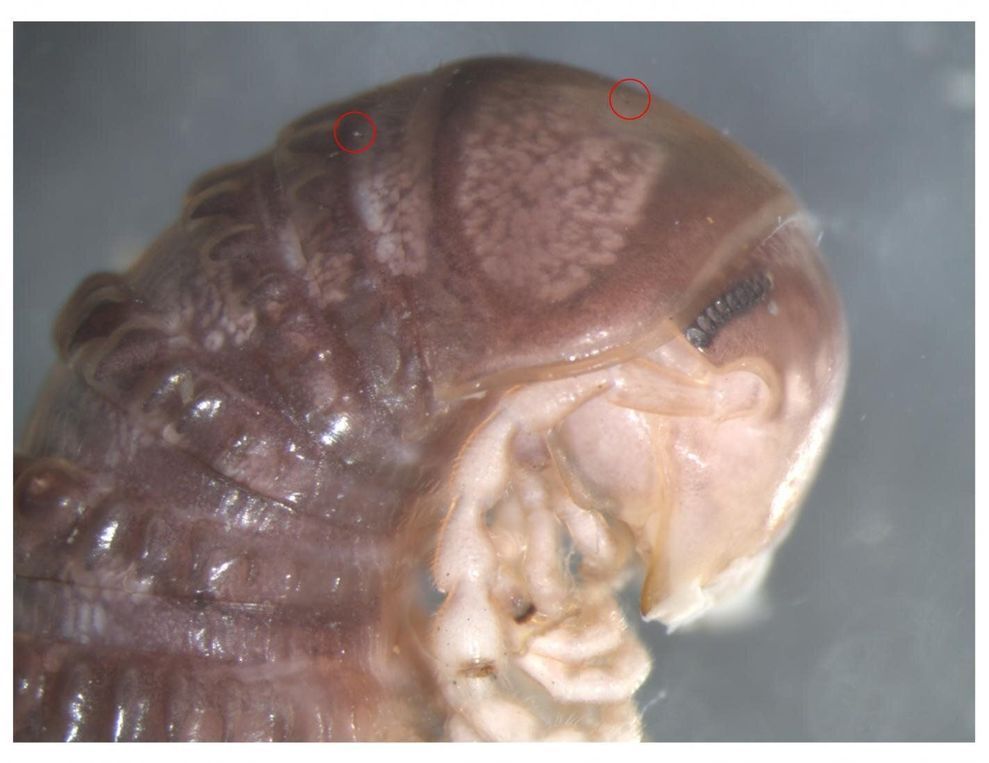
While many of us use social media to be tickled silly by cat videos or wowed by delectable cakes, others use them to discover new species. Included in the latter group are researchers from the University of Copenhagen’s Natural History Museum of Denmark. Indeed, they just found a new type of parasitic fungus via Twitter.
It all began as biologist and associate professor Ana Sofia Reboleira of the National Natural History Museum was scrolling though Twitter. There, she stumbled upon a photo of a North American millipede shared by her US colleague Derek Hennen of Virginia Tech. She spotted a few tiny dots that struck her well-trained eyes.
“I could see something looking like fungi on the surface of the millipede. Until then, these fungi had never been found on American millipedes. So, I went to my colleague and showed him the image. That’s when we ran down to the museum’s collections and began digging,” explains Ana Sofia Reboleira.
https://facebook.com/LongevityFB https://instagram.com/longevityyy/ https://twitter.com/Longevityyyyy https://linkedin.com/company/longevityy/
- Please also subscribe and hit the notification bell and click “all” on these YouTube channels:
https://youtube.com/channel/UCAvRKtQNLKkAX0pOKUTOuzw
https://youtube.com/user/BrentAltonNally
https://youtube.com/user/EternalLifeFan
https://youtube.com/user/MaxSam16
https://youtube.com/user/LifespanIO/videos
SHOW NOTES WITH TIME STAMPS:
:00 CHANNEL TRAILER
:22 Gene The Chromosome intro
:14 José interview begins. Follow José Cordeiro on social media: https://facebook.com/josecordeiro2045 https://linkedin.com/in/josecordeiro/ https://twitter.com/cordeiro https://instagram.com/josecordeiro2019/ https://youtube.com/channel/UCnf2guj8tjfigS3w2UV51Qg
:55 https://raadfest.com/ Watch 2019 RAADFest Roundup https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLGjySL94COVSO3hcnpZq-jCcgnUQIaALQ
:14 BUY LA MUERTE DE LA MUERTE (THE DEATH OF DEATH)
:20 Transhumanist’s 3 core beliefs
:22 Law of Accelerating Returns
:45 José believes we will cure human aging in the next 2–3 decades
:31 quantum computers
:33 Ray Kurzweil
:02 Longevity Escape Velocity
:56 The Singularity is Nearer
:46 the world is improving overall thanks to science and technology
:35 overpopulation fallacy
:14 Idiocracy
:53 Zero to One
:10 human aging and death is the biggest problem for humanity
:45 José plans to be biologically younger than 30 by 2040–2045
:02 How to convince religious people to believe in science and biorejuvenation
:44 everything is “impossible” until it becomes possible
:44 Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
:20 José is not afraid of Artificial Intelligence. José is afraid of human stupidity.
:00:20 Brent Nally & Vladimir Trufanov are co-founders of https://levscience.com Watch to learn more https://youtube.com/watch?v=iSGJs4_Qkd8&t=1266s
:01:15 Watch Brent’s interviews with Dr. Alex Zhavoronkov https://youtube.com/watch?v=w5csqq8RAqY & https://youtube.com/watch?v=G5IiEuXHvk8
:02:40 José shares what he believes causes human aging and the best treatments for aging
:09:04 Watch Brent’s interviews with Dr. Aubrey de Grey https://youtube.com/watch?v=TquJyz7tGfk&t=226s & https://youtube.com/watch?v=RWRa6kVKv8o
:11:30 Dr. David Sinclair
:12:01 non-aging related risks for human death
:13:08 Watch Transhumania cryonics video https://youtube.com/watch?v=8arbOJpDTMw
:22:30 We wish everyone incredible health and a long life!
:23:26 first ~3 minutes of Idiocracy https://youtube.com/watch?v=YwZ0ZUy7P3E
:25:55 Gennady Stolyarov II
:30:10 THE LIFE OF LIFE
:32:05 there are many biologically immortal species
:33:02 telomerase gene therapy
:37:38 Viva la Revolución!

