Drying droplets have fascinated scientists for decades. From water to coffee to paint, these everyday fluids leave behind intricate patterns as they evaporate. But blood is far more complex—a colloidal suspension packed with red blood cells, plasma proteins, salts, and countless biomolecules.
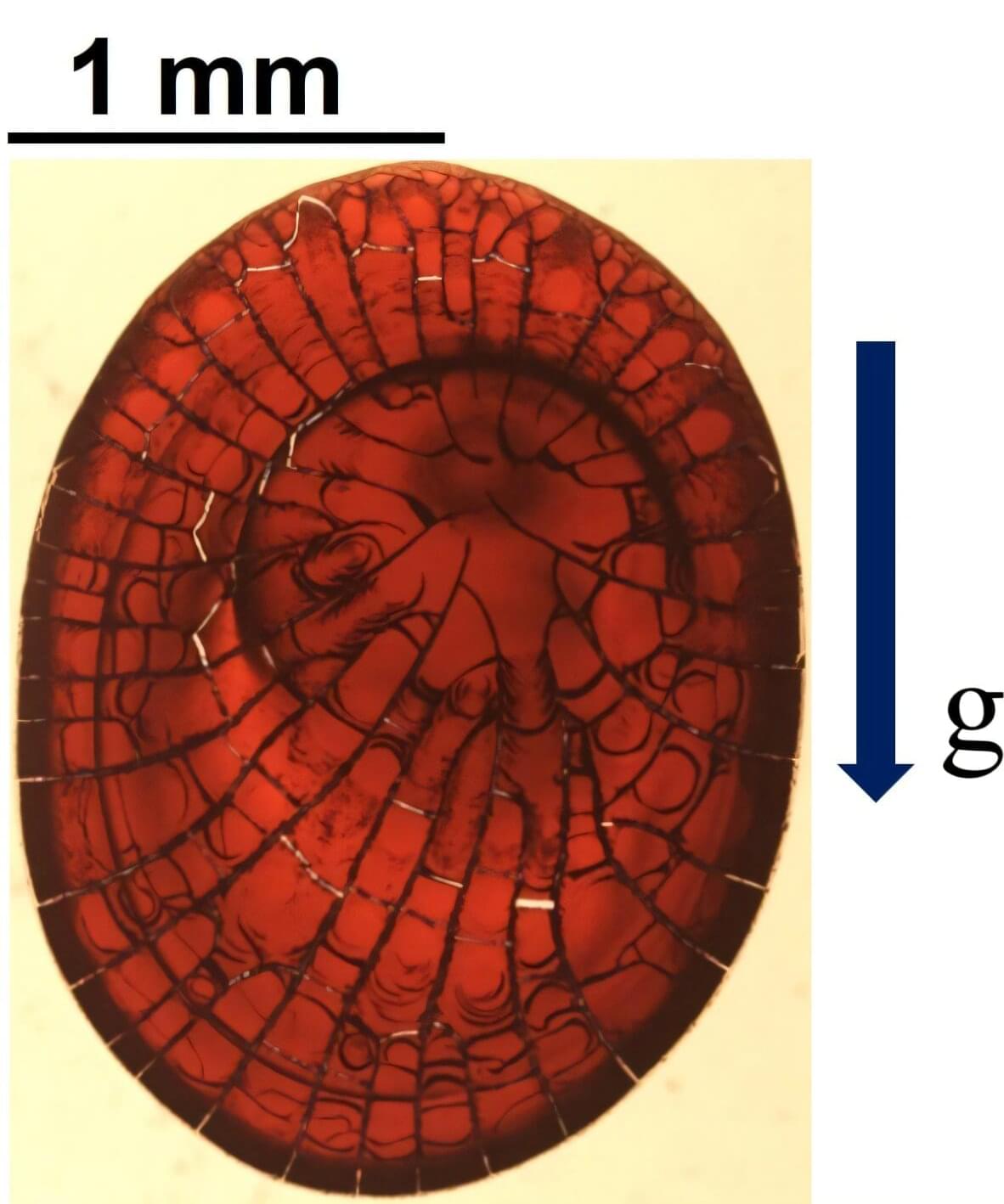
As blood dries, it leaves behind a complex microstructural pattern—cracks, rings, and folds—each shaped by the interplay of its cellular components, proteins, and evaporation dynamics. These features form a kind of physical fingerprint, quietly recording the complex interplay of physics that unfolded during the desiccation of the droplet.
In our recent experiments, we explored how blood droplets dry by varying both their size—from tiny 1-microliter drops to larger 10-microliter ones—and the angle of the surface, from completely horizontal to a steep 70° incline. Using an optical microscope, a high-speed camera, and a surface profiler, we tracked how the droplets dried, shrank and cracked.