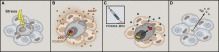
In this issue of Cell, Baar et al. show how FOXO4 protects senescent cell viability by keeping p53 sequestered in nuclear bodies, preventing it from inducing apoptosis. Disrupting this interaction with an all-D amino acid peptide (FOXO4-DRI) restores p53’s apoptotic role and ameliorates the consequences of senescence-associated loss of tissue homeostasis.
Most EV attention focuses on cars and SUVs, but medium and large electrified trucks for local and regional deliveries are coming to market, too, including from Volvo.
A SCIENTIST tabled an alternative theory on black holes during a documentary, building on Albert Einstein’s general relativity theory to claim it is possible to escape, “like a science fiction story”.
It’s hard living in a relativistic Universe, where even the nearest stars are so far away and the speed of light is absolute. It is little wonder then why science fiction franchises routinely employ FTL (Faster-than-Light) as a plot device.
Push a button, press a petal, and that fancy drive system – whose workings no one can explain – will send us to another location in space-time.
However, in recent years, the scientific community has become understandably excited and skeptical about claims that a particular concept – the Alcubierre Warp Drive – might actually be feasible.
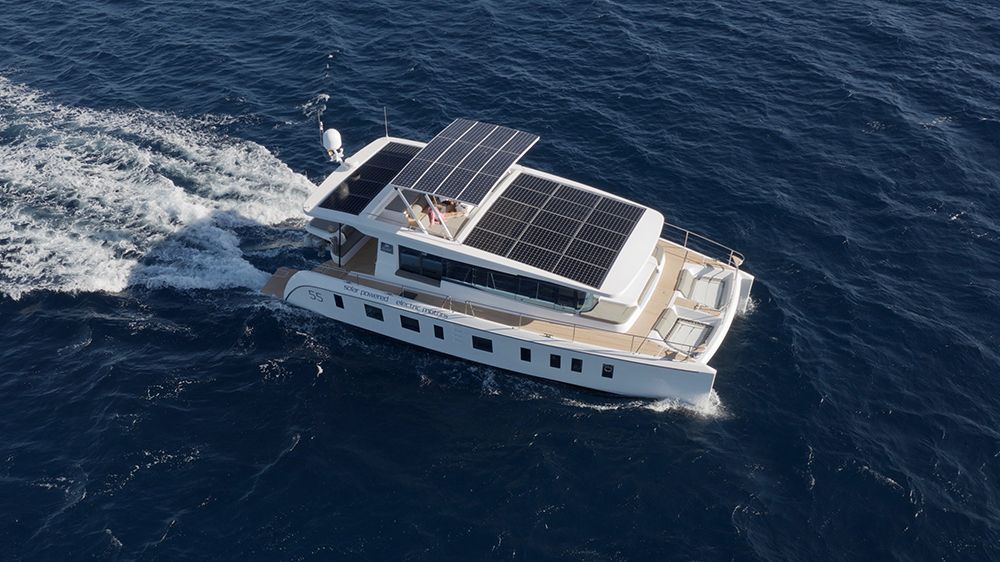
Thanks to solar-powered propulsion and household (meaning no generators are required to run the lights, air conditioning, etc.), and with electric propulsion when needed, the 56-foot catamaran has unlimited range, no noise or fumes, minimal vibration and is virtually maintenance-free. It’s smooth and serene cruising at its best where both the environment and owner’s enjoyment come first. And operation costs are kept to a minimum, too.
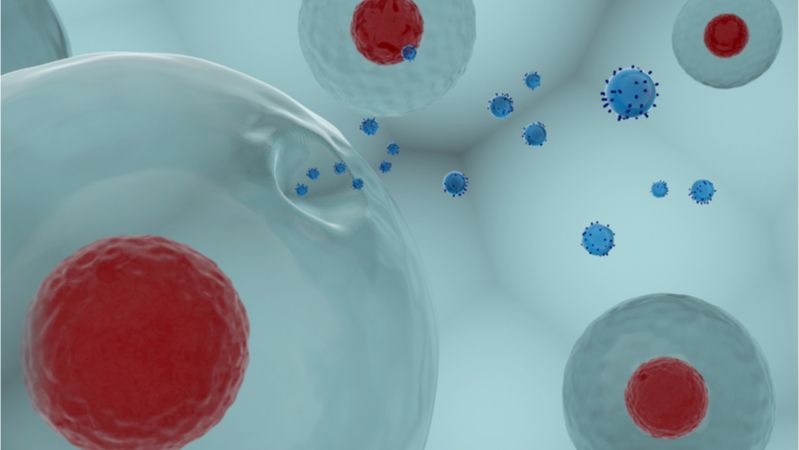
Researchers from North Carolina State University have demonstrated that exosomes harvested from human skin cells can repair sun-damaged skin cells in mice. The therapy also appears to be more effective than retinol and stem cell treatment, and best of all, delivery of the therapy is needle-free.
What are exosomes?
Exosomes are essentially membrane-wrapped packages that contain proteins and other molecules, are produced and released by cells, and deliver messages to other cells. When nearby cells intercept these packages, they change their behavior based on the information contained in these packages. You might think of exosomes being almost like messages in bottles traveling in the bloodstream between cells.
We’re continuing to release talks from Ending Age-Related Diseases 2019, our highly successful two-day conference that featured talks from leading researchers and investors, bringing them together to discuss the future of aging and rejuvenation biotechnology.
Dr. Kelsey Moody gave a detailed presentation on macular degeneration, discussing its origins in the lysosomes and how it progresses along with how his company, Ichor Therapeutics, is developing an exogenous enzyme treatment that may cure this crippling disease.
AI Learns To Play Hide And Seek
Posted in robotics/AI
OpenAI have taught their AI agents to play hide and seek to show how they can develop their own complex and intelligent behaviours 🤖.
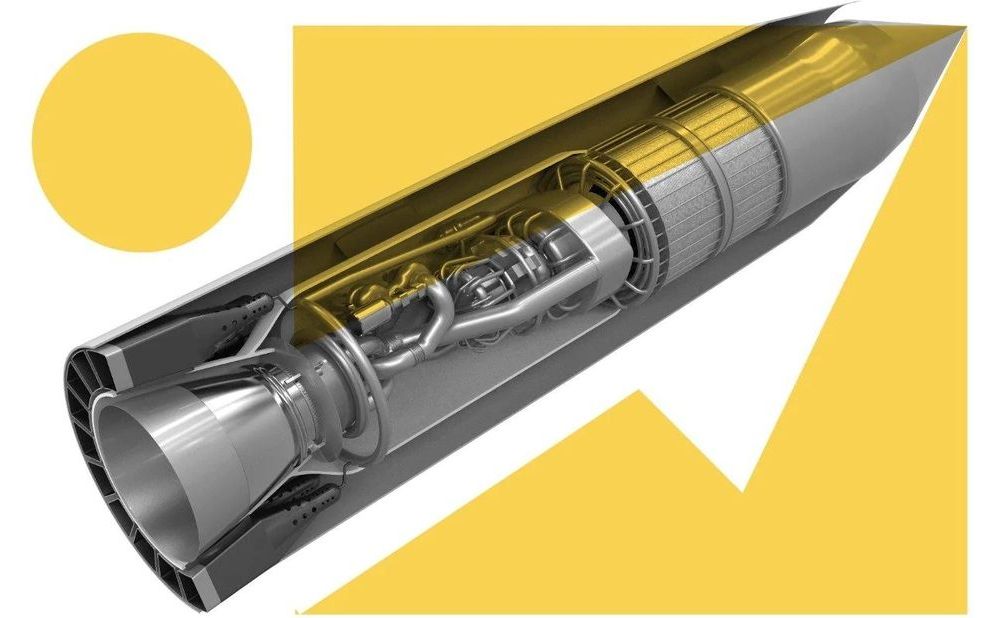
Tourists could fly from Britain to Australia in just four hours by the 2030s with a new hypersonic engine being developed by UK scientists, the head of the UK Space Agency has said.
Reaction Engines, who are based in Oxfordshire, are in the process of building a hybrid hydrogen air-breathing rocket that will allow a plane to fly at Mach 5.4 — more than twice the speed of Concorde — then speed up to to Mach 25 in space.
Not only would the new ‘Sabre’ engine allow speedier journeys — with a flight between London and New York slashed to just over an hour — but the hydrogen/oxygen engine would be far greener and cheaper than current air travel.