As much as we want to tell Mr Sulu to “Take us to warp factor five”, dangerous causality problems, tricky maths and negative energy could get in the way.
It has been widely acknowledged that self-replicating space-probes (SRPs) could explore the galaxy very quickly relative to the age of the galaxy. An obvious implication is that SRPs produced by extraterrestrial civilizations should have arrived in our solar system millions of years ago, and furthermore, that new probes from an ever-arising supply of civilizations ought to be arriving on a constant basis. The lack of observations of such probes underlies a frequently cited variation of the Fermi Paradox. We believe that a predilection for ETI-optimistic theories has deterred consideration of incompatible theories. Notably, SRPs have virtually disappeared from the literature. In this paper, we consider the most common arguments against SRPs and find those arguments lacking. By extension, we find recent models of galactic exploration which explicitly exclude SRPs to be unfairly handicapped and unlikely to represent natural scenarios.
We also consider several other models that seek to explain the Fermi Paradox, most notably percolation theory and two societal-collapse theories. In the former case, we find that it imposes unnatural assumptions which likely render it unrealistic. In the latter case, we present a new theory of interstellar transportation bandwidth which calls into question the validity of societal-collapse theories.
Finally, we offer our thoughts on how to design future SETI programs which take the conclusions of this paper into account to maximize the chance of detection.
Fermi Paradox paper on Arxiv http://arxiv.org/abs/1111.
Von Neumann Self-Replicating Probes. Percolation Theory, Interstellar Societal Collapse, ETI May Still Exist in our Galaxy.
==Conclusion==
This paper was arranged in three parts. First, we introduced SRPs, presented the prevalent arguments against them, and showed that such arguments leave room for future SRP consideration. Namely, we proposed that recent literature has been overzealous in its exclusion of SRPs and we encourage their return to the field.
Second, we presented percolation theory and its nonsociological explanation for the Fermi Paradox. We then showed that the theory can be extended in very reasonable ways which.
undermine its primary conclusion that galactic expansion might.
be intrinsically bounded.
Third, we reviewed two theories of interstellar societal collapse and showed a few counter-arguments to each theory. Furthermore, we introduced ITB theory and showed that its implications might suggest a fundamental error in such theories.
We then discussed one additional paper theorizing that interstellar societies shrink back to their homeworlds and explained that the model involves a number of unlikely assumptions. Following this final analysis, we described the best theory yet oered on the Fermi Paradox which permits intragalactic ETI, namely that exploration probes may currently reside in our solar system, yet undiscovered. Lastly, we offered our thoughts on how to design future SETI programs so as to maximize the likelihood of success.
Science, Technology \& the Future: http://scifuture.org.
Personalized content and ads can also include things like video recommendations, a customized YouTube homepage, and tailored ads based on past activity, like the videos you watch and the things you search for on YouTube. We also use cookies and data to tailor the experience to be age-appropriate, if relevant.
Select “More options” to see additional information, including details about managing your privacy settings. You can also visit g.co/privacytools at any time.
An experiment showing that quantum and classical communication can be carried out through the same fibre at the same time may open the door to building a quantum internet with existing infrastructure.
A new review by researchers from Oxford Population Health and the University of Iceland, published in Nature Aging, reveals how your DNA shapes reproductive health, fertility, and even life expectancy.
Led by researchers from the University of Oxford’s Leverhulme Centre for Demographic Science and the University of Iceland, the review explores how genetic variations can explain differences in reproductive health and longevity.
The study provides the most comprehensive review of male and female genetic discoveries of reproductive traits to date, and provides new insights into how our DNA affects when we have children, the timing of menopause, and even how that is connected to how long we live.
Scientists have long known that light can sometimes appear to exit a material before entering it—an effect dismissed as an illusion caused by how waves are distorted by matter.
Now, researchers at the University of Toronto, through innovative quantum experiments, say they have demonstrated that “negative time” isn’t just a theoretical idea—it exists in a tangible, physical sense, deserving closer scrutiny.
The findings, posted on the preprint server arXiv but not yet published in a peer-reviewed journal, have attracted both global attention and skepticism.
Considering what’s known about their brain structures, sensory systems and learning capacity, it appears that cephalopods as a group may be similar in intelligence to vertebrates as a group. Since many societies have animal welfare standards for mice, rats, chickens and other vertebrates, logic would suggest that there’s an equal case for regulations enforcing humane treatment of cephalopods.
Such rules generally specify that when a species is held in captivity, its housing conditions should support the animal’s welfare and natural behavior. This view has led some U.S. states to outlaw confined cages for egg-laying hens and crates too narrow for pregnant sows to turn around.
Animal welfare regulations say little about invertebrates, but guidelines for the care and use of captive cephalopods have started to appear over the past decade. In 2010, the European Union required considering ethical issues when using cephalopods for research. And in 2015, AAALAC International, an international accreditation organization for ethical animal research, and the Federation of European Laboratory Animal Science Associations promoted guidelines for the care and use of cephalopods in research. The U.S. National Institutes of Health is currently considering similar guidelines.
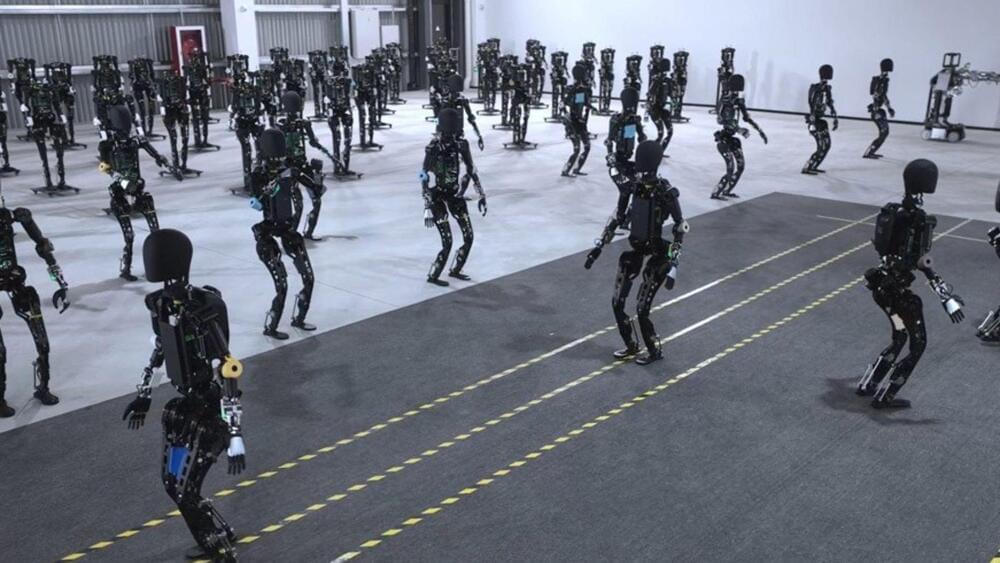
A Chinese robotics firm has started mass-producing humanoid robots for general use, while its US counterparts, like Tesla, are aiming for such a feat in 2026.
Agibot, or Zhiyuan Robotics, showcased footage of its manufacturing facility on its official website and revealed that it’s on course to produce 1,000 units by the end of the year, according to a Chinese online news outlet.
Founded in February 2023 by Peng Zhihui, a former participant in Huawei’s “Genius Youth” program, the Shanghai-based startup launched its first humanoid robot model, the Raise A1, in August 2023.
OpenAI is slowly inviting selected users to test a whole new set of reasoning models named o3 and o3 mini, successors to the o1 and o1-mini models that just entered full release earlier this month.
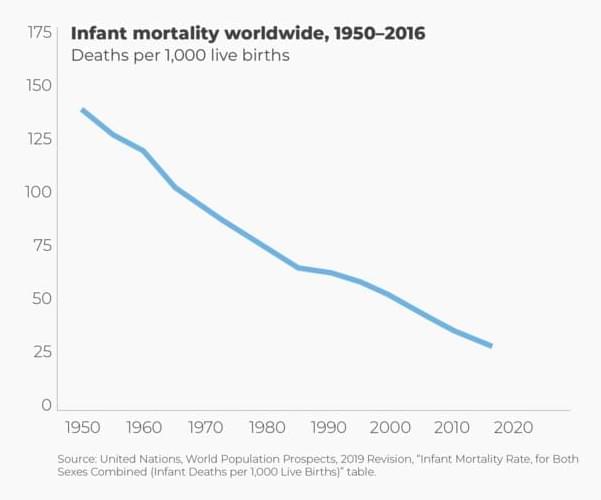
Demographers estimate that in premodern societies, out of every 1,000 babies born, about 300 died before reaching their first birthday. Most of those infants succumbed to infectious diseases and malnutrition.
By 1900, infant mortality rates had fallen to approximately 140 per 1,000 live births in modernizing countries, such as the United Kingdom and the United States. Infant mortality rates in the two countries continued to fall to about 56 per 1,000 live births in 1935 and down to about 30 per 1,000 live births by 1950. In 2017, the UK and U.S. infant mortality rates were, respectively, 3.8 and 5.9 per 1,000 live births. Since 1900, in other words, infant mortality in those two countries has fallen by more than 95 percent.
In the past few decades, infant mortality rates have been falling steeply in the rest of the world. The World Health Organization estimates that the global infant mortality rate was just under 160 per 1,000 live births in 1950. By 1990, the agency reports that the global infant mortality rate had dropped to 64.8 per 1,000 live births. In 2017, the global infant mortality rate was down to 29.4 per 1,000 live births, about the level of the United Kingdom and the United States in 1950.