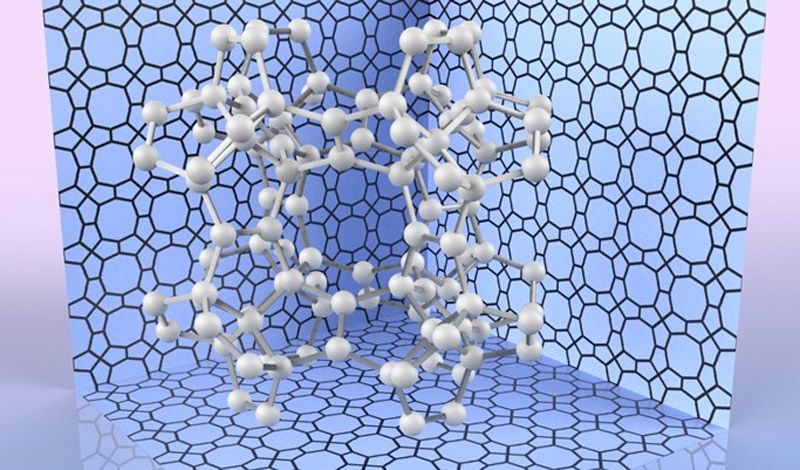
To calculate the most stable atomic configuration, as well as estimate its hardness, the team relied on a computational method called density functional theory (DFT). DFT has been successfully used throughout chemistry and solid-state physics to predict the structure and properties of materials. Keeping track of the quantum states of all the electrons in a sample, and their interactions, is usually an intractable task. Instead, DFT uses an approximation that focuses on the final density of electrons in space orbiting the atoms. This simplifies the calculation to make it suitable for computers, while still providing very precise results.
Based on these calculations, the scientists found that the Young’s modulus, a measure of hardness, for pentadiamond is predicted to be almost 1700 GPa – compared with about 1200 GPa for conventional diamond.
“Not only is pentadiamond harder than conventional diamond, its density is much lower, equal to that of graphite,” explains co-author Professor Mina Maruyama.