A genomic analysis of the creepy parasite H. salminicola reveals that the creature has no mitochondrial DNA and no way to breathe — two animal firsts.

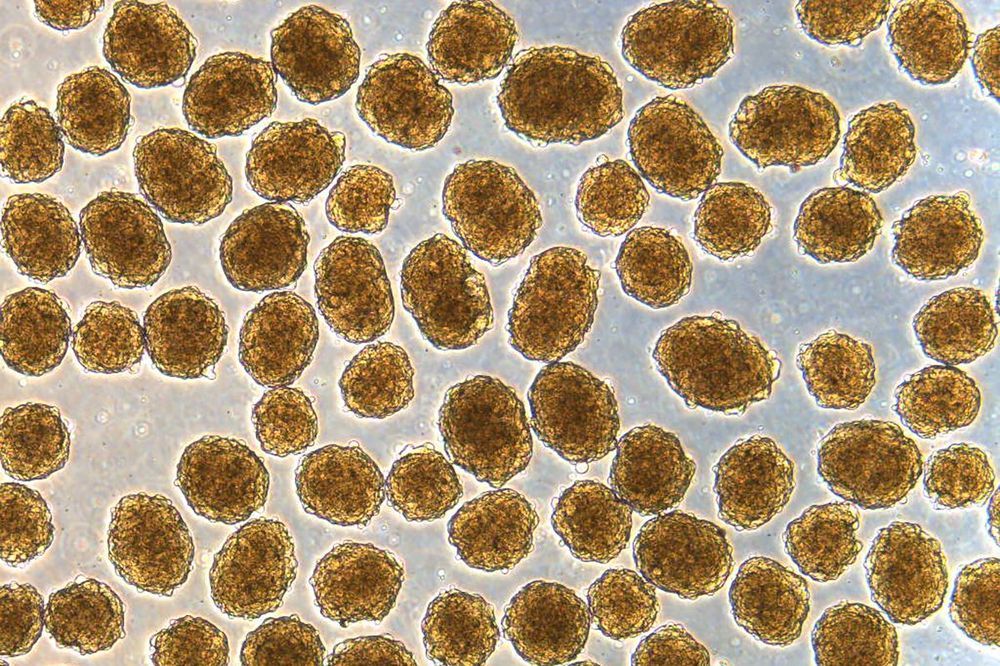
Diabetes is characterized by trouble producing or managing insulin, and one emerging treatment involves converting stem cells into beta cells that secrete the hormone. Now, scientists have developed a more efficient method of doing just that, and found that implanting these cells in diabetic mice functionally cured them of the disease.
The study builds on past research by the same team, led by Jeffrey Millman at Washington University. The researchers have previously shown that infusing mice with these cells works to treat diabetes, but the new work has had even more impressive results.
“These mice had very severe diabetes with blood sugar readings of more than 500 milligrams per deciliter of blood — levels that could be fatal for a person — and when we gave the mice the insulin-secreting cells, within two weeks their blood glucose levels had returned to normal and stayed that way for many months,” says Millman.
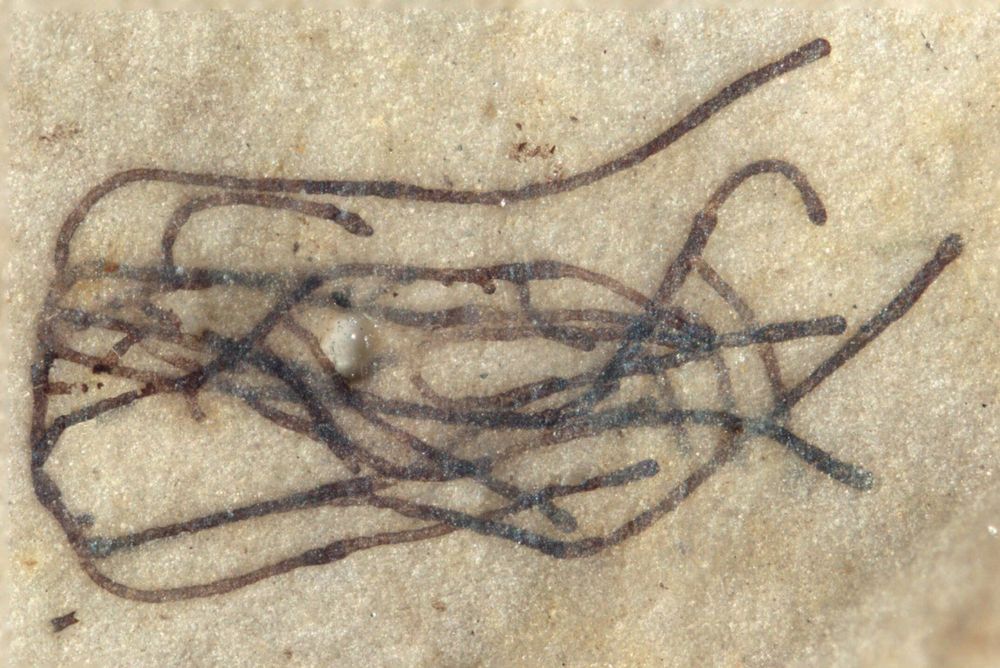

Virginia Tech paleontologists have made a remarkable discovery in China: 1 billion-year-old micro-fossils of green seaweeds that could be related to the ancestor of the earliest land plants and trees that first developed 450 million years ago.
The micro–fossil seaweeds—a form of algae known as Proterocladus antiquus—are barely visible to the naked eyed at 2 millimeters in length, or roughly the size of a typical flea. Professor Shuhai Xiao said the fossils are the oldest green seaweeds ever found. They were imprinted in rock taken from an area of dry land—formerly ocean—near the city of Dalian in the Liaoning Province of northern China. Previously, the earliest convincing fossil record of green seaweeds were found in rock dated at roughly 800 million years old.
The findings—led by Xiao and Qing Tang, a post-doctoral researcher, both in the Department of Geosciences, part of the Virginia Tech College of Science—are featured in the latest issue of Nature Ecology & Evolution (link not active until embargo lifts). “These new fossils suggest that green seaweeds were important players in the ocean long before their land-plant descendants moved and took control of dry land,” Xiao said.

A new study of the genetic history of Sardinia, a Mediterranean island off the western coast of Italy, tells how genetic ancestry on the island was relatively stable through the end of the Bronze Age, even as mainland Europe saw new ancestries arrive. The study further details how the island’s genetic ancestry became more diverse and interconnected with the Mediterranean starting in the Iron Age, as Phoenician, Punic, and eventually Roman peoples began arriving to the island.
The research, published in Nature Communications, analyzed genome-wide DNA data for 70 individuals from more than 20 Sardinian archaeological sites spanning roughly 6,000 years from the Middle Neolithic through the Medieval period. No previous study has used genome-wide DNA extracted from ancient remains to look at the population history of Sardinia.
“Geneticists have been studying the people of Sardinia for a long time, but we haven’t known much about their past,” said the senior author John Novembre, Ph.D., a leading computational biologist at the Univeristy of Chicago who studies genetic diversity in natural populations. “There have been clues that Sardinia has a particularly interesting genetic history, and understanding this history could also have relevance to larger questions about the peopling of the Mediterranean.”
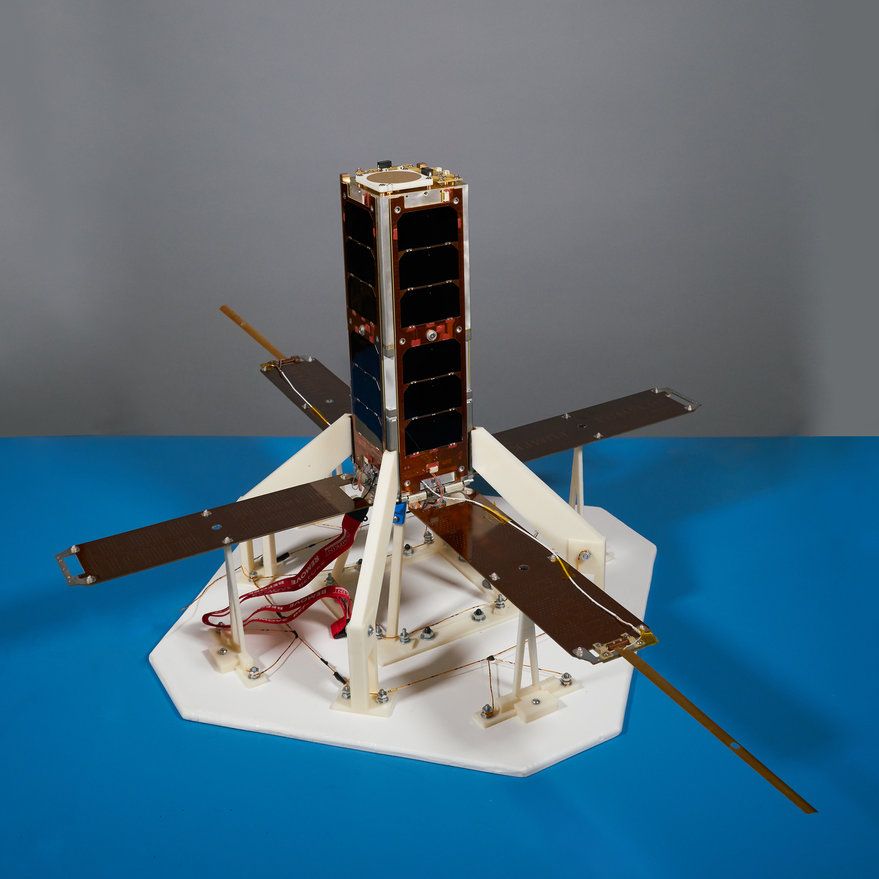
WASHINGTON — Lockheed Martin will acquire the satellite technology assets of Vector by default after a bankruptcy court received no qualified bids by a deadline last week.
In a Feb. 24 filing in the United States Bankruptcy Court for the District of Delaware, lawyers overseeing the bankruptcy proceedings for Vector said that they received no qualifying bids for the company’s GalacticSky software-defined spacecraft technology by a Feb. 21 deadline.
As a result, Lockheed Martin, which provided debtor-in-possession financing when Vector filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in December, will obtain the assets with a “stalking horse” bid of $4.25 million, according to the terms of a Jan. 24 filing. That deal will be finalized at a Feb. 28 court hearing.


Scientists in Australia are making some astonishing claims about a new nuclear reactor technology. Startup HB11, which spun out of the University of New South Wales, has applied for and received patents in the U.S., Japan, and China so far. The company’s technology uses lasers to trigger a nuclear fusion reaction in hydrogen and boron—purportedly with no radioactive fuel required. The secret is a cutting-edge laser and, well, an element of luck.
The laser doesn’t heat the materials. Instead, it speeds up the hydrogen to the point where it (hopefully) collides with the boron to begin a reaction.
Built on decades of previous research, a team from the University of Wisconsin-Madison teased out a tiny chunk of brain tissue within the thalamus, a nub above the brain stem, as a critical part of NCC. As proof of concept, they gave it several bouts of electrical shocks, and restored awareness in unconscious monkeys under heavy anesthesia.
The crux? As soon as the electrical stimulation stopped, the monkeys’ awareness also slipped away.
Although the thalamus has long been thought of as somehow involved in supporting consciousness, the study is one of the first to pinpoint exact neural circuits—highways between the thalamus and parts of the cortex—as “switches” for consciousness that we can control using brain stimulation. And that’s wonderful news for comatose patients.