New drugs based on proteasomes could treat previously undruggable diseases.
A new paper reveals a revolutionary method of targeting cancer cells that is completely non-invasive. In using lasers, the tumour can be destroyed before it grows.
Urolithin A, a metabolite of biomolecules found in pomegranates and other fruits, could help slow certain aging processes. EPFL spin-off Amazentis, in conjunction with EPFL and the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, has published a paper in the journal Nature Metabolism outlining the results of their clinical trial.
It is a fact of life that skeletal muscles begin to lose strength and mass once a person reaches the age of 50. A recent clinical trial involving two EPFL entities—spin-off Amazentis and the Laboratory of Integrative Systems Physiology (LISP) – showed that urolithin A, a compound derived from biomolecules found in fruits such as pomegranates, could slow down this process by improving the functioning of mitochondria—the cells’ powerhouses. A joint paper presenting the results of the trial, published today in Nature Metabolism, also demonstrates that ingesting the compound poses no risk to human health.
Beijing is still behind in terms of its space-based military capabilities, but the gap is closing fast, experts say.
What happened before the Big Bang? And what happened before that? Stephen Hawking’s answer—there was no beginning—is now the subject of intense debate.
A recent challenge to Stephen Hawking’s biggest idea — about how the universe might have come from nothing — has cosmologists choosing sides.
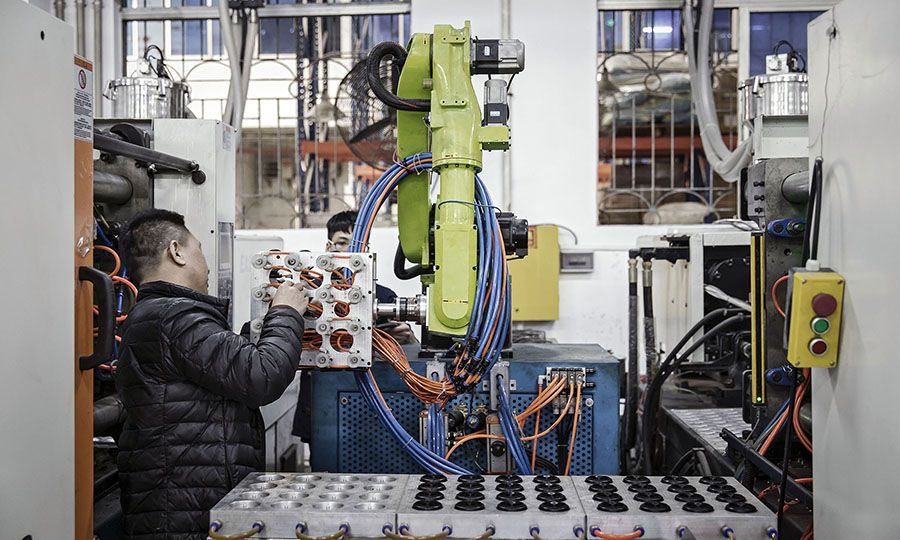
By comparison, the next biggest market, Japan, will be responsible for 11% of all shipments over that same period and the U.S. for 7%. Developing-world markets Mexico, India, Thailand, Vietnam and Brazil will collectively buy just 5% of industrial robots.
China is setting the pace in automation to create the factory of the future.
Since aging is a key driver of many diseases, targeting that process could be a handy catch-all for treating a range of diseases and improving quality of life for pretty much everybody. Researchers at EPFL have now reported a new step towards that goal, with human clinical trials of a fruit-derived compound showing promise in slowing mitochondrial aging in elderly patients, with no side effects found.
The Automobile Club de l’Ouest has announced a new top class for the Le Mans endurance race – a “hypercar” class that will begin in 2020–21, designed to entice some of the world’s most extreme streetcars to throw down and prove themselves. And one we’ll definitely see on track is the awesome Aston Martin Valkyrie.