Could speed up healing.
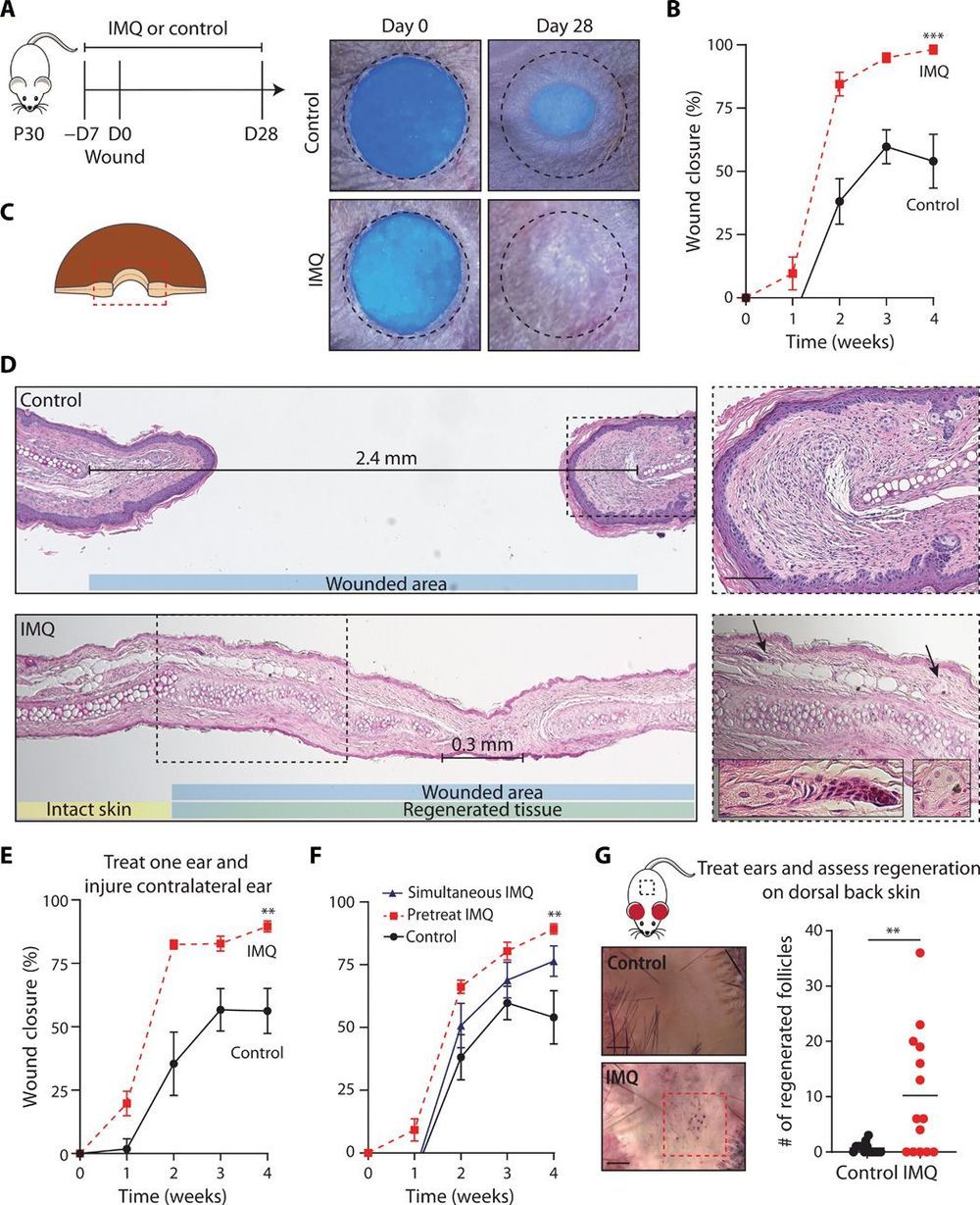
Wound healing in mammalian skin often results in fibrotic scars, and the mechanisms by which original nonfibrotic tissue architecture can be restored are not well understood. Here, Wei et al. have shown that pharmacological activation of the nociceptor TRPA1, which is found on cutaneous sensory neurons, can limit scar formation and promote tissue regeneration. They confirmed the efficacy of TRPA1 activation in three different skin wounding mouse models, and they also observed that localized activation could generate a response at distal wound sites. TRPA1 activation induced IL-23 production by dermal dendritic cells, which activated IL-17–producing γδ T cells and promoted tissue regeneration. These findings provide insight into neuroimmune signaling pathways in the skin that are critical to mammalian tissue regeneration.
Adult mammalian wounds, with rare exception, heal with fibrotic scars that severely disrupt tissue architecture and function. Regenerative medicine seeks methods to avoid scar formation and restore the original tissue structures. We show in three adult mouse models that pharmacologic activation of the nociceptor TRPA1 on cutaneous sensory neurons reduces scar formation and can also promote tissue regeneration. Local activation of TRPA1 induces tissue regeneration on distant untreated areas of injury, demonstrating a systemic effect. Activated TRPA1 stimulates local production of interleukin-23 (IL-23) by dermal dendritic cells, leading to activation of circulating dermal IL-17–producing γδ T cells. Genetic ablation of TRPA1, IL-23, dermal dendritic cells, or γδ T cells prevents TRPA1-mediated tissue regeneration.