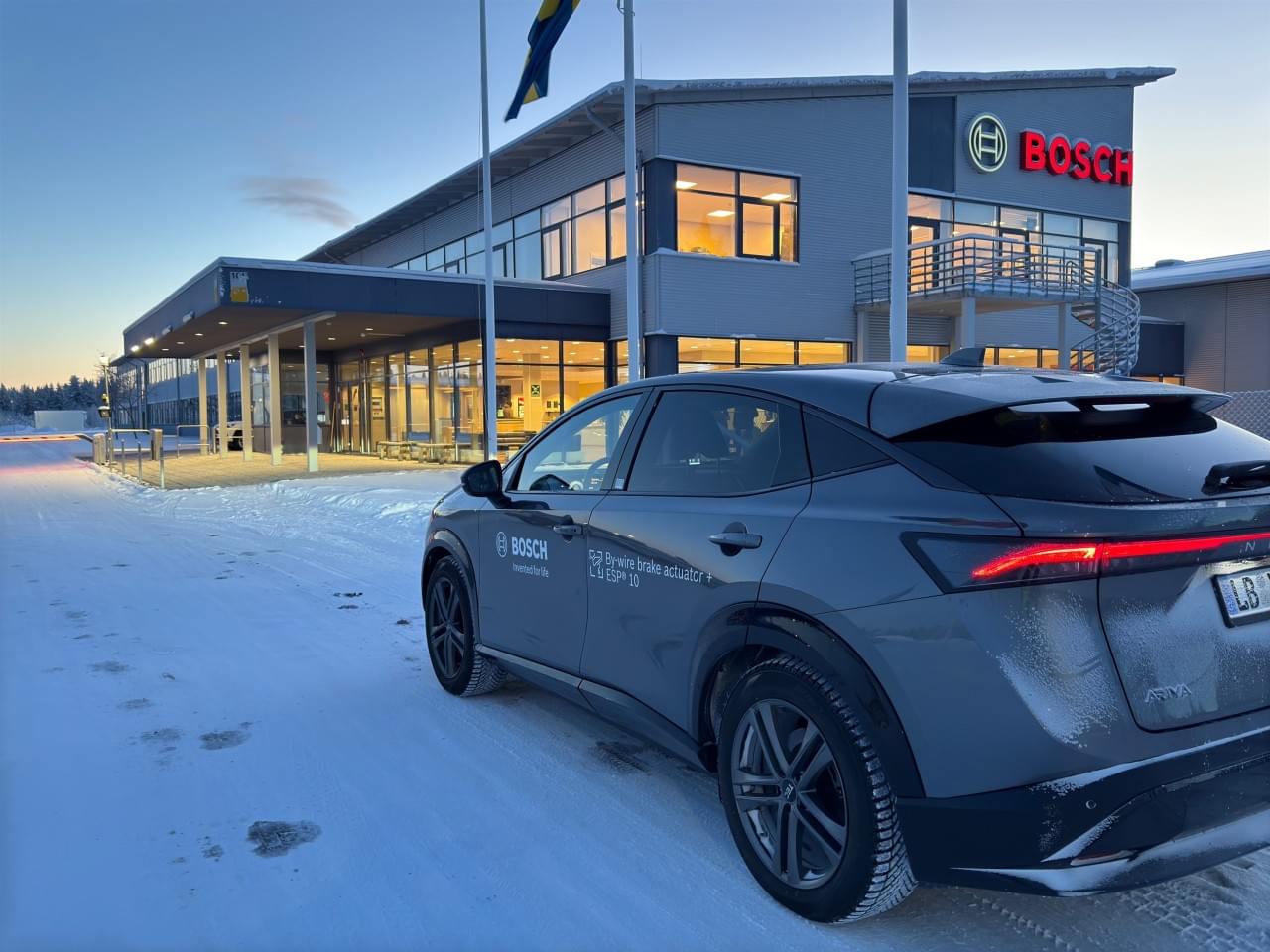
Plymouth, Mich. – For six days, over 2,050 miles and through different climate zones to the Arctic Circle: On an unusual test drive, a Bosch development team successfully tested the new hydraulic brake-by-wire system from Bosch for the first time on public roads. What sets brake-by-wire apart: This solution completely eliminates the mechanical connection between the brake pedal and the brake system. The driver’s brake request is transmitted to the brake-by-wire system purely as an electrical signal via redundant signal lines. For this fundamentally new approach, Bosch offers a robust and efficient solution with two independent hydraulic brake actuators – a by-wire brake actuator and an ESP®. Today’s brake systems, such as the integrated power brake from Bosch, still ensure the required redundancy in the event of a fault via a mechanical connection to the brake pedal. This coupling via an input rod to the brake pedal is eliminated in the new Bosch brake-by-wire solution.
Advantages of the Bosch brake-by-wire system
New freedom in installation: Due to the omission of the mechanical connection, there is no longer any need to mount the brake system components at the vehicle’s firewall. Instead, the components can now be installed where it is most optimal in terms of crash safety, NVH, and manufacturing. The flexibility in choosing where to install the brake actuators helps to avoid the need for different variants for right-hand and left-hand drive vehicles. By-wire technology enables new pedal concepts with significantly shorter brake pedal travel to create space for new interior designs. The hydraulic brake-by-wire solution from Bosch is based on proven brake system technology and is a combination of a by-wire brake actuator and an ESP®. Its slim design saves installation space and reduces the weight of the brake system. Since both the by-wire brake actuator and the ESP® are assigned to different channels of the redundant electrical system, they can each independently build up the required brake pressure at all four wheel brakes in the event of a fault. Therefore, this Bosch solution is also suitable for highly automated vehicles, meeting the protection of the brake system required for safety reasons.