USC scientists have developed a wearable system that enables more natural and emotionally engaging interactions in shared digital spaces, opening new possibilities for remote work, education, health care and beyond.
Touch plays a vital role in how humans communicate and bond. From infancy through adulthood, physical contact helps foster emotional bonds, build trust and regulate stress. Yet in today’s increasingly digital world, where screens mediate many of our relationships, it is often missing.
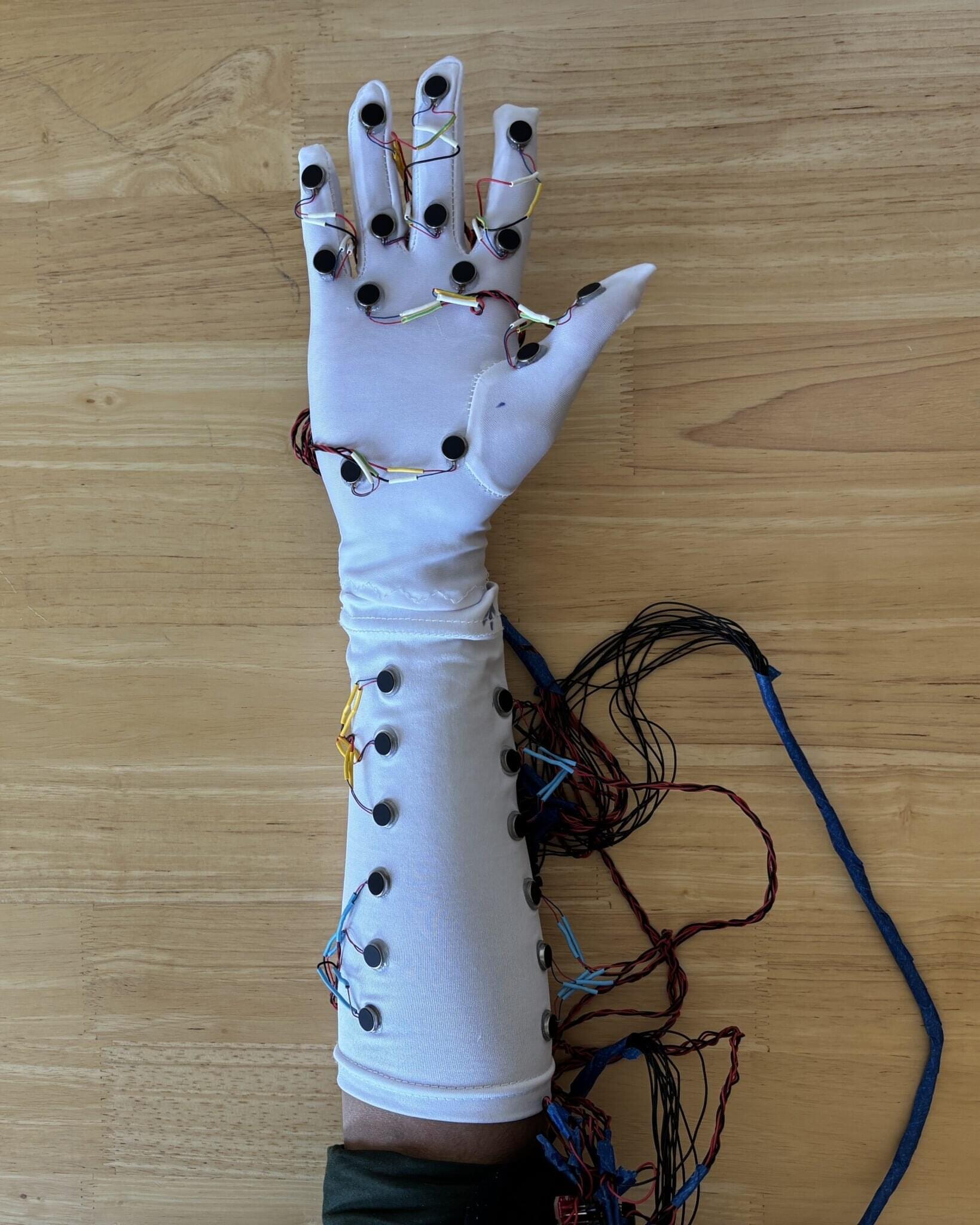
To bridge the gap, researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering have developed a wearable haptic system that lets users exchange physical gestures in virtual reality and feel them in real time, even when they’re miles apart. Their paper is published on the arXiv preprint server.