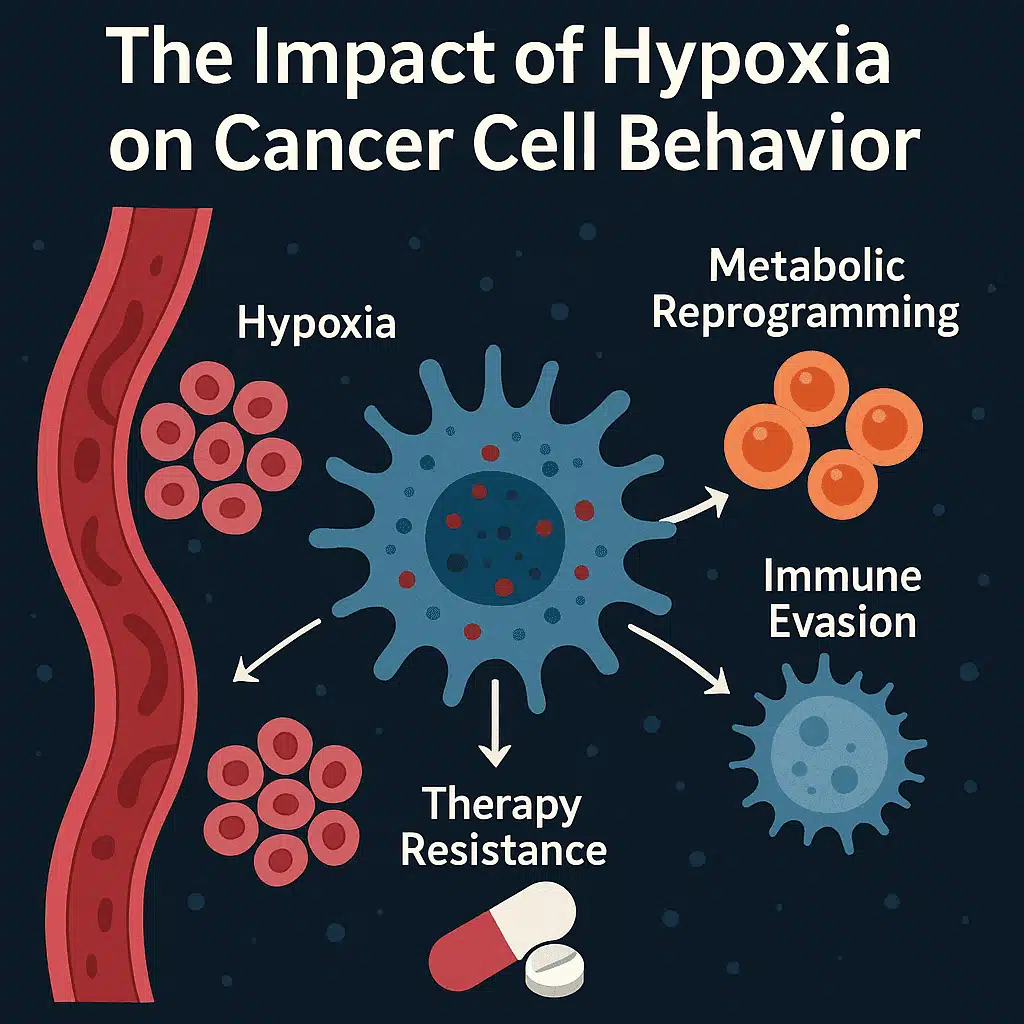
Questions to inspire discussion.
⚡ Q: What advantages does XAI’s proprietary cluster offer? A: XAI’s proprietary clusters, designed specifically for training, are uncatchable by competitors as they can’t be bought with money, creating an unbreachable moat in AI development.
Tesla’s Autonomy and Robotaxis.
🚗 Q: When is Tesla expected to launch unsupervised FSD? A: Tesla is expected to launch unsupervised FSD in the third quarter after polishing and testing, with version 14 potentially being unsupervised even if not allowed for public use.
🤖 Q: What is the significance of Tesla’s upcoming robotaxi launch? A: Tesla’s robotaxi launch is anticipated to be a historic moment, demonstrating that the complexity of autonomous driving technology has been overcome, allowing for leverage and scaling.
💰 Q: How might Tesla monetize its Autonomy feature? A: Tesla may charge monthly fees of $50-$100 for unsupervised use, including insurance, on top of personal insurance costs.