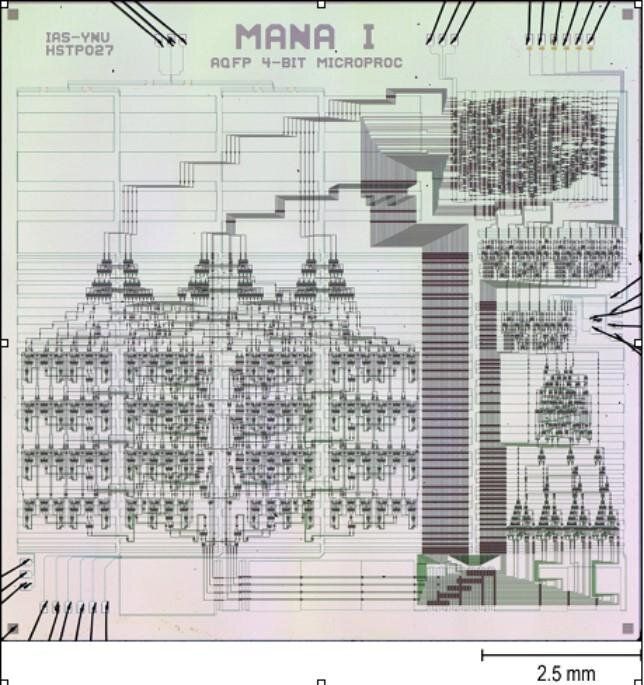
Researchers from Yokohama National University in Japan have developed a prototype microprocessor using superconductor devices that are about 80 times more energy efficient than the state-of-the-art semiconductor devices found in the microprocessors of today’s high-performance computing systems.
As today’s technologies become more and more integrated in our daily lives, the need for more computational power is ever increasing. Because of this increase, the energy use of that increasing computational power is growing immensely. For example, so much energy is used by modern day data centers that some are built near rivers so that the flowing water can be used to cool the machinery.
“The digital communications infrastructure that supports the Information Age that we live in today currently uses approximately 10% of the global electricity. Studies suggest that in the worst case scenario, if there is no fundamental change in the underlying technology of our communications infrastructure such as the computing hardware in large data centers or the electronics that drive the communication networks, we may see its electricity usage rise to over 50% of the global electricity by 2030,” says Christopher Ayala, an associate professor at Yokohama National University, and lead author of the study.