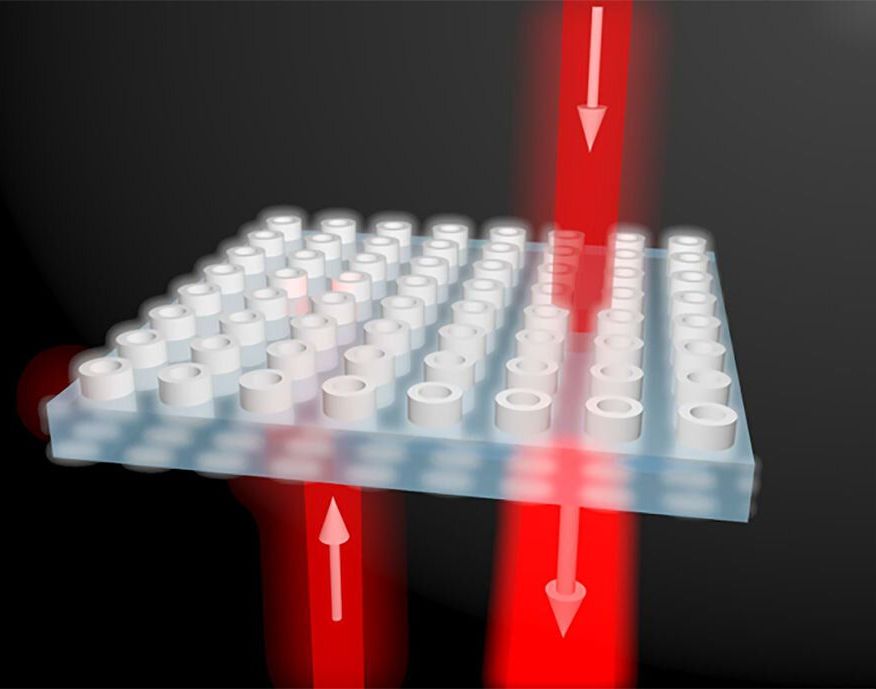
An international research team lead by Aalto University has found a new and simple route to break the reciprocity law in the electromagnetic world, by changing a material’s property periodically in time. The breakthrough could help to create efficient nonreciprocal devices, such as compact isolators and circulators, that are needed for the next generation of microwave and optical communications systems.
When we look through a window and see our neighbor on the street, the neighbor can also see us. This is called reciprocity, and it is the most common physical phenomenon in nature. Electromagnetic signals propagating between two sources is always governed by reciprocity law: if the signal from source A can be received by source B, then the signal from source B can also be received by source A with equal efficiency.
Researchers from Aalto University, Stanford University, and Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL) have successfully demonstrated that the reciprocity law can be broken if the property of the propagation medium periodically changes in time. Propagation medium refers to a material in which light and electromagnetic waves survive and propagate from one point to another.