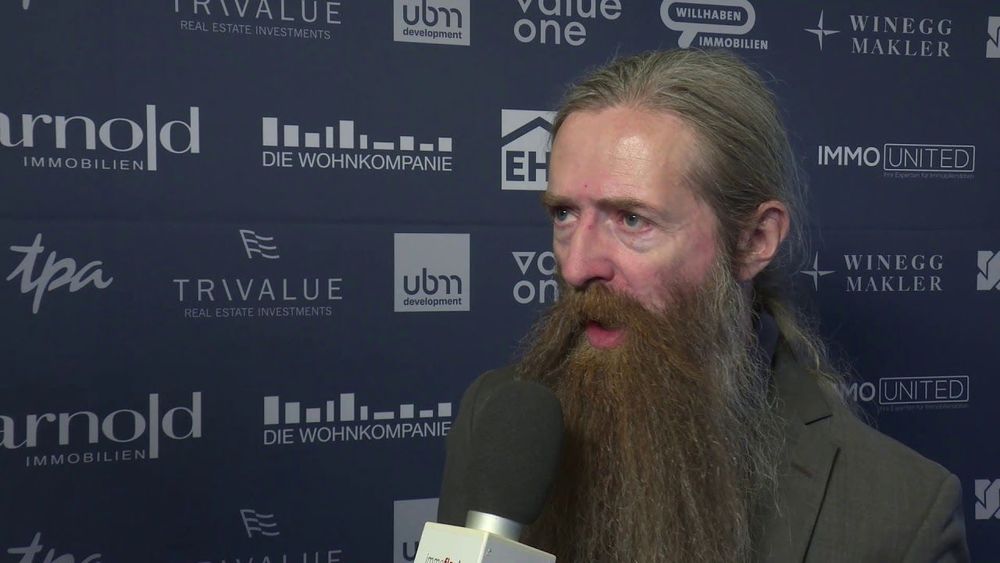
He Jiankui’s original research, published for the first time, could have failed, scientists say.
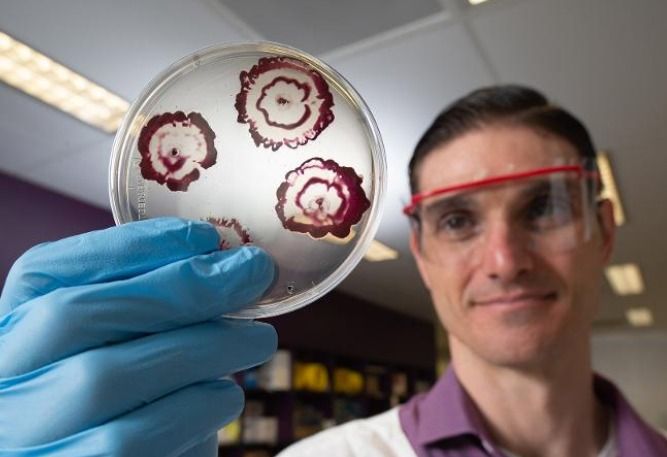
Bacterial biofilms that develop around golden staph infections make treatment difficult and prolonged, but researchers have shown in laboratory work that the hybrid antibiotics they have developed can destroy staph biofilms.
Eradicating deadly staph using a new breed of antibiotics has revealed promising results in research released by QUT, to help overcome one of the biggest modern medical challenges.
The bacteria attach to medical devices including catheters, artificial joints, implants and patients’ burns and wounds, establishing bacterial biofilms, a leading cause of failing antibiotic therapies and chronic infections.
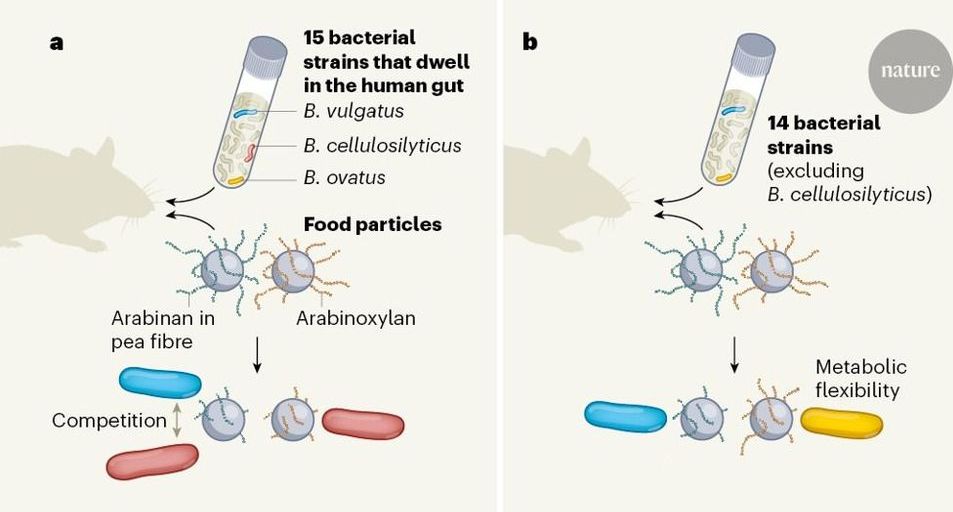
Knowing how dietary fibre nourishes gut microorganisms might suggest ways to boost health-promoting bacteria. A method developed to pinpoint bacteria that consume particular types of dietary fibre could advance such efforts. Method pinpoints bacteria that consume particular types of dietary fibre.
Survivor Stories
Posted in biotech/medical
Cancer Survivor, John KrechDiagnosed with Stage 3 Testicular Cancer, and later with Bladder Cancer, John shares his personal story and advice for surviving cancer.read moreCancer Survivor, Suzy GriswoldDiagnosed with…
Energy is a critical resource that powers our homes and businesses, and also supports every facet of the U.S. economy and our nation’s security. As technology advances and we become more connected, the likelihood that there will be a successful cyber or physical attack on critical infrastructure increases.
This month we recognize National Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience Month, which is a great time to reinforce that our nation’s electric companies are working across the industry and with our government partners to protect the energy grid and ensure that customers have access to the safe and reliable energy they need. We also are focusing on strategies to mitigate the potential impact of an attack and to accelerate recovery should an incident occur.
We know that cyberattacks constantly are evolving and increasing in sophistication. As the vice president for security and preparedness at the Edison Electric Institute (EEI), the association that represents all U.S. investor-owned electric companies, I have a deep appreciation for how any threat to the energy grid endangers our communities and the national and economic security of our country.
As the threat of cyber-attacks on critical infrastructure such as power grids ramps up, the Securing Energy Infrastructure Act (SEIA) is taking technology back to its retro roots. But is it a good idea?
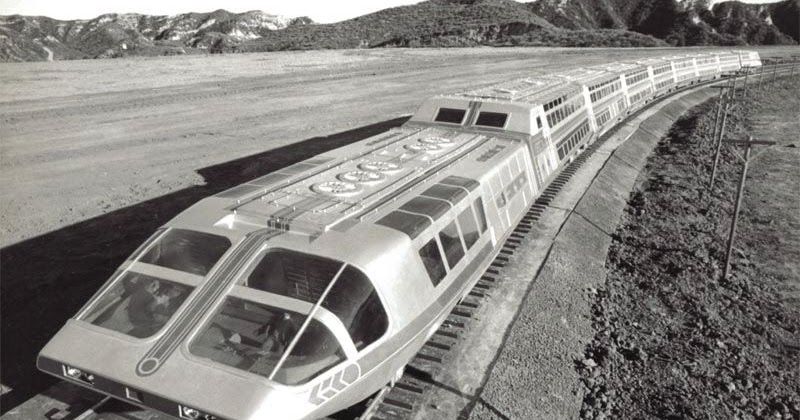
A nuclear-powered bullet train that was equipped with amenities more appropriate to a cruise ship, it had luxuries such as swimming pools and shopping centers.
Supertrain was an American television drama/adventure series that ran on NBC from February 7 to May 5, 1979. Nine episodes were made. Most of the cast of a given episode were guest stars. The production was elaborate, with huge sets and a high-tech model train for outside shots.
On February 7th, 1979, thousands of Americans were introduced to the Supertrain, which ran from New York to Los Angeles. Nuclear-powered, the super-wide-bodied train topped out at 190 miles per hour and boasted on-board luxuries like a swimming pool, a discotheque, a shopping center and a movie theater. It even had a dedicated on-board Social Director.
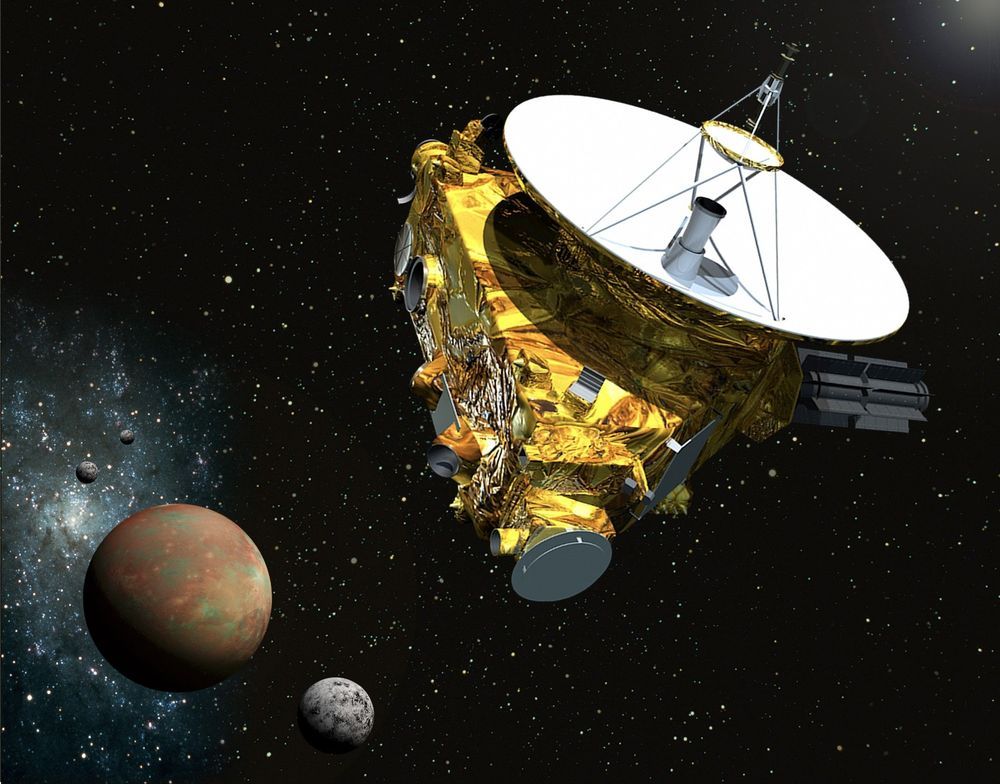
An instrument aboard NASA’s New Horizons is sending back data that could help scientists predict when the unmanned deep-space probe will reach interstellar space. Using the Solar Wind Around Pluto (SWAP) instrument aboard the spacecraft, a team of researchers led by Southwest Research Institute are learning more about how the solar winds change in the outer regions of the solar system.
Though the solar system may look like a big ball of nuclear fire at the center surrounded by a scattering of tiny, solid objects sitting in a lot of very hard vacuum, all that nothingness is permeated by the solar winds – an unceasing flow of ionized particles from the Sun that forms an uneven bubble around our family of planets called the heliosphere.
The outer limit of the heliosphere is where it encounters materials from interstellar space. This is the point where the solar wind slow down to subsonic speeds due to interacting and then is stopped altogether by the interstellar medium. These two points are called, respectively, the termination shock and the heliopause.
3D printing technology is changing and will change pretty much everything. Besides printing the intermittent novelty project at home with a desktop printer, additive manufacturing or 3D printing technology is being used in a large group of businesses changing the manner in which we design, build, create, and even eat.
NASA is planning to use 3D printing technology to construct housing on Mars for future colonies while organizations like byFlow are using the emerging technology to create food and intricate edible tableware. The uses and applications appear to be both limitless and exciting, yet this is only the beginning. Things being what they are, what sort of changes can we expect to see in the medical industry?