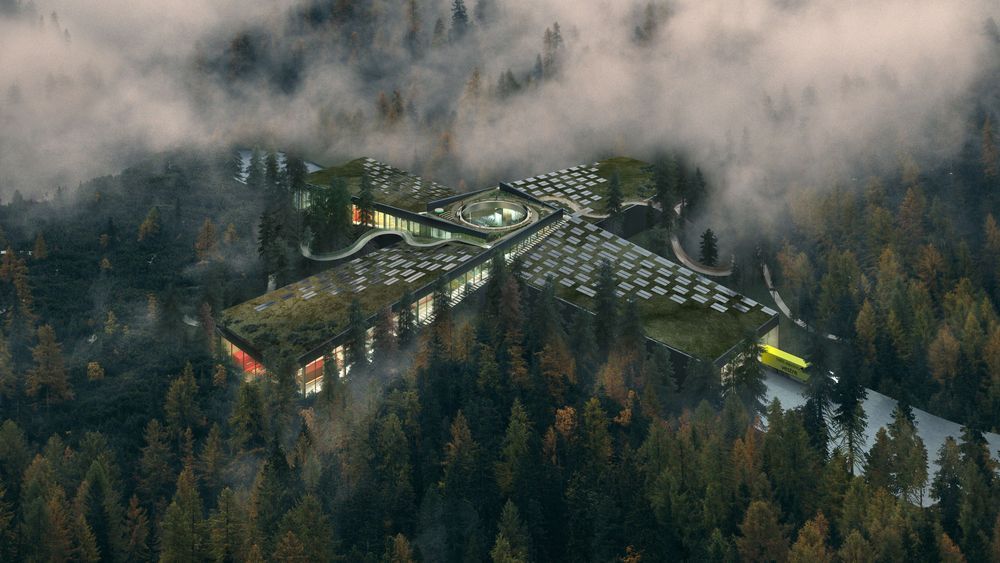
The buildings that produce the goods we use every single day are changing.



Even before the pandemic, public health agencies around the world were struggling to counter increasingly sophisticated efforts to turn people against vaccines. With vaccination rates against measles and other infectious diseases falling in some locations, the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2019 listed “vaccine hesitancy” as one of 10 major global health threats.
To stop the pandemic, the world’s public health experts must win the coming “story war” over vaccine misinformation.
The Hubble Space Telescope has been enhancing our understanding of the universe through breathtaking images for 30 years — PBS Digital Studios celebrates Hubble’s 30th anniversary.

Well this is interesting:
A Henry Ford Health System study shows the controversial anti-malaria drug hydroxychloroquine helps lower the death rate of COVID-19 patients, the Detroit-based health system said Thursday.
Officials with the Michigan health system said the study found the drug “significantly” decreased the death rate of patients involved in the analysis.
The study analyzed 2,541 patients hospitalized among the system’s six hospitals between March 10 and May 2 and found 13% of those treated with hydroxychloroquine died while 26% of those who did not receive the drug died.
Heads of the Michigan health system said Thursday the study found the drug “significantly” decreased the death rate of patients.
face_with_colon_three Circa 2012
Scientists have been able to generate the world’s fastest laser pulse with a beam shot for 67 attoseconds (0.000000000000000067 seconds). This breaks the previous record of 80 attoseconds that was established in 2008. This could help engineers see extremely rapid quantum mechanical processes, like the movements of electrons during chemical reactions.
The researchers published their findings in the journal Optics Letters. This will allow the study of electron motions with attosecond pulses. The blast was obtained by sending pulses from a titanium-sapphire near-infrared laser through a system known as double optical gating (DOG) in which the gate concentrates the energy of extreme ultraviolet light pulses and focuses them on a cell filled with neon gas.
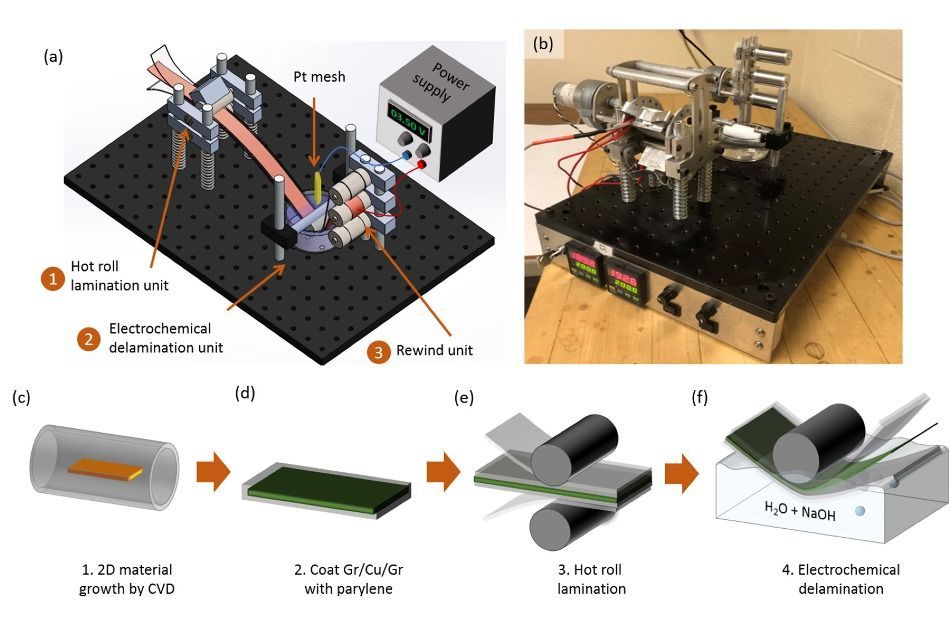
A new technique of manufacturing graphene could revolutionize solar power by enabling the creation of ultra-lightweight, flexible solar panels.
A novel technique developed by researchers at the Michigan Institute of Technology (MIT) that allows for the creation of large sheets of graphene — a layer of single carbon atoms extracted from graphite — could have a significant impact on the development of future electronic devices.
In particular, the development could give a significant boost to the field of solar power where graphene is used as a replacement for indium tin oxide (ITO) in the creation of electrodes. The resultant transparent and light electrodes can bend up to 78 ⁰ — much more flexible than traditional ITO electrodes.
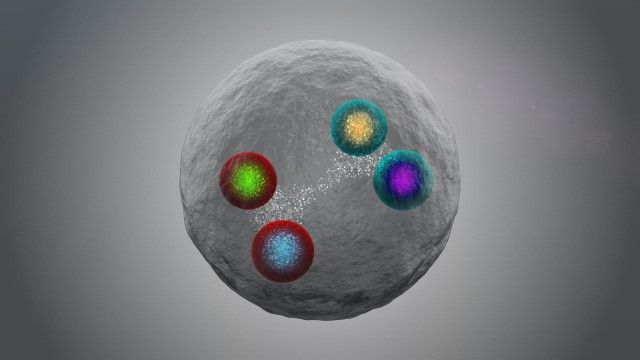
The first tetraquark comprising all charm quarks and antiquarks may have been spotted by physicists working on the LHCb experiment on the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN. The exotic hadron was discovered as it decayed into two J/ψ mesons, each of which is made from a charm quark and charm antiquark. The particle appears to be the first known tetraquark to be made entirely of “heavy quarks”, which are the charm and beauty quarks (but not the top quark, which is the heaviest quark but does not form hadrons).
“Particles made up of four quarks are already exotic, and the one we have just discovered is the first to be made up of four heavy quarks of the same type, specifically two charm quarks and two charm antiquarks,” explains Giovanni Passaleva, who is just stepping down as spokesperson for LHCb. “Up until now, the LHCb and other experiments had only observed tetraquarks with two heavy quarks at most and none with more than two quarks of the same type.”
The new tetraquark is dubbed X(6900), with the number referring to its mass of 6900 MeV/c2 (6.9 GeV/c2). The X denotes the fact that LHCb physicists are not yet certain about key properties of the particle including its spin, parity and quark content.

:3333
Rimac Automobili went very quickly from a company that built subassemblies for others to one that produces some of the quickest, most desirable electric hypercars on the market. The man behind it all is Mate Rimac, a 32-year-old Croatian with a passion for electricity and innovation and, we presume, never-take-no-for-an-answer kind of attitude.